Beyond Balancing The Books – by George Marino, CPA, CFP
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We hear a lot about the importance of mindfulness, yet how can Zen-like non-attachment to the material world go well with actually surviving (let alone thriving) in a Capitalist society?
Books that try to connect the two often end up botching it badly to the level of early 2000s motivational posters.
So, what does this book do differently? Mostly it’s because rather than a motivational speech with exhortations to operate on a higher plain and manifest your destiny and all that, it gives practical, down-to-earth advice and offers small simple things you can do or change to mindfully engage with the world of business rather than operating on auto-pilot.
Basically: how to cut out the stress without cutting out your performance.
All in all, we think both your health and your productivity will thank you for it!
Take Your Business (and Brain) “Beyond Balancing The Books” Today
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What are house dust mites and how do I know if I’m allergic to them?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
People often believe they are allergic to house dust. But of the 20% of Australians suffereing with allergies, a number are are actually allergic to microscopic house dust mites.
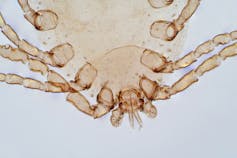
House dust mites belong to the same family as spiders and ticks. They measure just 0.2-0.3 mm, with 50 fitting on a single pinhead. They live for 65–100 days, and females lay 60–100 eggs in their life.
Some 50 house dust mites can fit on one pinhead. Choksawatdikorn/Shutterstock House dust mites love temperate climates and humidity. They feed off the skin cells we and animals shed, as well as mould, which they digest using special enzymes. These enzymes are excreted in their poo about 20 times a day. They also shed fragments of their exoskeletons.
All these fragments trigger allergies in people with this type of allergic rhinitis (which is also known as hay fever)
shuttertock. PeopleImages.com – Yuri A/Shutterstock What are the symptoms?
When people with house dust mite allergy inhale the allergens, they penetrate the mucous membranes of the airways and eyes. Their body recognises the allergens as a threat, releasing chemicals including one called histamine.
This causes symptoms including a runny nose, an itchy nose, eyes and throat, sneezing, coughing and a feeling of mucus at the back of your throat (known as a post-nasal drip).
People with this type of allergy usually mouth breath, snore, rub their nose constantly (creating a nasal crease called the “dust mite salute”) and have dark shadows under their eyes.
House dust mite allergy can also cause poor sleep, constant tiredness, reduced concentration at work or school and lower quality of life.
For people with eczema, their damaged skin barrier can allow house dust mite proteins in. This prompts immune cells in the skin to release chemicals which make already flared skin become redder, sorer and itchier, especially in children.
Symptoms of house dust mite allergy occur year round, and are often worse after going to bed and when waking in the morning. But people with house dust mite allergy and pollen allergies find their year-round symptoms worsen in spring.
How is it diagnosed?
House dust mite allergy symptoms often build up over months, or even years before people seek help. But an accurate diagnosis means you can not only access the right treatment – it’s also vital for minimising exposure.
Your clinician can talk you through treatment options and how to minimise exposure. Monkey Business Images/Shutterstock Doctor and nurse practitioners can order a blood test to check for house dust mite allergy.
Alternatively, health care providers with specialised allergy training can perform skin prick tests. This involves placing drops of the allergens on the arm, along with a positive and negative “control”. After 15 minutes, those who test positive will have developed a mosquito bite-like mark.
How is it treated?
Medication options include one or a combination of:
- daily non-sedating antihistamines
- a steroid nasal spray
- allergy eye drops.
Your health care professional will work with you to develop a rhinitis (hay fever) medical management plan to reduce your symptoms. If you’re using a nasal spray, your health provider will show you how to use it, as people often use it incorrectly.
If you also have asthma or eczema which is worsened by dust mites, your health provider will adapt your asthma action plan or eczema care plan accordingly.
If you experience severe symptoms, a longer-term option is immunotherapy. This aims to gradually turn off your immune system’s ability to recognise house dust mites as a harmful allergen.
Immunotherapy involves taking either a daily sublingual tablet, under the tongue, or a series of injections. Injections require monthly attendances over three years, after the initial weekly build-up phase.
These are effective, but are costly (as well as time-consuming). So it’s important to weigh up the potential benefits and downsides with your health-care provider.
How can you minimise house dust mites?
There are also important allergy minimisation measures you can take to reduce allergens in your home.
Each week, wash your bedding and pyjamas in hot water (over 60°C). This removes house dust mite eggs and debris.
Opt for doonas, covers or quilts that can be washed in hot water above 60°C. Alternatively, low-cost waterproof or leak proof covers can keep house dust mites out.
If you can, favour blinds and wood floors over curtains and carpet. Dust blinds and surfaces with a damp cloth each week and vacuum while wearing a mask, or have someone else do it, as house dust mites can become airborne during cleaning.
But beware of costly products with big marketing budgets and little evidence to support their use. A new mattress, for example, will always be house dust mite-free. But once slept on, the house dust mite life cycle can start.
Mattress protectors and toppers commonly claim to be “hypoallergenic”, “anti-allergy” or “allergy free”. But their pore sizes are not small enough to keep house dust mites and their poo out, or shed skin going through.
Sprays claiming to kill mites require so much spray to penetrate the product that it’s likely to become wet, may smell like the spray and, unless dried properly, may grow mould.
Finally, claims that expensive vacuum cleaners can extract all the house dust mites are unsubstantiated.
For more information, visit healthdirect.gov.au or the Australian Society of Clinical Immunology and Allergy.
Deryn Lee Thompson, Eczema and Allergy Nurse; Lecturer, University of South Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Pistachios vs Almonds – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing pistachios to almonds, we picked the almonds.
Why?
It was very close! And those who’ve been following our “This or That” comparisons might be aware that pistachios and almonds have both been winning their respective comparisons with other nuts so far, so today we put them head-to-head.
In terms of macros, almonds have a little more protein and a little more fiber—as well as slightly more fat, though the fats are healthy. Pistachios, meanwhile, are higher in carbs. A moderate win for almonds on the macro front.
When it comes to vitamins, pistachios have more of vitamins A, B1, and B6, while almonds have more of vitamins B2, B3, and E. We could claim a slight victory for pistachios, based on the larger margins, or else a slight victory for almonds, based on vitamin E being a more common nutritional deficiency than vitamin A, and therefore the more useful vitamin to have more of. We’re going to call this category a tie.
In the category of minerals, almonds lead with more calcium, magnesium, manganese, and zinc, while pistachios boast more copper, potassium, and selenium, though the margins are more modest for pistachios. A moderate win for almonds on minerals, therefore.
Adding up the sections gives a win for almonds, but of course, do enjoy both, because both are excellent in their own right.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
- Pistachios vs Walnuts – Which is Healthier?
- Almonds vs Cashews – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
8 Critical Signs Of Blood Clots That You Shouldn’t Ignore
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Blood clots can form as part of deep vein thrombosis or for other reasons; wherever they form (unless they are just doing their job healing a wound) they can cause problems. But how to know what’s going on inside our body?
Telltale signs
Our usual medical/legal disclaimer applies here, and we are not doctors, let alone your doctors, and even if we were we couldn’t diagnose from afar… But for educational purposes, here are the eight signs from the video:
- Swelling: especially if only on one leg (assuming you have no injury to account for it), which may feel tight and uncomfortable
- Warmness: does the area warmer to the touch? This may be because of the body’s inflammatory response trying to deal with a blood clot
- Tenderness: again, caused by the inflammation in response to the clot
- Discolored skin: it could be reddish, or bruise-like. This could be patchy or spread over a larger area, because of a clot blocking the flow of blood
- Shortness of breath: if a clot makes it to the lungs, it can cause extra problems there (pulmonary embolism), and shortness of breath is the first sign of this
- Coughing up blood: less common than the above but a much more serious sign; get thee to a hospital
- Chest pain: a sharp or stabbing pain, in particular. The pain may worsen with deep breaths or coughing. Again, seek medical attention.
For more on recognizing these signs (including helpful visuals), and more on what to do about them and how to avoid them in the first place, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Further reading
You might like to read:
Dietary Changes for Artery Health
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
What does it mean to be immunocompromised?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our immune systems help us fight off disease, but certain health conditions and medications can weaken our immune systems. People whose immune systems don’t work as well as they should are considered immunocompromised.
Read on to learn more about how the immune system works, what causes people to be immunocompromised, and how we can protect ourselves and the immunocompromised people around us from illness.
What is the immune system?
The immune system is a network of cells, organs, and chemicals that helps our bodies fight off infections caused by invaders, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites.
Some important parts of the immune system include:
- White blood cells, which attack and kill germs that don’t belong inside our bodies.
- Lymph nodes, which help our bodies filter out germs.
- Antibodies, which help our bodies recognize invaders.
- Cytokines, which tell our immune cells what to do.
What causes people to be immunocompromised?
Some health conditions and medications can prevent our immune systems from functioning optimally, which makes us more vulnerable to infection. Health conditions that compromise the immune system fall into two categories: primary immunodeficiency and secondary immunodeficiency.
Primary immunodeficiency
People with primary immunodeficiency are born with genetic mutations that prevent their immune systems from functioning as they should. There are hundreds of types of primary immunodeficiencies. Since these mutations affect the immune system to varying degrees, some people may experience symptoms and get diagnosed early in life, while others may not know they’re immunocompromised until adulthood.
Secondary immunodeficiency
Secondary immunodeficiency happens later in life due to an infection like HIV, which weakens the immune system over time, or certain types of cancer, which prevent the body from producing enough white blood cells to adequately fight off infection. Studies have also shown that getting infected with COVID-19 may cause immunodeficiency by reducing our production of “killer T-cells,” which help fight off infections.
Sometimes necessary treatments for certain medical conditions can also cause secondary immunodeficiency. For example, people with autoimmune disorders—which cause the immune system to become overactive and attack healthy cells—may need to take immunosuppressant drugs to manage their symptoms. However, the drugs can make them more vulnerable to infection.
People who receive organ transplants may also need to take immunosuppressant medications for life to prevent their body from rejecting the new organ. (Given the risk of infection, scientists continue to research alternative ways for the immune system to tolerate transplantation.)
Chemotherapy for cancer patients can also cause secondary immunodeficiency because it kills the immune system’s white blood cells as it’s trying to kill cancer cells.
What are the symptoms of a compromised immune system?
People who are immunocompromised may become sick more frequently than others or may experience more severe or longer-term symptoms than others who contract the same disease.
Other symptoms of a compromised immune system may include fatigue; digestive problems like cramping, nausea, and diarrhea; and slow wound healing.
How can I find out if I’m immunocompromised?
If you think you may be immunocompromised, talk to your health care provider about your medical history, your symptoms, and any medications you take. Blood tests can determine whether your immune system is producing adequate proteins and cells to fight off infection.
I’m immunocompromised—how can I protect myself from infection?
If you’re immunocompromised, take precautions to protect yourself from illness.
Wash your hands regularly, wear a well-fitting mask around others to protect against respiratory viruses, and ensure that you’re up to date on recommended vaccines.
Immunocompromised people may need more doses of vaccines than people who are not immunocompromised—including COVID-19 vaccines. Talk to your health care provider about which vaccines you need.
How can I protect the immunocompromised people around me?
You never know who may be immunocompromised. The best way to protect immunocompromised people around you is to avoid spreading illnesses.
If you know you’re sick, isolate whenever possible. Wear a well-fitting mask around others—especially if you know that you’re sick or that you’ve been exposed to germs. Make sure you’re up to date on recommended vaccines, and practice regular hand-washing.
If you’re planning to spend time with someone who is immunocompromised, ask them what steps you can take to keep them safe.
For more information, talk to your health care provider.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
“The Longevity Vitamin” (That’s Not A Vitamin)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Magic of Mushrooms
“The Longevity Vitamin that’s not a vitamin” is a great tagline for what’s actually an antioxidant amino acid nutraceutical, but in this case, we’re not the ones spearheading its PR, but rather, the Journal of Nutritional Science:
Is ergothioneine a “longevity vitamin” limited in the American diet?
It can be found in all foods, to some extent, but usually in much tinier amounts than would be useful. The reason for this is that it’s synthesized by a variety of microbes (mostly fungi and actinobacteria), and enters the food chain via vegetables that are grown in soil that contain such (which is basically all soil, unless you were to go out of your way to sterilize it, or something really unusually happened).
About those fungi? That includes common popular edible fungi, where it is found quite generously. An 85g (3oz) portion of (most) mushrooms contains about 5mg of ergothioneine, the consumption of which is associated with a 16% reduced all-cause mortality:
However… Most Americans don’t eat that many mushrooms, and those polled averaged 1.1mg/day ergothioneine (in contrast with, for example, Italians’ 4.6mg/day average).
Antioxidant properties
While its antioxidant properties aren’t the most exciting quality, they are worth a mention, on account of their potency:
The biology of ergothioneine, an antioxidant nutraceutical
This is also part of its potential bid to get classified as a vitamin, because…
❝Decreased blood and/or plasma levels of ergothioneine have been observed in some diseases, suggesting that a deficiency could be relevant to the disease onset or progression❞
Source: Ergothioneine: a diet-derived antioxidant with therapeutic potential
Healthy aging
Building on from the above, ergothioneine has been specifically identified as being associated with healthy aging and the prevention of cardiometabolic diseases:
❝An increasing body of evidence suggests ergothioneine may be an important dietary nutrient for the prevention of a variety of inflammatory and cardiometabolic diseases and ergothioneine has alternately been suggested as a vitamin, “longevity vitamin”, and nutraceutical❞
~ Dr. Bernadette Moore et al., citing more references every few words there
Source: Ergothioneine: an underrecognised dietary micronutrient required for healthy ageing?
Good for the heart = good for the brain
As a general rule of thumb, “what’s good for the heart is good for the brain” is almost always true, and it appears to be so in this case, too:
❝Ergothioneine crosses the blood–brain barrier and has been reported to have beneficial effects in the brain. In this study, we discuss the cytoprotective and neuroprotective properties of ergotheioneine, which may be harnessed for combating neurodegeneration and decline during aging.❞
Source: Ergothioneine: A Stress Vitamin with Antiaging, Vascular, and Neuroprotective Roles?
Want to get some?
You can just eat a portion of mushrooms per day! But if you don’t fancy that, it is available as a supplement in convenient 1/day capsule form too.
We don’t sell it, but for your convenience, here is an example product on Amazon
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How the HHS impacts your community’s health
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services is responsible for programs that impact every community in the country. But most Americans aren’t aware of the department’s scope.
“Most of the power in the agency, most of the administrative authority comes from laws that Congress has passed,” former HHS Secretary Kathleen Sebelius told NPR. She added that the HHS secretary “could redefine terms that had a huge impact on people. And that could be done all administratively, not by going back to Congress.”
HHS is comprised of 13 agencies, all of which play an important role in promoting the health of all Americans. These are just some of the ways that HHS affects people’s lives and health.
Vaccines
One of HHS’s most salient roles is developing, approving, and monitoring vaccines after they are on the market. The National Institutes of Health funds and conducts research to develop new vaccines and improve existing ones. The NIH’s Vaccine Research Center spearheads research to develop vaccines against deadly diseases like HIV/AIDS, malaria, and tuberculosis.
The Food and Drug Administration is responsible for overseeing clinical trials that test product safety and effectiveness, approving new vaccines, and monitoring the safety of all vaccines before and after approval. In conjunction with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the FDA also manages the national surveillance systems that record and flag potential vaccine side effects.
In addition to safety monitoring, the CDC conducts research on vaccine safety and effectiveness and issues vaccination guidance. The agency’s recommended immunization schedule guides school and child care vaccination requirements and health care provider recommendations nationwide.
Although the CDC does not have the authority over school and childcare vaccination requirements at the state level, changes to the agency’s recommendations could have wide-ranging impacts.
“If this recommendation changes, there’s downstream effects, like insurance companies could stop covering them. And adding cost could easily deter uptake,” epidemiologist and creator of the Your Local Epidemiologist newsletter Katelyn Jetelina told PBS.
However, CDC vaccine recommendations are just that: recommendations. The agency cannot dictate, for example, vaccine requirements for school enrollment. Those standards are set at the state level, with the possible exception during a national public health emergency.
Drug safety
The FDA oversees all clinical trials in the United States. Every prescription drug and many medical products undergo a rigorous, closely regulated, multistep trial to test their safety and effectiveness. At the end of that process, the FDA determines whether a drug meets its standards for approval. Without FDA approval, a drug cannot be sold in the U.S.
Like with vaccines, the FDA monitors potential safety concerns related to over-the-counter and prescription medications, medical devices, and other products the agency regulates. Health care providers, FDA-regulated companies, and patients can report suspected safety issues to the agency, which evaluates each report for further investigation.
The FDA also alerts the public to safety concerns related to medical products by releasing safety notices, adding warning labels, and issuing drug recalls.
Pandemic and public health emergency response
Several HHS agencies are tasked with preventing, preparing for, and responding to disease outbreaks. This responsibility includes tracking potentially dangerous infectious diseases in the U.S. and globally, developing pandemic response strategies, and issuing guidance to contain ongoing outbreaks.
Both the CDC and FDA inform the public about public health concerns, including pandemics. The Administration for Strategic Preparedness and Response works with communities, medical facilities, local and state governments, and industry partners to enhance responses to disasters and public health emergencies.
The CDC also tracks pathogens like the flu, norovirus, and sexually transmitted infections to better understand where diseases are spreading, how they are evolving, and how best to prepare for outbreaks.
In the event of a public health emergency, the CDC may issue guidance on how to stay safe and minimize health impacts. For example, in January, the agency released tips on how to protect against smoke during the wildfires affecting southern California and how to avoid frostbite and hypothermia, as extreme cold weather affected much of the country.
The FDA can issue emergency use authorizations, which allow the use of “unapproved medical products or unapproved uses of approved medical products … to diagnose, treat, or prevent serious or life-threatening diseases … when certain criteria are met” during public health emergencies. These authorizations help ensure that the standard FDA approval process is not a barrier to the public receiving lifesaving medical products, such as authorizing specific vaccines during a pandemic.
Food and water safety
The FDA, along with the U.S. Department of Agriculture, plays an important role in regulating food safety. The agency approves and monitors the safety of food additives, like sweeteners, dyes, and preservatives. It also regulates how food is prepared, packaged, and stored, including conducting inspections of food facilities and farms.
FDA food safety testing detects dangerous foodborne illnesses like salmonella and E. coli. For example, in late December 2024, the FDA began testing raw (unpasteurized) milk products for bird flu contamination. The CDC investigates outbreaks of foodborne illnesses and, along with the FDA and USDA, provides the public with information about food safety.
The FDA also regulates most food labels, including nutrition facts, ingredient lists, and health claims on food packaging. In January, the agency proposed new front-of-package nutrition labels that highlight sugar, fat, and sodium content in packaged food products.
HHS and the USDA are responsible for updating the Dietary Guidelines for Americans, which are updated every five years. These guidelines are the basis of all federal food assistance programs for children, older adults, and low-income families.
HHS sets the guidelines for the maximum fluoride level in drinking water and periodically makes recommendations about fluoride levels. However, the department has no authority to require or ban fluoridation, which is regulated at the state and local level. U.S. cities began adding fluoride to drinking water in the 1940s to improve dental health and reduce cavities by 25 percent.
Health care access
The HHS secretary regulates the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, which provides health insurance to adults 65 and older, people with disabilities, low-income families, and eligible children through the Children’s Health Insurance Program. Together, Medicare, Medicaid, and CHIP insure over 145 million Americans, or roughly 42 percent of the U.S. population. Changes to either of these programs could impact health care access and quality for millions of Americans.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: