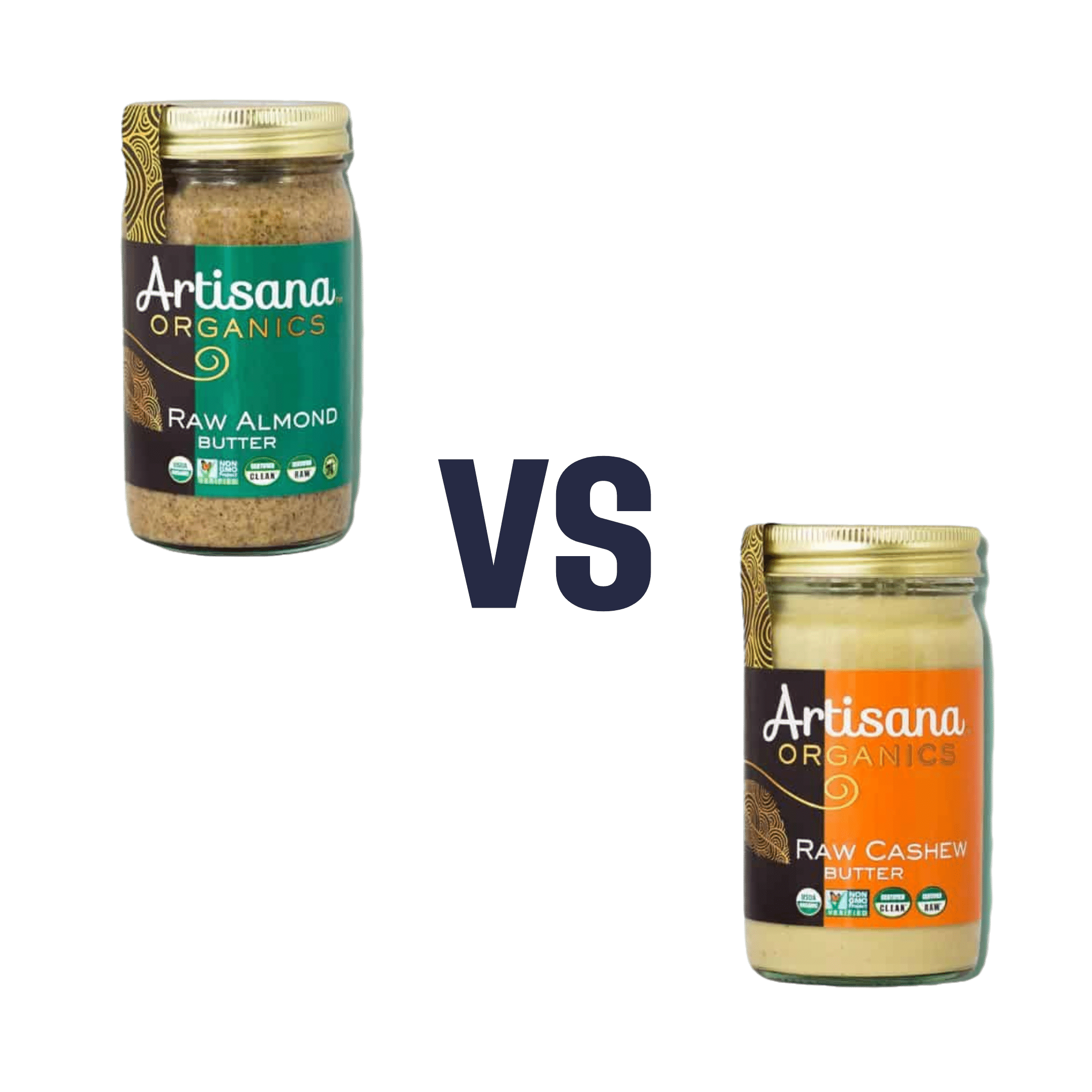
Almond Butter vs Cashew Butter – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing almond butter to cashew butter, we picked the almond.
Why?
They’re both good! But, our inherent pro-almond bias notwithstanding, the almond butter does have a slightly better spread of nutrients.
In terms of macros, almond butter has more protein while cashew butter has more carbs, and of their fats, they’re broadly healthy in both cases, but almond butter does have less saturated fat.
In the category of vitamins, both are good sources of vitamin E, but almond butter has about 4x more. The rest of the vitamins they both contain aren’t too dissimilar, aside from some different weightings of various different B-vitamins, that pretty much balance out across the two nut butters. The only noteworthy point in cashew butter’s favor here is that it is a good source of vitamin K, which almond butter doesn’t have.
When it comes to minerals, both are good sources of lots of minerals, but most significantly, almond butter has a lot more calcium and quite a bit more potassium. In contrast, cashew butter has more selenium.
In short, they’re both great, but almond butter has more relative points in its favor than cashew butter.
Here are the two we depicted today, by the way, in case you’d like to try them:
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Health Care AI, Intended To Save Money, Turns Out To Require a Lot of Expensive Humans
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Preparing cancer patients for difficult decisions is an oncologist’s job. They don’t always remember to do it, however. At the University of Pennsylvania Health System, doctors are nudged to talk about a patient’s treatment and end-of-life preferences by an artificially intelligent algorithm that predicts the chances of death.
But it’s far from being a set-it-and-forget-it tool. A routine tech checkup revealed the algorithm decayed during the covid-19 pandemic, getting 7 percentage points worse at predicting who would die, according to a 2022 study.
There were likely real-life impacts. Ravi Parikh, an Emory University oncologist who was the study’s lead author, told KFF Health News the tool failed hundreds of times to prompt doctors to initiate that important discussion — possibly heading off unnecessary chemotherapy — with patients who needed it.
He believes several algorithms designed to enhance medical care weakened during the pandemic, not just the one at Penn Medicine. “Many institutions are not routinely monitoring the performance” of their products, Parikh said.
Algorithm glitches are one facet of a dilemma that computer scientists and doctors have long acknowledged but that is starting to puzzle hospital executives and researchers: Artificial intelligence systems require consistent monitoring and staffing to put in place and to keep them working well.
In essence: You need people, and more machines, to make sure the new tools don’t mess up.
“Everybody thinks that AI will help us with our access and capacity and improve care and so on,” said Nigam Shah, chief data scientist at Stanford Health Care. “All of that is nice and good, but if it increases the cost of care by 20%, is that viable?”
Government officials worry hospitals lack the resources to put these technologies through their paces. “I have looked far and wide,” FDA Commissioner Robert Califf said at a recent agency panel on AI. “I do not believe there’s a single health system, in the United States, that’s capable of validating an AI algorithm that’s put into place in a clinical care system.”
AI is already widespread in health care. Algorithms are used to predict patients’ risk of death or deterioration, to suggest diagnoses or triage patients, to record and summarize visits to save doctors work, and to approve insurance claims.
If tech evangelists are right, the technology will become ubiquitous — and profitable. The investment firm Bessemer Venture Partners has identified some 20 health-focused AI startups on track to make $10 million in revenue each in a year. The FDA has approved nearly a thousand artificially intelligent products.
Evaluating whether these products work is challenging. Evaluating whether they continue to work — or have developed the software equivalent of a blown gasket or leaky engine — is even trickier.
Take a recent study at Yale Medicine evaluating six “early warning systems,” which alert clinicians when patients are likely to deteriorate rapidly. A supercomputer ran the data for several days, said Dana Edelson, a doctor at the University of Chicago and co-founder of a company that provided one algorithm for the study. The process was fruitful, showing huge differences in performance among the six products.
It’s not easy for hospitals and providers to select the best algorithms for their needs. The average doctor doesn’t have a supercomputer sitting around, and there is no Consumer Reports for AI.
“We have no standards,” said Jesse Ehrenfeld, immediate past president of the American Medical Association. “There is nothing I can point you to today that is a standard around how you evaluate, monitor, look at the performance of a model of an algorithm, AI-enabled or not, when it’s deployed.”
Perhaps the most common AI product in doctors’ offices is called ambient documentation, a tech-enabled assistant that listens to and summarizes patient visits. Last year, investors at Rock Health tracked $353 million flowing into these documentation companies. But, Ehrenfeld said, “There is no standard right now for comparing the output of these tools.”
And that’s a problem, when even small errors can be devastating. A team at Stanford University tried using large language models — the technology underlying popular AI tools like ChatGPT — to summarize patients’ medical history. They compared the results with what a physician would write.
“Even in the best case, the models had a 35% error rate,” said Stanford’s Shah. In medicine, “when you’re writing a summary and you forget one word, like ‘fever’ — I mean, that’s a problem, right?”
Sometimes the reasons algorithms fail are fairly logical. For example, changes to underlying data can erode their effectiveness, like when hospitals switch lab providers.
Sometimes, however, the pitfalls yawn open for no apparent reason.
Sandy Aronson, a tech executive at Mass General Brigham’s personalized medicine program in Boston, said that when his team tested one application meant to help genetic counselors locate relevant literature about DNA variants, the product suffered “nondeterminism” — that is, when asked the same question multiple times in a short period, it gave different results.
Aronson is excited about the potential for large language models to summarize knowledge for overburdened genetic counselors, but “the technology needs to improve.”
If metrics and standards are sparse and errors can crop up for strange reasons, what are institutions to do? Invest lots of resources. At Stanford, Shah said, it took eight to 10 months and 115 man-hours just to audit two models for fairness and reliability.
Experts interviewed by KFF Health News floated the idea of artificial intelligence monitoring artificial intelligence, with some (human) data whiz monitoring both. All acknowledged that would require organizations to spend even more money — a tough ask given the realities of hospital budgets and the limited supply of AI tech specialists.
“It’s great to have a vision where we’re melting icebergs in order to have a model monitoring their model,” Shah said. “But is that really what I wanted? How many more people are we going to need?”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
This article first appeared on KFF Health News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Share This Post
-
The Stress-Proof Brain – by Dr. Melanie Greenberg
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The premise of the book is as stated in the subtitle: using mindfulness and neuroplasticity to manage our stress response.
As such, it’s divided into three parts:
- Understanding your stress (and different types of stressors)
- Calming your amygdalae (thus, dealing with your stress response while the stressor is stressing you)
- Moving forward with your prefrontal cortex (and thus, gradually improving automatic stress responses over time, as we learn new, better responses to do automatically)
The content ranges from the neurophysiological to “therapist’s couch” stuff; Dr. Greenberg having her PhD in psychology has prepared her to write both of those different-but-touching fields with equal competence. In-line citations are given throughout, for those who want to look up studies.
The style is direct and informative, with little to no attention given to making it an entertaining read. As a result, it’s information dense (which is good), and/but not necessarily a “couldn’t put it down” page-turner.
Bottom line: if you’d like to improve your ability to deal with stress, this book is as good as any.
Click here to check out The Stress-Proof Brain, and stress-proof yours!
Share This Post
-
25 Healthy Habits That Will Change Your Life
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Cori Lefkowith, of “Redefining Strength” and “Strong At Every Age” fame, has compiled a list of the simple habits that make a big difference, and here they are!
The Tips
Her recommendations include…
- The healthy activities you’re most prone to skipping? Do those first
- Create staple meals… Consciously! This means: instead of getting into a rut of cooking the same few things in rotation because it’s what you have the ingredients in for, consciously and deliberately make a list of at least 7 meals that, between them, constitute a healthy balanced diet, and choose to make them your staples. That doesn’t mean don’t eat anything else (indeed, variety is good!) but having a robust collection of healthy staples to fall back on will help you avoid falling into unhealthy eating traps.
- Schedule time for healthy activities that you love. Instead of thinking “it would be nice to…”, actually figure out a timeslot, plan in advance, making it recurring, and do it!
- Have (healthy!) no-spoil food options always available. No-spoil doesn’t have to mean “won’t spoil ever”, but does mean at least that it has a long shelf-life. Nuts are a good example, assuming you’re not allergic. Sundried fruits are good too; not nearly as good as fresh fruit, but a lot better than some random processed snack because it’s what in. If you eat fish, then see if you can get dried fish in; it’s high in protein and keeps for a very long time indeed.
- Stock up on spices! Not only do they all have great health-giving properties (at least, we can’t think of a refutation by counterexample, Arrakis be damned), but also, they literally spice up our culinary repertoire, and bring joy to cooking and eating healthy food.
If you like these, check out the rest:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically
Further reading
For more about actually making habits stick quickly and reliably,enjoy:
How To Really Pick Up (And Keep!) Those Habits
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
A Fresh Take On Hypothyroidism
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Three Rs To Boost Thyroid-Related Energy Levels
This is Dr. Izabella Wentz. She’s a doctor of pharmacology, and after her own diagnosis with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, she has taken it up as her personal goal to educate others on managing hypothyroidism.
Dr. Wentz is also trained in functional medicine through The Institute for Functional Medicine, Kalish Functional Medicine, and the American Academy of Anti-Aging Medicine. She is a Fellow of the American Society of Consultant Pharmacists, and holds certifications in Medication Therapy Management as well as Advanced Diabetes Care through the American Pharmacists Association. In 2013, she received the Excellence in Innovation Award from the Illinois Pharmacists Association.
Dr. Wentz’s mission
Dr. Wentz was disenchanted by the general medical response to hypothyroidism in three main ways. She tells us:
- Thyroid patients are not diagnosed appropriately.
- For this, she criticises over-reliance on TSH tests that aren’t a reliable marker of thyroid function, especially if you have Hashimoto’s.
- Patients should be better optimized on their medications.
- For this, she criticizes many prescribed drugs that are actually pro-drugs*, that don’t get converted adequately if you have an underactive thyroid.
- Lifestyle interventions are often ignored by mainstream medicine.
- Medicines are great; they truly are. But medicating without adjusting lifestyle can be like painting over the cracks in a crumbling building.
*a “pro-drug” is what it’s called when the drug we take is not the actual drug the body needs, but is a precursor that will get converted to that actual drug we need, inside our body—usually by the liver, but not always. An example in this case is T4, which by definition is a pro-drug and won’t always get correctly converted to the T3 that a thyroid patient needs.
Well that does indeed sound worthy of criticism. But what does she advise instead?
First, she recommends a different diagnostic tool
Instead of (or at least, in addition to) TSH tests, she advises to ask for TPO tests (thyroid peroxidase), and a test for Tg antibodies (thyroglobulin). She says these are elevated for many years before a change in TSH is seen.
Next, identify the root cause and triggers
These can differ from person to person, but in countries that add iodine to salt, that’s often a big factor. And while gluten may or may not be a factor, there’s a strong correlation between celiac disease and Hashimoto’s disease, so it is worth checking too. Same goes for lactose.
By “checking”, here we mean testing eliminating it and seeing whether it makes a difference to energy levels—this can be slow, though, so give it time! It is best to do this under the guidance of a specialist if you can, of course.
Next, get to work on repairing your insides.
Remember we said “this can be slow”? It’s because your insides won’t necessarily bounce back immediately from whatever they’ve been suffering from for what’s likely many years. But, better late than never, and the time will pass anyway, so might as well get going on it.
For this, she recommends a gut-healthy diet with specific dietary interventions for hypothyroidism. Rather than repeat ourselves unduly here, we’ll link to a couple of previous articles of ours, as her recommendations match these:
She also recommends regular blood testing to see if you need supplementary TSH, TPO antibodies, and T3 and T4 hormones—as well as vitamin B12.
Short version
After diagnosis, she recommends the three Rs:
- Remove the causes and triggers of your hypothyroidism, so far as possible
- Repair the damage caused to your body, especially your gut
- Replace the thyroid hormones and related things in which your body has become deficient
Learn more
If you’d like to learn more about this, she offers a resource page, with resources ranging from on-screen information, to books you can get, to links to hook you up with blood tests if you need them, as well as recommended supplements to consider.
She also has a blog, which has an interesting relevant article added weekly.
Enjoy, and take care of yourself!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
- Thyroid patients are not diagnosed appropriately.
-
If You’re Poor, Fertility Treatment Can Be Out of Reach
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Mary Delgado’s first pregnancy went according to plan, but when she tried to get pregnant again seven years later, nothing happened. After 10 months, Delgado, now 34, and her partner, Joaquin Rodriguez, went to see an OB-GYN. Tests showed she had endometriosis, which was interfering with conception. Delgado’s only option, the doctor said, was in vitro fertilization.
“When she told me that, she broke me inside,” Delgado said, “because I knew it was so expensive.”
Delgado, who lives in New York City, is enrolled in Medicaid, the federal-state health program for low-income and disabled people. The roughly $20,000 price tag for a round of IVF would be a financial stretch for lots of people, but for someone on Medicaid — for which the maximum annual income for a two-person household in New York is just over $26,000 — the treatment can be unattainable.
Expansions of work-based insurance plans to cover fertility treatments, including free egg freezing and unlimited IVF cycles, are often touted by large companies as a boon for their employees. But people with lower incomes, often minorities, are more likely to be covered by Medicaid or skimpier commercial plans with no such coverage. That raises the question of whether medical assistance to create a family is only for the well-to-do or people with generous benefit packages.
“In American health care, they don’t want the poor people to reproduce,” Delgado said. She was caring full-time for their son, who was born with a rare genetic disorder that required several surgeries before he was 5. Her partner, who works for a company that maintains the city’s yellow cabs, has an individual plan through the state insurance marketplace, but it does not include fertility coverage.
Some medical experts whose patients have faced these issues say they can understand why people in Delgado’s situation think the system is stacked against them.
“It feels a little like that,” said Elizabeth Ginsburg, a professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Harvard Medical School who is president-elect of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine, a research and advocacy group.
Whether or not it’s intended, many say the inequity reflects poorly on the U.S.
“This is really sort of standing out as a sore thumb in a nation that would like to claim that it cares for the less fortunate and it seeks to do anything it can for them,” said Eli Adashi, a professor of medical science at Brown University and former president of the Society for Reproductive Endocrinologists.
Yet efforts to add coverage for fertility care to Medicaid face a lot of pushback, Ginsburg said.
Over the years, Barbara Collura, president and CEO of the advocacy group Resolve: The National Infertility Association, has heard many explanations for why it doesn’t make sense to cover fertility treatment for Medicaid recipients. Legislators have asked, “If they can’t pay for fertility treatment, do they have any idea how much it costs to raise a child?” she said.
“So right there, as a country we’re making judgments about who gets to have children,” Collura said.
The legacy of the eugenics movement of the early 20th century, when states passed laws that permitted poor, nonwhite, and disabled people to be sterilized against their will, lingers as well.
“As a reproductive justice person, I believe it’s a human right to have a child, and it’s a larger ethical issue to provide support,” said Regina Davis Moss, president and CEO of In Our Own Voice: National Black Women’s Reproductive Justice Agenda, an advocacy group.
But such coverage decisions — especially when the health care safety net is involved — sometimes require difficult choices, because resources are limited.
Even if state Medicaid programs wanted to cover fertility treatment, for instance, they would have to weigh the benefit against investing in other types of care, including maternity care, said Kate McEvoy, executive director of the National Association of Medicaid Directors. “There is a recognition about the primacy and urgency of maternity care,” she said.
Medicaid pays for about 40% of births in the United States. And since 2022, 46 states and the District of Columbia have elected to extend Medicaid postpartum coverage to 12 months, up from 60 days.
Fertility problems are relatively common, affecting roughly 10% of women and men of childbearing age, according to the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development.
Traditionally, a couple is considered infertile if they’ve been trying to get pregnant unsuccessfully for 12 months. Last year, the ASRM broadened the definition of infertility to incorporate would-be parents beyond heterosexual couples, including people who can’t get pregnant for medical, sexual, or other reasons, as well as those who need medical interventions such as donor eggs or sperm to get pregnant.
The World Health Organization defined infertility as a disease of the reproductive system characterized by failing to get pregnant after a year of unprotected intercourse. It terms the high cost of fertility treatment a major equity issue and has called for better policies and public financing to improve access.
No matter how the condition is defined, private health plans often decline to cover fertility treatments because they don’t consider them “medically necessary.” Twenty states and Washington, D.C., have laws requiring health plans to provide some fertility coverage, but those laws vary greatly and apply only to companies whose plans are regulated by the state.
In recent years, many companies have begun offering fertility treatment in a bid to recruit and retain top-notch talent. In 2023, 45% of companies with 500 or more workers covered IVF and/or drug therapy, according to the benefits consultant Mercer.
But that doesn’t help people on Medicaid. Only two states’ Medicaid programs provide any fertility treatment: New York covers some oral ovulation-enhancing medications, and Illinois covers costs for fertility preservation, to freeze the eggs or sperm of people who need medical treatment that will likely make them infertile, such as for cancer. Several other states also are considering adding fertility preservation services.
In Delgado’s case, Medicaid covered the tests to diagnose her endometriosis, but nothing more. She was searching the internet for fertility treatment options when she came upon a clinic group called CNY Fertility that seemed significantly less expensive than other clinics, and also offered in-house financing. Based in Syracuse, New York, the company has a handful of clinics in upstate New York cities and four other U.S. locations.
Though Delgado and her partner had to travel more than 300 miles round trip to Albany for the procedures, the savings made it worthwhile. They were able do an entire IVF cycle, including medications, egg retrieval, genetic testing, and transferring the egg to her uterus, for $14,000. To pay for it, they took $7,000 of the cash they’d been saving to buy a home and financed the other half through the fertility clinic.
She got pregnant on the first try, and their daughter, Emiliana, is now almost a year old.
Delgado doesn’t resent people with more resources or better insurance coverage, but she wishes the system were more equitable.
“I have a medical problem,” she said. “It’s not like I did IVF because I wanted to choose the gender.”
One reason CNY is less expensive than other clinics is simply that the privately owned company chooses to charge less, said William Kiltz, its vice president of marketing and business development. Since the company’s beginning in 1997, it has become a large practice with a large volume of IVF cycles, which helps keep prices low.
At this point, more than half its clients come from out of state, and many earn significantly less than a typical patient at another clinic. Twenty percent earn less than $50,000, and “we treat a good number who are on Medicaid,” Kiltz said.
Now that their son, Joaquin, is settled in a good school, Delgado has started working for an agency that provides home health services. After putting in 30 hours a week for 90 days, she’ll be eligible for health insurance.
One of the benefits: fertility coverage.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
For women with antenatal depression, micronutrients might help them and their babies – new study
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Getty Images Julia J Rucklidge, University of Canterbury; Elena Moltchanova, University of Canterbury; Roger Mulder, University of Otago, and Siobhan A Campbell, University of Canterbury
Antenatal depression affects 15% to 21% of pregnant women worldwide. It can influence birth outcomes and children’s development, as well as increase the risk of post-natal depression.
Current treatments like therapy can be inaccessible and antidepressants can carry risks for developing infants.
Over the past two decades, research has highlighted that poor nutrition is a contributing risk factor to mental health challenges. Most pregnant women in New Zealand aren’t adhering to nutritional guidelines, according to a longitudinal study. Only 3% met the recommendations for all food groups.
Another cohort study carried out in Brazil shows that ultra-processed foods (UPF) accounted for at least 30% of daily dietary energy during pregnancy, displacing healthier options.
UPFs are chemically manufactured and contain additives to improve shelf life, as well as added sugar and salt. Importantly, they are low in essential micronutrients (vitamins and minerals).
The consumption of these foods is concerning because a nutrient-poor diet during pregnancy has been linked to poorer mental health outcomes in children. This includes depression, anxiety, hyperactivity, and inattention.
Increasing nutrients in maternal diets and reducing consumption of UPFs could improve the mental health of the mother and the next generation. Good nutrition can have lifelong benefits for the offspring.
However, there are multiple factors that mean diet change alone may not in itself be sufficient to address mental health challenges. Supplementing with additional nutrients may also be important to address nutritional needs during pregnancy.
Micronutrients as treatment for depression
Our earlier research suggests micronutrient supplements for depression have benefits outside pregnancy.
But until now there have been no published randomised controlled trials specifically designed to assess the efficacy and safety of broad-spectrum micronutrients on antenatal depression and overall functioning.
The NUTRIMUM trial, which ran between 2017 and 2022, recruited 88 women in their second trimester of pregnancy who reported moderate depressive symptoms. They were randomly allocated to receive either 12 capsules (four pills, three times a day) of a broad-spectrum micronutrient supplement or an active placebo containing iodine and riboflavin for a 12-week period.
Micronutrient doses were generally between the recommended dietary allowance and the tolerable upper level.
Based on clinician ratings, micronutrients significantly improved overall psychological functioning compared to the placebo. The findings took into account all noted changes based on self-assessment and clinician observations. This includes sleep, mood regulation, coping, anxiety and side effects.
Adding micronutrients to the diet of pregnant women with antenatal depression significantly improved their overall psychological functioning. Getty Images Both groups reported similar reductions in symptoms of depression. More than three quarters of participants were in remission at the end of the trial. But 69% of participants in the micronutrient group rated themselves as “much” or “very much” improved, compared to 39% in the placebo group.
Participants taking the micronutrients also experienced significantly greater improvements in sleep and overall day-to-day functioning, compared to participants taking the placebo. There were no group differences on measures of stress, anxiety and quality of life.
Importantly, there were no group differences in reported side effects, and reports of suicidal thoughts dropped over the course of the study for both groups. Blood tests confirmed increased vitamin levels (vitamin C, D, B12) and fewer deficiencies in the micronutrient group.
Micronutrients were particularly helpful for women with chronic mental health challenges and those who had taken psychiatric medications in the past. Those with milder symptoms improved with or without the micronutrients, suggesting general care and monitoring might suffice for some women.
The benefits of micronutrients were comparable to psychotherapy but with less contact. There are no randomised controlled trials of antidepressant medication to compare these results.
Retention in the study was good (81%) and compliance excellent (90%).
Beyond maternal mental health
We followed the infants of mothers enrolled in the NUTRIMUM trial (who were therefore exposed to micronutrients during pregnancy) for 12 months, alongside infants from the general population of Aotearoa New Zealand.
This second group of infants from the general population contained a smaller sub-group who were exposed to antidepressant medication for the treatment of antenatal depression.
We assessed the neuro-behavioural development of each infant within the first four weeks of life, and temperament up to one year after birth.
These observational follow-ups showed positive effects of micronutrients on the infants’ ability to regulate their behaviour. These results were on par with or better than typical pregnancies, and better than treatments with antidepressants.
Micronutrients during pregnancy improved the neurological and behavioural development of infants. Getty Images Infants exposed to micronutrients during pregnancy were significantly better at attending to external stimuli. They were also better able to block out external stimuli during sleep. They showed fewer signs of stress and had better muscle tone compared to infants not exposed to micronutrients.
They also displayed greater ability to interact with their environment. They were better at regulating their emotional state and had fewer abnormal muscle reflexes than infants exposed to antidepressant medication in pregnancy.
Reassuringly, micronutrients had no negative impact on infant temperament.
These findings highlight the potential of micronutrients as a safe and effective alternative to traditional medication treatments for antenatal depression.
The prenatal environment sets the foundation for a child’s future. Further investigation into the benefits of micronutrient supplementation would gives us more confidence in their use for other perinatal (from the start of pregnancy to a year after birth) mental health issues. This could provide future generations with a better start to life.
We would like to acknowledge the contribution of Dr Hayley Bradley to this research project.
Julia J Rucklidge, Professor of Psychology, University of Canterbury; Elena Moltchanova, Professor of Statistics, University of Canterbury; Roger Mulder, Professor of Psychiatry, University of Otago, and Siobhan A Campbell, Intern Psychologist, Researcher – Te Puna Toiora (Mental Health and Nutrition Research Lab), University of Canterbury
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: