Alzheimer’s Sex Differences May Not Be What They Appear
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Alzheimer’s Sex Differences May Not Be What They Appear
Women get Alzheimer’s at nearly twice the rate than men do, and deteriorate more rapidly after onset, too.
So… Why?
There are many potential things to look at, but four stand out for quick analysis:
- Chromosomes: women usually have XX chromosomes, to men’s usual XY. There are outliers to both groups, people with non-standard combinations of chromosomes, but not commonly enough to throw out the stats.
- Hormones: women usually have high estrogen and low testosterone, compared to men. Again there are outliers and this is a huge oversimplification that doesn’t even look at other sex hormones, but broadly speaking (which sounds vague, but is actually what is represented in epidemiological studies), it will be so.
- Anatomy: humans have some obvious sexual dimorphism (again, there are outliers, but again, not enough to throw out the stats); this seems least likely to be relevant (Alzheimer’s is probably not stored in the breasts, for examples), though average body composition (per muscle:fat ratio) could admittedly be a factor.
- Social/lifestyle: once again, #NotAllWomen etc, but broadly speaking, women and men often tend towards different social roles in some ways, and as we know, of course lifestyle can play a part in disease pathogenesis.
As a quick aside before we continue, if you’re curious about those outliers, then a wiki-walk into the fascinating world of intersex conditions, for example, could start here. But by and large, this won’t affect most people.
So… Which parts matter?
Back in 2018, Dr. Maria Teresa Ferretti et al. kicked up some rocks in this regard, looking not just at genes (as much research has focussed on) or amyloid-β (again, well-studied) but also at phenotypes and metabolic and social factors—bearing in mind that all three of those are heavily influenced by hormones. Noting, for example, that (we’ll quote directly here):
- Men and women with Alzheimer disease (AD) exhibit different cognitive and psychiatric symptoms, and women show faster cognitive decline after diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment (MCI) or AD dementia.
- Brain atrophy rates and patterns differ along the AD continuum between the sexes; in MCI, brain atrophy is faster in women than in men.
- The prevalence and effects of cerebrovascular, metabolic and socio-economic risk factors for AD are different between men and women.
See: Sex differences in Alzheimer disease—the gateway to precision medicine
So, have scientists controlled for each of those factors?
Mostly not! But they have found clues, anyway, while noting the limitations of the previous way of conducting studies. For example:
❝Women are more likely to develop Alzheimer’s disease and experience faster cognitive decline compared to their male counterparts. These sex differences should be accounted for when designing medications and conducting clinical trials❞
~ Dr. Feixiong Cheng
Read: Research finds sex differences in immune response and metabolism drive Alzheimer’s disease
Did you spot the clue?
It was “differences in immune response and metabolism”. These things are both influenced by (not outright regulated by, but strongly influenced by) sex hormones.
❝As [hormonal] sex influences both the immune system and metabolic process, our study aimed to identify how all of these individual factors influence one another to contribute to Alzheimer’s disease❞
~ Dr. Justin Lathia
Ignoring for a moment progesterone’s role in metabolism, estrogen is an immunostimulant and testosterone is an immunosuppressant. These thus both also have an effect in inflammation, which yes, includes neuroinflammation.
But wait a minute, shouldn’t that mean that women are more protected, not less?
It should! Except… Alzheimer’s is an age-related disease, and in the age-bracket that generally gets Alzheimer’s (again, there are outliers), menopause has been done and dusted for quite a while.
Which means, and this is critical: post-menopausal women not on HRT are essentially left without the immune boost usually directed by estrogen, while men of the same age will be ticking over with their physiology that (unlike that of the aforementioned women) was already adapted to function with negligible estrogen.
Specifically:
❝The metabolic consequences of estrogen decline during menopause accelerate neuropathology in women❞
~ Dr. Rasha Saleh
Critical idea to take away from all this:
Alzheimer’s research is going to be misleading if it doesn’t take into account sex differences, and not just that, but also specifically age-relevant sex differences—because that can flip the narrative. If we don’t take age into account, we could be left thinking estrogen is to blame, when in fact, it appears to be the opposite.
In the meantime, if you’re a woman of a certain age, you might talk with a doctor about whether HRT could be beneficial for you, if you haven’t already:
❝Women at genetic risk for AD (carrying at least one APOE e4 allele) seem to be particularly benefiting from MHT❞
(MHT = Menopausal Hormone Therapy; also commonly called HRT, which is the umbrella term for Hormone Replacement Therapies in general)
~ Dr. Herman Depypere
Source study: Menopause hormone therapy significantly alters pathophysiological biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease
Pop-sci press release version: HRT could ward off Alzheimer’s among at-risk women
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Water’s Counterintuitive Properties
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Why are we told to drink more water for everything, even if sometimes it seems like the last thing we need? Bloated? Drink water. Diarrhea? Drink water. Nose running like a tap? Drink water❞
While water will not fix every ill, it can fix a lot, or at least stop it from being worse!
Our bodies are famously over 60% water (exact figure will depend on how well-hydrated you are, obviously, as well as your body composition in terms of muscle and fat). Our cells (which are mostly full of mostly water) need replacing all the time, and almost everything that needs transporting almost anywhere is taken there by blood (which is also mostly water). And if we need something moving out of the body? Water is usually going to be a large part of how it gets ejected.
In the cases of the examples you gave…
- Bloating: bloating is often a matter of water retention, which often happens as a result of having too much salt, and/or sometimes too much fat. So the body’s homeostatic system (the system that tries to maintain all kinds of equilibrium, keeping salt balance, temperature, pH, and many other things in their respective “Goldilocks zones”) tries to add more water to where it’s needed to balance out the salt etc.
- Consequently, drinking more water means the body will note “ok, balance restored, no need to keep retaining water there, excess salts being safely removed using all this lovely water”.
- Diarrhea: this is usually a case of a bacterial infection, though there can be other causes. Whether for that reason or another, the body has decided that it needs to give your gut an absolute wash-out, and it can only do that from the inside—so it uses as much of the body’s water as it needs to do that.
- Consequently, drinking more water means that you are replenishing the water that the body has already 100% committed to using. If you don’t drink water, you’ll still have diarrhea, you’ll just start to get dangerously dehydrated.
- Runny nose: this is usually a case of either fighting a genuine infection, or else fighting something mistaken for a pathogen (e.g. pollen, or some other allergen). The mucus is an important part of the body’s defense: it traps the microbes (be they bacteria, virus, whatever) and water-slides them out of the body.
- Consequently, drinking more water means the body can keep the water-slide going. Otherwise, you’ll just get gradually more dehydrated (because as with diarrhea, your body will prioritize this function over maintaining water reserves—water reserves are there to be used if necessary, is the body’s philosophy) and if the well runs dry, you’ll just be dehydrated and have a higher pathogen-count still in your body.
Some previous 10almonds articles that might interest you:
- Hydration Mythbusting
- When To Take Electrolytes (And When We Shouldn’t!)
- Keeping Your Kidneys Healthy (Especially After 60)
Would you like this section to be bigger? If so, send us more questions!
Share This Post
- Bloating: bloating is often a matter of water retention, which often happens as a result of having too much salt, and/or sometimes too much fat. So the body’s homeostatic system (the system that tries to maintain all kinds of equilibrium, keeping salt balance, temperature, pH, and many other things in their respective “Goldilocks zones”) tries to add more water to where it’s needed to balance out the salt etc.
-
Cannabis Myths vs Reality
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Cannabis Myths vs Reality
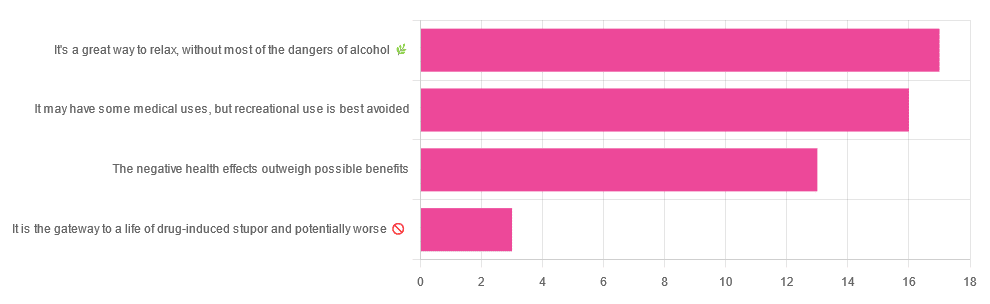
We asked you for your (health-related) opinion on cannabis use—specifically, the kind with psychoactive THC, not just CBD. We got the above-pictured, below-described, spread of responses:
- A little over a third of you voted for “It’s a great way to relax, without most of the dangers of alcohol”.
- A little under a third of you voted for “It may have some medical uses, but recreational use is best avoided”.
- About a quarter of you voted for “The negative health effects outweigh the possible benefits”
- Three of you voted for “It is the gateway to a life of drug-induced stupor and potentially worse”
So, what does the science say?
A quick legal note first: we’re a health science publication, and are writing from that perspective. We do not know your location, much less your local laws and regulations, and so cannot comment on such. Please check your own local laws and regulations in that regard.
Cannabis use can cause serious health problems: True or False?
True. Whether the risks outweigh the benefits is a personal and subjective matter (for example, a person using it to mitigate the pain of late stage cancer is probably unconcerned with many other potential risks), but what’s objectively true is that it can cause serious health problems.
One subscriber who voted for “The negative health effects outweigh the possible benefits” wrote:
❝At a bare minimum, you are ingesting SMOKE into your lungs!! Everyone SEEMS TO BE against smoking cigarettes, but cannabis smoking is OK?? Lung cancer comes in many forms.❞
Of course, that is assuming smoking cannabis, and not consuming it as an edible. But, what does the science say on smoking it, and lung cancer?
There’s a lot less research about this when it comes to cannabis, compared to tobacco. But, there is some:
❝Results from our pooled analyses provide little evidence for an increased risk of lung cancer among habitual or long-term cannabis smokers, although the possibility of potential adverse effect for heavy consumption cannot be excluded.❞
Read: Cannabis smoking and lung cancer risk: Pooled analysis in the International Lung Cancer Consortium
Another study agreed there appears to be no association with lung cancer, but that there are other lung diseases to consider, such as bronchitis and COPD:
❝Smoking cannabis is associated with symptoms of chronic bronchitis, and there may be a modest association with the development of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Current evidence does not suggest an association with lung cancer.❞
Read: Cannabis Use, Lung Cancer, and Related Issues
Cannabis edibles are much safer than smoking cannabis: True or False?
Broadly True, with an important caveat.
One subscriber who selected “It may have some medical uses, but recreational use is best avoided”, wrote:
❝I’ve been taking cannabis gummies for fibromyalgia. I don’t know if they’re helping but they’re not doing any harm. You cannot overdose you don’t become addicted.❞
Firstly, of course consuming edibles (rather than inhaling cannabis) eliminates the smoke-related risk factors we discussed above. However, other risks remain, including the much greater ease of accidentally overdosing.
❝Visits attributable to inhaled cannabis are more frequent than those attributable to edible cannabis, although the latter is associated with more acute psychiatric visits and more ED visits than expected.❞
Note: that “more frequent” for inhaled cannabis, is because more people inhale it than eat it. If we adjust the numbers to control for how much less often people eat it, suddenly we see that the numbers of hospital admissions are disproportionately high for edibles, compared to inhaled cannabis.
Or, as the study author put it:
❝There are more adverse drug events associated on a milligram per milligram basis of THC when it comes in form of edibles versus an inhaled cannabis. If 1,000 people smoked pot and 1,000 people at the same dose in an edible, then more people would have more adverse drug events from edible cannabis.❞
See the numbers: Acute Illness Associated With Cannabis Use, by Route of Exposure
Why does this happen?
- It’s often because edibles take longer to take effect, so someone thinks “this isn’t very strong” and has more.
- It’s also sometimes because someone errantly eats someone else’s edibles, not realising what they are.
- It’s sometimes a combination of the above problems: a person who is now high, may simply forget and/or make a bad decision when it comes to eating more.
On the other hand, that doesn’t mean inhaling it is necessarily safer. As well as the pulmonary issues we discussed previously, inhaling cannabis has a higher risk of cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome (and the resultant cyclic vomiting that’s difficult to treat).
You can read about this fascinating condition that’s sometimes informally called “scromiting”, a portmanteau of screaming and vomiting:
Cannabinoid Hyperemesis Syndrome
You can’t get addicted to cannabis: True or False?
False. However, it is fair to say that the likelihood of developing a substance abuse disorder is lower than for alcohol, and much lower than for nicotine.
See: Prevalence of Marijuana Use Disorders in the United States Between 2001–2002 and 2012–2013
If you prefer just the stats without the science, here’s the CDC’s rendering of that:
Addiction (Marijuana or Cannabis Use Disorder)
However, there is an interesting complicating factor, which is age. One is 4–7 times more likely to develop a substance abuse disorder, if one starts use as an adolescent, rather than later in life:
Cannabis is the gateway to use of more dangerous drugs: True or False?
False, generally speaking. Of course, for any population there will be some outliers, but there appears to be no meaningful causal relation between cannabis use and other substance use:
Interestingly, the strongest association (where any existed at all) was between cannabis use and opioid use. However, rather than this being a matter of cannabis use being a gateway to opioid use, it seems more likely that this is a matter of people looking to both for the same purpose: pain relief.
As a result, growing accessibility of cannabis may actually reduce opioid problems:
- Cannabis as a Gateway Drug for Opioid Use Disorder
- Association between medical cannabis laws and opioid overdose mortality has reversed over time
Some final words…
Cannabis is a complex drug with complex mechanisms and complex health considerations, and research is mostly quite young, due to its historic illegality seriously cramping science by reducing sample sizes to negligible. Simply put, there’s a lot we still don’t know.
Also, we covered some important topics today, but there were others we didn’t have time to cover, such as the other potential psychological benefits—and risks. Likely we’ll revisit those another day.
Lastly, while we’ve covered a bunch of risks today, those of you who said it has fewer and lesser risks than alcohol are quite right—the only reason we couldn’t focus on that more, is because to talk about all the risks of alcohol would make this feature many times longer!
Meanwhile, whether you partake or not, stay safe and stay well.
Share This Post
-
The Rise Of The Machines
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In this week’s health science news, several pieces of technology caught our eye. Let’s hope these things roll out widely!
When it comes to UTIs, antimicrobial resistance is taking the p—
This has implications far beyond UTIs—though UTIs can be a bit of a “canary in the coal mine” for antimicrobial resistance. The more people are using antibiotics (intentionally, or because they are in the food chain), the more killer bugs are proliferating instead of dying when we give them something to kill them. And yes: they do proliferate sometimes when given antibiotics, not because the antibiotics did anything directly good for them, but because they killed their (often friendly bacteria) competition. Thus making for a double-whammy of woe.
This development tackles that, by using AI modelling to crunch the numbers of a real-time data-driven personalized approach to give much more accurate treatment options, in a way that a human couldn’t (or at least, couldn’t at anything like the same speed, and most family physicians don’t have a mathematician locked in the back room to spend the night working on a patient’s data).
Read in full: AI can help tackle urinary tract infections and antimicrobial resistance
Related: AI: The Doctor That Never Tires?
When it comes to CPR and women, people are feint of heart
When CPR is needed, time is very much of the essence. And yet, bystanders are much less likely to give CPR to a woman than to a man. Not only that, but CPR-training is part of what leads to this reluctance when it comes to women: the mannequins used are very homogenous, being male (94%) and lean (99%). They’re also usually white (88%) even in countries where the populations are not, but that is less critical. After all, a racist person is less likely to give CPR to a person of color regardless of what color the training mannequin was.
However, the mannequins being male and lean is an issue, because it means people suddenly lack confidence when faced with breasts and/or abundant body fat. Both can prompt the bystander to wonder if some different technique is needed (it isn’t), and breasts can also prompt the bystander to fear doing something potentially “improper” (the proper course of action is: save a person’s life; do not get distracted by breasts).
Read in full: Women are less likely to receive CPR than men. Training on manikins with breasts could help ← there are also CPR instructions (and a video demonstration) there, for anyone who wants a refresher, if perhaps your last first-aid course was a while ago!
Related: Heart Attack: His & Hers (Be Prepared!)
When technology is a breath of fresh air
A woman with COPD and COVID has had her very damaged lungs replaced using a da Vinci X robot to perform a minimally-invasive surgery (which is quite a statement, when it comes to replacing someone’s lungs).
Not without human oversight though—surgeon Dr. Stephanie Chang was directing the transplant. Surgery is rarely fun for the person being operated on, but advances like this make things go a lot more smoothly, so this kind of progress is good to see.
Read in full: Woman receives world’s first robotic double-lung transplant
Related: Why Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Is More Likely Than You Think
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
What will aged care look like for the next generation? More of the same but higher out-of-pocket costs
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Aged care financing is a vexed problem for the Australian government. It is already underfunded for the quality the community expects, and costs will increase dramatically. There are also significant concerns about the complexity of the system.
In 2021–22 the federal government spent A$25 billion on aged services for around 1.2 million people aged 65 and over. Around 60% went to residential care (190,000 people) and one-third to home care (one million people).
The final report from the government’s Aged Care Taskforce, which has been reviewing funding options, estimates the number of people who will need services is likely to grow to more than two million over the next 20 years. Costs are therefore likely to more than double.
The taskforce has considered what aged care services are reasonable and necessary and made recommendations to the government about how they can be paid for. This includes getting aged care users to pay for more of their care.
But rather than recommending an alternative financing arrangement that will safeguard Australians’ aged care services into the future, the taskforce largely recommends tidying up existing arrangements and keeping the status quo.
No Medicare-style levy
The taskforce rejected the aged care royal commission’s recommendation to introduce a levy to meet aged care cost increases. A 1% levy, similar to the Medicare levy, could have raised around $8 billion a year.
The taskforce failed to consider the mix of taxation, personal contributions and social insurance which are commonly used to fund aged care systems internationally. The Japanese system, for example, is financed by long-term insurance paid by those aged 40 and over, plus general taxation and a small copayment.
Instead, the taskforce puts forward a simple, pragmatic argument that older people are becoming wealthier through superannuation, there is a cost of living crisis for younger people and therefore older people should be required to pay more of their aged care costs.
Separating care from other services
In deciding what older people should pay more for, the taskforce divided services into care, everyday living and accommodation.
The taskforce thought the most important services were clinical services (including nursing and allied health) and these should be the main responsibility of government funding. Personal care, including showering and dressing were seen as a middle tier that is likely to attract some co-payment, despite these services often being necessary to maintain independence.
The task force recommended the costs for everyday living (such as food and utilities) and accommodation expenses (such as rent) should increasingly be a personal responsibility.
Aged care users will pay more of their share for cooking and cleaning.
Lizelle Lotter/ShutterstockMaking the system fairer
The taskforce thought it was unfair people in residential care were making substantial contributions for their everyday living expenses (about 25%) and those receiving home care weren’t (about 5%). This is, in part, because home care has always had a muddled set of rules about user co-payments.
But the taskforce provided no analysis of accommodation costs (such as utilities and maintenance) people meet at home compared with residential care.
To address the inefficiencies of upfront daily fees for packages, the taskforce recommends means testing co-payments for home care packages and basing them on the actual level of service users receive for everyday support (for food, cleaning, and so on) and to a lesser extent for support to maintain independence.
It is unclear whether clinical and personal care costs and user contributions will be treated the same for residential and home care.
Making residential aged care sustainable
The taskforce was concerned residential care operators were losing $4 per resident day on “hotel” (accommodation services) and everyday living costs.
The taskforce recommends means tested user contributions for room services and everyday living costs be increased.
It also recommends that wealthier older people be given more choice by allowing them to pay more (per resident day) for better amenities. This would allow providers to fully meet the cost of these services.
Effectively, this means daily living charges for residents are too low and inflexible and that fees would go up, although the taskforce was clear that low-income residents should be protected.
Moving from buying to renting rooms
Currently older people who need residential care have a choice of making a refundable up-front payment for their room or to pay rent to offset the loans providers take out to build facilities. Providers raise capital to build aged care facilities through equity or loan financing.
However, the taskforce did not consider the overall efficiency of the private capital market for financing aged care or alternative solutions.
Instead, it recommended capital contributions be streamlined and simplified by phasing out up-front payments and focusing on rental contributions. This echoes the royal commission, which found rent to be a more efficient and less risky method of financing capital for aged care in private capital markets.
It’s likely that in a decade or so, once the new home care arrangements are in place, there will be proportionally fewer older people in residential aged care. Those who do go are likely to be more disabled and have greater care needs. And those with more money will pay more for their accommodation and everyday living arrangements. But they may have more choice too.
Although the federal government has ruled out an aged care levy and changes to assets test on the family home, it has yet to respond to the majority of the recommendations. But given the aged care minister chaired the taskforce, it’s likely to provide a good indication of current thinking.
Hal Swerissen, Emeritus Professor, La Trobe University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How Gluconolactone Restores Immune Regulation In Lupus
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Let’s be clear up front: this will not cure lupus.
However, it will interrupt the pathology of lupus in such a way as to, as the title says, restore immune regulation—so that your body stops attacking itself, or at the very least, attacks itself significantly less.
What is gluconolactone anyway?
Gluconolactone (also called glucono-δ-lactone) an oxidized derivative of glucose, when glucose is exposed to oxygen and a certain enzyme (glucose oxidase). It’s used in various food-related fermentation processes, and also helps such foods to have a tangy flavor.
It’s also known as E575, showing that E-numbers need not always be scary 🙂
How does it work?
First, a recap on how lupus works: lupus is an autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks its own tissues, causing inflammation and organ damage (to oversimplify it in very few words).
Next, how lupus is currently treated: mostly with immunosuppressant drugs, which reduce symptoms but have significant side effects, not least of all the fact that your immune system will be suppressed, leaving you vulnerable to infections, cancer, aging, and the like. So, there’s really a “damned if you do, damned if you don’t” aspect here (because untreated lupus will run your immune system into the ground with its chronic inflammation, which will also leave you vulnerable to the aforementioned things).
See also: How to Prevent (or Reduce) Inflammation
Now, how gluconolactone works: it increases the number of regulatory T-cells (also called “Tregs” by scientists who don’t want to have to say/write “regulatory T-cells” many times per day), which are the ones that tell the rest of your immune system what not to attack. It also inhibits pro-inflammatory T-helper-cells that are otherwise involved in autoimmune dysfunction.
Where is the science for this?
It’s a shiny new paper that covers three angles:
- In lupus-suffering mouse in vivo studies, it improved Treg function and reduced inflammatory skin rashes
- In human cell culture in vitro studies (with cell cultures from human lupus patients), it bolstered Treg count and improved immune regulation
- In human patient in vivo studies, a gluconolactone cream controlled skin inflammation and improved the clinical and histologic appearance of the skin lesions within 2 weeks
❝These results suggest that gluconolactone could be a targeted treatment option with fewer side effects for autoimmune diseases such as lupus.
Gluconolactone acts like a ‘power food’ for regulatory T cells—a real win-win situation for immune regulation❞
~ Dr. Antonios Kolios
You can find the paper itself here:
Where can I get gluconolactone?
At the moment, this is still in the clinical trials phase, so it’s not something you can get a prescription for yet, alas.
But definitely keep an eye out for it!
We would hypothesize that eating foods fermented with E575 (it’s sometimes used in feta cheese, hence today’s featured image, and it’s also often used as a pickling agent) may well help, but that’s just our hypothesis as it isn’t what was tested in the above studies.
Want to learn more?
In the meantime, if you’d like to learn more about lupus, we recommend this very comprehensive book:
*The “et al.” are: Jemima Albayda, MD; Divya Angra, MD; Alan N. Baer, MD; Sasha Bernatsky, MD, PhD; George Bertsias, MD, PhD; Ashira D. Blazer, MD; Ian Bruce, MD; Jill Buyon, MD; Yashaar Chaichian, MD; Maria Chou, MD; Sharon Christie, Esq; Angelique N. Collamer, MD; Ashté Collins, MD; Caitlin O. Cruz, MD; Mark M. Cruz, MD; Dana DiRenzo, MD; Jess D. Edison, MD; Titilola Falasinnu, PhD; Andrea Fava, MD; Cheri Frey, MD; Neda F. Gould, PhD; Nishant Gupta, MD; Sarthak Gupta, MD; Sarfaraz Hasni, MD; David Hunt, MD; Mariana J. Kaplan, MD; Alfred Kim, MD; Deborah Lyu Kim, DO; Rukmini Konatalapalli, MD; Fotios Koumpouras, MD; Vasileios C. Kyttaris, MD; Jerik Leung, MPH; Hector A. Medina, MD; Timothy Niewold, MD; Julie Nusbaum, MD; Ginette Okoye, MD; Sarah L. Patterson, MD; Ziv Paz, MD; Darryn Potosky, MD; Rachel C. Robbins, MD; Neha S. Shah, MD; Matthew A. Sherman, MD; Yevgeniy Sheyn, MD; Julia F. Simard, ScD; Jonathan Solomon, MD; Rodger Stitt, MD; George Stojan, MD; Sangeeta Sule, MD; Barbara Taylor, CPPM, CRHC; George Tsokos, MD; Ian Ward, MD; Emma Weeding, MD; Arthur Weinstein, MD; Sean A. Whelton, MD
The reason we mention this is to render it clear that this isn’t one man’s opinions (as happens with many books about certain topics), but rather, a panel of that many doctors all agreeing that this is correct and good, evidence-based, up-to-date (as of the publication of this latest revised edition) information.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Beat The Heat, With Fat
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Surviving Summer
Summer is upon us, for those of us in the Northern Hemisphere anyway, and given that nowadays each year tends to be hotter than the one before, on average, it pays to be prepared.
We’ve talked about dealing with the heat before:
Sun, Sea, And Sudden Killers To Avoid
All the above advice stands this summer too, but today we’re going to speak a little extra on not having a “default body”.
For much of medical literature and common health advice, the default body is that of a slim and/or athletic white cis man aged 25–35 with no disabilities.
When it comes to “women’s health”, this is often confined to “the bikini zone” and everything else is commonly treated based on research conducted with men.
Today we’ll be looking at a particular challenge for a wide variety of people, when it comes to heat…
Beating the heat, with fat
If you are fat, and/or have a bit of a tummy, and/or have breasts, this one’s for you.
Fat acts as an insulator, which naturally does no favors in hot weather. Carrying the weight around is also extra exercise, which also becomes a problem in hot weather. Fat people usually sweat more than thin people do, as a result.
Sweat is great for cooling down the body, because it takes heat with it when it evaporates off. However, that only works if it can evaporate off, and it can’t evaporate off if it’s trapped in a skin fold / fat roll.
If you’re fat, you may have plenty of those; if you have a bit of a tummy (if you’re not fat generally, this might be a leftover from pregnancy, or weight loss, or something else; how it got there doesn’t matter for our purposes today), you’ll have at least one under it, and if you have breasts, unless they’re quite small, you’ll have one under each breast, and potentially your cleavage may become an issue too.
Note: if you are perhaps a man who has fat in the place where breasts go, then medically this goes for you too, except that there’s not a societal expectation that you wear bra. Use today’s information as you see fit.
Sweat-wicking hacks
We don’t want sweat to stay in those folds—both because then it’s not doing its cooling-down job, and also, because it can cause a rash, and even yeast infections and/or bacterial infections.
So, we want there to be some barrier there. You could use something like vaseline or baby powder, as to prevent chafing, but fat better (more effective, and less messy) is to have some kind of cloth there that can wick the sweat away.
There are made-for-purpose curved cotton bands that exist, called “tummy liners”; here’s an example product on Amazon, or you could make your own if you’re so inclined. They’re breathable, absorbent, and reduce friction too, making everything a lot more comfortable.
And for breasts? Same deal, there are made-for-purpose cotton bra-liners that exist; here’s an example product on Amazon, or again, you could make your own if you feel so inclined. The important part is that it makes things so much comfortable, because let’s face it: wearing a bra in the summer is not comfortable.
So with these, it can become more comfortable (and the cotton liners are flat, so they’re not visible if one’s wearing a t-shirt or similar-coverage garment). You could go braless, of course, but then you’re back to having sweaty folds, so if you’re doing something other than swimming or lying on your back, you might want something there.
Different hydration rules
“People should drink this much per day” and guess what, those guidelines were based on, drumroll please, not fat people.
Sweating more means needing to hydrate more, and even without breaking a sweat, having a larger body than average (be it muscle, fat, or both) means having more body to hydrate. That’s simple math.
So instead, a good general guideline is half an ounce of water per your weight in pounds, per day:
How much water do I need each day?
Another good general guideline is to simply drink “little and often”, that is to say, always have a (hydrating!) drink on the go.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: