Mythbusting Cookware Materials
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
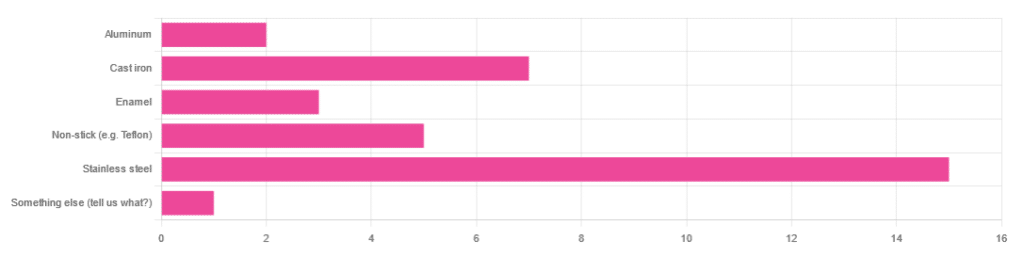
In Wednesday’s newsletter, we asked you what kind of cookware you mostly use, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 45% said stainless steel
- About 21% said cast iron
- About 15% said non-stick (e.g. Teflon)
- About 9% said enamel
- About 6% said aluminum
- And 1 person selected “something else”, but then commented to the contrary, writing “I use all of the above”
So, what does the science say about these options?
Stainless steel cookware is safe: True or False?
True! Assuming good quality and normal use, anyway. There really isn’t a lot to say about this, because it’s very unexciting. So long as it is what it is labelled as: there’s nothing coating it, nothing comes out of it unless you go to extremes*, and it’s easy to clean.
*If you cook for long durations at very high temperatures, it can leach nickel and chromium into food. What this means in practical terms: if you are using stainless steel to do deep-frying, then maybe stop that, and also consider going easy on deep-frying in general anyway, because obviously deep-frying is unhealthy for other reasons.
Per normal use, however: pretty much the only way (good quality) stainless steel cookware will harm you is if you touch it while it’s hot, or if it falls off a shelf onto your head.
That said, do watch out for cheap stainless steel cookware that can contain a lot of impurities, including heavy metals. Since you probably don’t have a mass spectrometer and/or chemistry lab at home to check for those impurities, your best guard here is simply to buy from a reputable brand with credible certifications.
Ceramic cookware is safe: True or False?
True… Most of the time! Ceramic pans usually have metal parts and a ceramic cooking surface coated with a very thin layer of silicon. Those metal parts will be as safe as the metals used, so if that’s stainless steel, you’re just as safe as the above. As for the silicon, it is famously inert and body-safe (which is why it’s used in body implants).
However: ceramic cookware that doesn’t have an obvious metal part and is marketed as being pure ceramic, will generally be sealed with some kind of glaze that can leach heavy metals contaminants into the food; here’s an example:
Lead toxicity from glazed ceramic cookware
Copper cookware is safe: True or False?
False! This is one we forgot to mention in the poll, as one doesn’t see a lot of it nowadays. The copper from copper pans can leach into food. Now, of course copper is an important mineral that we must get from our diet, but the amount of copper that that can leach into food from copper pans is far too much, and can induce copper toxicity.
In addition, copper cookware has been found to be, on average, highly contaminated with lead:
Non-stick cookware contaminates the food with microplastics: True or False?
True! If we were to discuss all the common non-stick contaminants here, this email would no longer fit (there’s a size limit before it gets clipped by most email services).
Suffice it to say: the non-stick coating, polytetrafluoroethylene, is itself a PFAS, that is to say, part of the category of chemicals considered environmental pollutants, and associated with a long list of health issues in humans (wherein the level of PFAS in our bloodstream is associated with higher incidence of many illnesses):
You may have noticed, of course, that the “non-stick” coating doesn’t stick very well to the pan, either, and will tend to come off over time, even if used carefully.
Also, any kind of wet cooking (e.g. saucepans, skillets, rice cooker inserts) will leach PFAS into the food. In contrast, a non-stick baking tray lined with baking paper (thus: a barrier between the tray and your food) is really not such an issue.
We wrote about PFAS before, so if you’d like a more readable pop-science article than the scientific paper above, then check out:
PFAS Exposure & Cancer: The Numbers Are High
Aluminum cookware contaminates the food with aluminum: True or False?
True! But not usually in sufficient quantities to induce aluminum toxicity, unless you are aluminum pans Georg who eats half a gram of aluminum per day, who is a statistical outlier and should not be counted.
That’s a silly example, but an actual number; the dose required for aluminum toxicity in blood is 100mg/L, and you have about 5 liters of blood.
Unless you are on kidney dialysis (because 95% of aluminum is excreted by the kidneys, and kidney dialysis solution can itself contain aluminum), you will excrete aluminum a lot faster than you can possibly absorb it from cookware. On the other hand, you can get too much of it from it being a permitted additive in foods and medications, for example if you are taking antacids they often have a lot of aluminum oxide in them—but that is outside the scope of today’s article.
However, aluminum may not be the real problem in aluminum pans:
❝In addition, aluminum (3.2 ± 0.25 to 4.64 ± 0.20 g/kg) and copper cookware (2.90 ± 0.12 g/kg) were highly contaminated with lead.
The time and pH-dependent study revealed that leaching of metals (Al, Pb, Ni, Cr, Cd, Cu, and Fe, etc.) into food was predominantly from anodized and non-anodized aluminum cookware.
More metal leaching was observed from new aluminum cookware compared to old. Acidic food was found to cause more metals to leach during cooking.❞
~ the same paper we cited when talking about copper
Cast iron cookware contaminates the food with iron: True or False?
True, but unlike with the other metals discussed, this is purely a positive, and indeed, it’s even recommended as a good way to fortify one’s diet with iron:
The only notable counterpoint we could find for this is if you have hemochromatosis, a disorder in which the body is too good at absorbing iron and holding onto it.
Thinking of getting some new cookware?
Here are some example products of high-quality safe materials on Amazon, but of course feel free to shop around:
Stainless Steel | Ceramic* | Cast Iron
*it says “non-stick” in the description, but don’t worry, it’s ceramic, not Teflon etc, and is safe
Bonus: rice cooker with stainless steel inner pot
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Live Long, Die Short – by Dr. Roger Landry
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First know: “die short” is not about your height—although on average, short people do live longer, partly because insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1) promotes both tallness and accelerated DNA damage (thus, aging and cancer), and partly because if someone is very tall, it can cause circulatory problems, and without a nice easy flow of blood through the brain, bad things happen (such as accumulation of harmful detritus in the brain, and increased stroke risk too).
Next know: “die short” is, in this book, actually about shortening the decline at the end of life. Sometimes people say “I don’t want to live 10 years longer; they’ll be the 10 most miserable years”, but in fact if we look after our health, we will be healthy for perhaps >9.5 of our last 10 years, while an unhealthy person may just get their expected “10 most miserable years” 10 or 20 years earlier (and then die).
So, in short (so to speak), it’s about increasing healthspan.
To enjoy the longest and healthiest healthspan, Dr. Landry offers 10 tips. We’ll not keep them a secret; they are:
- Use it or lose it
- Keep moving
- Challenge your brain
- Stay connected
- Lower your risks
- Never act your age
- Wherever you are, be fully there
- Find your purpose
- Have children in your life
- Laugh to a better life
Each of these has a chapter devoted to them, in section 2 of the book (section 1 is about what we know about healthy aging, and section 3 is about where we go from here).
You’ll notice that one item not generally found on such lists is “have children in your life”; to be clear, they don’t have to be your children, and/but they do have to be actual current children; any now-grown-up progeny aren’t what’s being talked about here (wonderful as they may be, any support role they may play gets filed under “stay connected” instead).
The style is mostly impersonal pop-science with occasional personal anecdotes, and the book’s formatting (many subheadings within chapters) makes it easy to read a bit at a time, if that’s your preference. There’s a modest, but extant, bibliography.
Bottom line: if you’d like to stay younger as you get older, this book goes into a lot of detail about 10 ways to do just that.
Click here to check out Live Long, Die Short, and live long, die short!
Share This Post
-
Here’s how to help protect babies and kids from RSV
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What you need to know
- RSV is a respiratory virus that is especially dangerous for babies and young children.
- There are two ways to help protect babies from RSV: vaccination during pregnancy and giving babies nirsevimab, an RSV antibody shot.
- If someone in your household has RSV, watch for signs of severe illness and take steps to help prevent it from spreading.
Respiratory syncytial virus, or RSV, is a very contagious seasonal respiratory illness that is especially dangerous for infants and young children. Cases rose dramatically last month, and an increasing number of kids and older adults with RSV are being hospitalized across the United States.
Fortunately, pregnant people can get vaccinated during pregnancy or get their infants and young children an RSV antibody shot to help them stay healthy.
Read on to learn about symptoms of RSV, how to help prevent infants and children from getting very sick, and what families should do if someone in their household is sick with the virus.
What are the symptoms of RSV in babies and young children?
RSV symptoms in young children may include a runny nose, decreased eating and drinking, and coughing, which may lead to wheezing and difficulty breathing.
Infants with RSV may show symptoms like irritability, decreased activity and appetite, and life-threatening pauses in breathing (apnea) that last for more than 10 seconds. Most infants with RSV will not develop a fever, but babies who are born prematurely, have weakened immune systems, or have chronic lung disease are more likely to become very sick.
Who is eligible for an RSV antibody shot?
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that babies younger than 8 months whose gestational parent did not receive an RSV vaccine during pregnancy receive nirsevimab between October and March, when RSV typically peaks. This antibody shot delivers proteins that can help protect them against RSV.
Nirsevimab is also recommended for children between 8 and 19 months who are at increased risk of severe RSV, including children who are born prematurely, have chronic lung disease or severe cystic fibrosis, are immunocompromised, or are American Indians or Alaska Natives.
Nirsevimab is typically covered by insurance or costs $495 out of pocket. Children who are eligible for the CDC’s Vaccines for Children Program can receive nirsevimab at no cost.
How can families help prevent RSV from spreading?
It’s recommended that children and adults who are sick with RSV stay home and away from others. If your infant or child has difficulty breathing or develops blue or gray skin, take them to an emergency room right away.
People who are infected with RSV can spread the disease when they cough or sneeze; have close contact with others; or touch, cough, or sneeze on shared surfaces. Help protect your family from catching and spreading RSV at home and in public places by ensuring that everyone covers their mouths during coughing and sneezing, washes their hands often, and wears a high-quality, well-fitting mask.
For more information, talk to your health care provider.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Share This Post
-
Myofascial Training – by Ester Albini
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Fascia is an oft-forgotten part of the body—if something that is so ubiquitous and varied can be described as a single part. And yet, it arguably is—precisely because it is the connective tissue that holds everything else together, so by its nature, it’s ultimately a one-piece thing.
This “one-piece thing” is responsible for permitting us movement, and is also responsible for restricting our movement. As such, when it comes to mobility, we can stretch our muscles all day long and it won’t mean a thing if our fascia is stiff. And notably, fascia has a much slower turnover time (in terms of how quickly the body replaces it) than muscle, so fascia is almost always going to be the limiting factor.
Pilates instructor (with many certifications) Albini gives the reader the tools to loosen up that limiting factor. It’ll take time and consistency (it takes the body around 18 months to fully rebuild fascia, so that’s the timeframe for an ultimate “job done” to then just be maintained), but there are also some results to be enjoyed immediately, by virtue of myofascial release
In style, the book is half textbook, half workbook. She explains a lot of the anatomy and physiology of fascia (and does so very well). This book is, in this reviewer’s opinion, better than the usual go-to professional guidebook to fascia (i.e., for physiotherapists etc) that costs more than twice the price and is half as clear (the other book’s diagrams are unnecessarily abstract, the photos fuzzy, and the prose tedious). This book, in contrast, has very clear diagrams, hundreds of high-quality color photos, and excellent explanations that are aimed at the layperson, and/but aren’t afraid to get technical either; she just explains the technicalities well too.
The workbook side of things is a vast array of exercises to do, including for specific issues and to combat various lifestyle problems, as well as to just support general health and more mobility than most people think is possible for them.
Bottom line: if you’d like better mobility and have been neglecting your fascia (or have been a bit confused by it), this book is going to be your new best friend.
Click there to check out Myofascial Training, and free your body’s movements!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Twenty-Four Hour Mind – by Dr. Rosalind Cartwright
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve reviewed books about sleep before, and even about dreaming, so what does this one have to offer that’s new?
Quite a lot, actually! Before Dr. Cartwright, there were mainly two models of sleep and dreaming:
- The “top-down” model of psychoanalysts: our minds shape our dreams which in turn reveal things about us as people
- The “bottom-up” model of neuroscientists: our brains need to go through regular maintaince cycles, of which vivid hallucinations are a quirky side-effect.
And now, as Dr. Cartwright puts it:
❝I will lay out a new [horizontal] psychological model of the twenty-four hour mind; that is, how the predominantly conscious (waking) and unconscious (sleeping) forms of mental behavior interact through the brain’s regular, but differently organized, states of waking, sleeping, and dreaming.❞
This she does in the exploratory style of a 224-page lecture, which sounds like it might be tedious, but is actually attention-grabbing and engaging throughout. This book is more of a page-turner than soporific bedtime reading!
Bottom line: if you’d like to know more about the effect your waking and sleeping brain have on each other (to include getting in between those and making adjutments as appropriate), this is very much an elucidating read!
Click here to check out The Twenty-Four Hour Mind, and learn more about yours!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Everything You Need To Know About The Menopause – by Kate Muir
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Kate Muir has made a career out of fighting for peri-menopausal health to be taken seriously. Because… it’s actually far more serious than most people know.
What people usually know:
- No more periods
- Hot flushes
- “I dunno, some annoying facial hairs maybe”
The reality encompasses a lot more, and Muir covers topics including:
- Workplace struggles (completely unnecessary ones)
- Changes to our sex life (not usually good ones, by default!)
- Relationship between menopause and breast cancer
- Relationship between menopause and Alzheimer’s
“Wait”, you say, “correlation is not causation, that last one’s just an age thing”, and that’d be true if it weren’t for the fact that receiving Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) or not is strongly correlated with avoiding Alzheimer’s or not.
The breast cancer thing is not to be downplayed either. Taking estrogen comes with a stated risk of breast cancer… But what they don’t tell you, is that for many people, not taking it comes with a higher risk of breast cancer (but that’s not the doctor’s problem, in that case). It’s one of those situations where fear of litigation can easily overrule good science.
This kind of thing, and much more, makes up a lot of the meat of this book.
Hormonal treatment for the menopause is often framed in the wider world as a whimsical luxury, not a serious matter of health…. If you’ve ever wondered whether you might want something different, something better, as part of your general menopause plan (you have a plan for this important stage of your life, right?), this is a powerful handbook for you.
Additionally, if (like many!) you justifiably fear your doctor may brush you off (or in the case of mood disorders, may try to satisfy you with antidepressants to treat the symptom, rather than HRT to treat the cause), this book will arm you as necessary to help you get what you need.
Grab your copy of “Everything You Need To Know About The Menopause” from Amazon today!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Huperzine A: A Natural Nootropic
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Huperzine A: A Natural Nootropic
Huperzine A is a compound, specifically a naturally occurring sesquiterpene alkaloid, that functions as an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. If that seems like a bunch of big words, don’t worry, we’ll translate in a moment.
First, a nod to its origins: it is found in certain kinds of firmoss, especially the “toothed clubmoss”, Huperzia serrata, which grows in many Asian countries.
What’s an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor?
Let’s do this step-by-step:
- An acetylcholinesterase inhibitor is a compound that inhibits acetylcholinesterase.
- Acetylcholinesterase is an enzyme that catalyzes (speeds up) the breakdown of acetylcholine.
- Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter; it’s an ester of acetic acid and choline.
- This is the main neurotransmitter of the parasympathetic nervous system, and is also heavily involved in cognitive functions including memory and creative thinking.
What this means: if you take an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor like huperzine A, it will inhibit acetylcholinesterase, meaning you will have more acetylcholine to work with. That’s good.
What can I expect from it?
Huperzine A has been well-studied for a while, mostly for the prevention and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease:
- New insights into huperzine A for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease
- Huperzine A: Is it an Effective Disease-Modifying Drug for Alzheimer’s Disease?
- Huperzine A and Its Neuroprotective Molecular Signaling in Alzheimer’s Disease
However, research has suggested that huperzine A is much better as a prevention than a treatment:
❝A central event in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the accumulation of senile plaques composed of aggregated amyloid-β (Aβ) peptides.
Ex vivo electrophysiological experiments showed that 10 μM of Aβ1-40 significantly decreased the effect of the AChE inhibitor huperzine A on the synaptic potential parameters. ❞
~ Dr. Irina Zueva
In other words: the answer to the titular question is “Yes, yes it can”
And, to translate Dr. Zueva’s words into simple English:
- People with Alzheimer’s have amyloid-β plaque in their brains
- That plaque reduces the effectiveness of huperzine A
So, what if we take it in advance? That works much better:
❝Pre-treatment with [huperzine A] at concentrations of 50, 100, and 150 µg/mL completely inhibited the secretion of PGE2, TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β compared to post-treatment with [huperzine A].
This suggests that prophylactic treatment is better than post-inflammation treatment. ❞
~ Dr. Thu Kim Dang
Source: Anti-neuroinflammatory effects of alkaloid-enriched extract from Huperzia serrata
As you may know, neuroinflammation is a big part of Alzheimer’s pathology, so we want to keep that down. The above research suggests we should do that sooner rather than later.
Aside from holding off dementia, can it improve memory now, too?
There’s been a lot less research done into this (medicine is generally more concerned with preventing/treating disease, than improving the health of healthy people), but there is some:
^This is a small (n=68) old (1999) study for which the full paper has mysteriously disappeared and we only get to see the abstract. It gave favorable results, though.
The effects of huperzine A and IDRA 21 on visual recognition memory in young macaques
^This, like most non-dementia research into HupA, is an animal study. But we chose to spotlight this one because, unlike most of the studies, it did not chemically lobotomize the animals first; they were and remained healthy. That said, huperzine A improved the memory scores most for the monkeys that performed worst without it initially.
Where can I get it?
As ever, we don’t sell it, but here’s an example product on Amazon for your convenience
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:







