Are You Taking PIMs?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Getting Off The Overmedication Train
The older we get, the more likely we are to be on more medications. It’s easy to assume that this is because, much like the ailments they treat, we accumulate them over time. And superficially at least, that’s what happens.
And yet, almost half of people over 65 in Canada are taking “potentially inappropriate medications”, or PIMs—in other words, medications that are not needed and perhaps harmful. This categorization includes medications where the iatrogenic harms (side effects, risks) outweigh the benefits, and/or there’s a safer more effective medication available to do the job.
You may be wondering: what does this mean for the US?
Well, we don’t have the figures for the US because we’re working from Canadian research today, but given the differences between the two country’s healthcare systems (mostly socialized in Canada and mostly private in the US), it seems a fair hypothesis that if it’s almost half in Canada, it’s probably more than half in the US. Socialized healthcare systems are generally quite thrifty and seek to spend less on healthcare, while private healthcare systems are generally keen to upsell to new products/services.
The three top categories of PIMs according to the above study:
- Gabapentinoids (anticonvulsants also used to treat neuropathic pain)
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs)
- Antipsychotics (especially, to people without psychosis)
…but those are just the top of the list; there are many many more.
The list continues: opioids, anticholinergics, sulfonlyurea, NSAIDs, benzodiazepines and related rugs, and cholinesterase inhibitors. That’s where the Canadian study cuts off (although it also includes “others” just before NSAIDs), but still, you guessed it, there are more (we’re willing to bet statins weigh heavily in the “others” section, for a start).
There are two likely main causes of overmedication:
The side effect train
This is where a patient has a condition and is prescribed drug A, which has some undesired side effects, so the patient is prescribed drug B to treat those. However, that drug also has some unwanted side effects of its own, so the patient is prescribed drug C to treat those. And so on.
For a real-life rundown of how this can play out, check out the case study in:
The Hidden Complexities of Statins and Cardiovascular Disease (CVD)
The convenience factor
No, not convenient for you. Convenient for others. Convenient for the doctor if it gets you out of their office (socialized healthcare) or because it was easy to sell (private healthcare). Convenient for the staff in a hospital or other care facility.
This latter is what happens when, for example, a patient is being too much trouble, so the staff give them promazine “to help them settle down”, notwithstanding that promazine is, besides being a sedative, also an antipsychotic whose common side effects include amenorrhea, arrhythmias, constipation, drowsiness and dizziness, dry mouth, impotence, tiredness, galactorrhoea, gynecomastia, hyperglycemia, insomnia, hypotension, seizures, tremor, vomiting and weight gain.
This kind of thing (and worse) happens more often towards the end of a patient’s life; indeed, sometimes precipitating that end, whether you want it or not:
Mortality, Palliative Care, & Euthanasia
How to avoid it
Good practice is to be “open-mindedly skeptical” about any medication. By this we mean, don’t reject it out of hand, but do ask questions about it.
Ask your prescriber not only what it’s for and what it’ll do, but also what the side effects and risks are, and an important question that many people don’t think to ask, and for which doctors thus don’t often have a well-prepared smooth-selling reply, “what will happen if I don’t take this?”
And look up unbiased neutral information about it, from reliable sources (Drugs.com and The BNF are good reference guides for this—and if it’s important to you, check both, in case of any disagreement, as they function under completely different regulatory bodies, the former being American and the latter being British. So if they both agree, it’s surely accurate, according to best current science).
Also: when you are on a medication, keep a journal of your symptoms, as well as a log of your vitals (heart rate, blood pressure, weight, sleep etc) so you know what the medication seems to be helping or harming, and be sure to have a regular meds review with your doctor to check everything’s still right for you. And don’t be afraid to seek a second opinion if you still have doubts.
Want to know more?
For a more in-depth exploration than we have room for here, check out this book that we reviewed not long back:
To Medicate or Not? That is the Question! – by Dr. Asha Bohannon
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Mango vs Papaya – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing mango to papaya, we picked the mango.
Why?
Both are great! But there are some things to set them apart:
In terms of macros, this one’s not so big of a difference. They are equal in fiber, while mango has more protein and slightly more carbs. They are both low glycemic index, so we’ll call this one a tie, or the slenderest nominal win for papaya.
When it comes to vitamins, mango has more of vitamins A, B1, B3, B5, B7, B9, E, K, and choline, while papaya has more vitamin C. However, a cup of mango already gives the RDA of vitamin C, so at this point, it’s not even really much of a bonus that papaya has more. In any case, a clear and overwhelming win in the vitamins category for mango.
As for minerals, this one’s closer; mango has more copper, manganese, phosphorus, and zinc, while papaya has more calcium, iron, and magnesium. Still, a 4:3 win for mango.
Adding these up makes for a clear win for mango. However, one extra thing to bear in mind about both:
Both of these fruits interact with warfarin and many other anticoagulants. So if you’re taking those, you might want to skip these, or at least consult with your doctor/pharmacist for input on your personal situation.
Aside from that; enjoy both; diversity is good! But mango is the more nutritionally dense, and thus the winner here.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
5 Ways To Make Your Smoothie Blood Sugar Friendly (Avoid the Spike!)
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Chatter – by Dr. Ethan Kross
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This book is about much more than just one’s internal monologue. It does tackle that, but also the many non-verbal rabbit-holes that our brains can easily disappear into.
The author is an experimental psychologist, and brings his professional knowledge and experience to bear on this problem—citing many studies, including his own studies from his own lab, in which he undertook to answer precisely the implicit questions of “How can I…” in terms of tackling these matters, from root anxiety (for example) to end-state executive dysfunction (for example).
The writing style isn’t dense science though, and is very approachable for all.
The greatest value in this book lies in its prescriptive element, that is to say, its advice, especially in the category of evidence-based things we can do to improve matters for ourselves; beyond generic things like “mindfulness-based stress reduction” to much more specific things like “observe yourself in the 3rd person for a moment” and “take a break to imagine looking back on this later” and “interrupt yourself with a brief manual task”. With these sorts of interventions and more, we can shift the voice in our head from critic to coach.
Bottom line: if you would like your brain to let you get on with the things you actually want to do instead of constantly sidetracking you, this is the book for you.
Share This Post
-
Almond Butter vs Cashew Butter – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing almond butter to cashew butter, we picked the almond.
Why?
They’re both good! But, our inherent pro-almond bias notwithstanding, the almond butter does have a slightly better spread of nutrients.
In terms of macros, almond butter has more protein while cashew butter has more carbs, and of their fats, they’re broadly healthy in both cases, but almond butter does have less saturated fat.
In the category of vitamins, both are good sources of vitamin E, but almond butter has about 4x more. The rest of the vitamins they both contain aren’t too dissimilar, aside from some different weightings of various different B-vitamins, that pretty much balance out across the two nut butters. The only noteworthy point in cashew butter’s favor here is that it is a good source of vitamin K, which almond butter doesn’t have.
When it comes to minerals, both are good sources of lots of minerals, but most significantly, almond butter has a lot more calcium and quite a bit more potassium. In contrast, cashew butter has more selenium.
In short, they’re both great, but almond butter has more relative points in its favor than cashew butter.
Here are the two we depicted today, by the way, in case you’d like to try them:
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The 4 Bad Habits That Cause The Most Falls While Walking
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The risk of falling becomes greater (both in probability and in severity of consequences) as we get older. But, many people who do fall do so for the same reasons, some of which are avoidable. Dr. Doug Weiss has advice based on extensive second-hand experience:
Best foot forward!
If any of these prompt a “surely nobody does that” response, then, good for you to not have that habit, but Dr. Weiss has seen many patients who thusly erred. And if any of these do describe how you walk, then well, you’re not alone—time to fix it, though!
- Walking with Stiff Legs: walking with a hyperextended (straight) knee instead of a slight bend (5-15°) makes it harder to adjust balance, increasing the risk of falls. This can also put extra pressure on the joints, potentially leading to osteoarthritis.
- Crossing Legs While Turning: turning by crossing one leg over the other is a common cause of falls, particularly in the elderly. To avoid this, when turning step first with the foot that is on the side you are going to go. If you have the bad habit, this may feel strange at first, but you will soon adapt.
- Looking Down While Walking: focusing only on the ground directly in front of you can cause you to miss obstacles ahead, leading to falls. Instead, practice “scanning”, alternating between looking down at the ground and looking up to maintain awareness of your surroundings.
- Shuffling Instead of Tandem Walking: shuffling with feet far apart, rather than walking with one foot in front of the other, reduces balance and increases the risk of tripping. Tandem walking, where one foot is placed directly in front of the other, is the safer and more balanced way to walk.
It also helps disguise your numbers.
For more details on all of these, plus visual demonstrations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Fall Special (How To Not Fall, And How To Minimize Injury If You Do) ← this never seems like an urgent thing to learn, but trust us, it’s more fun to read it now, than from your hospital bed later
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
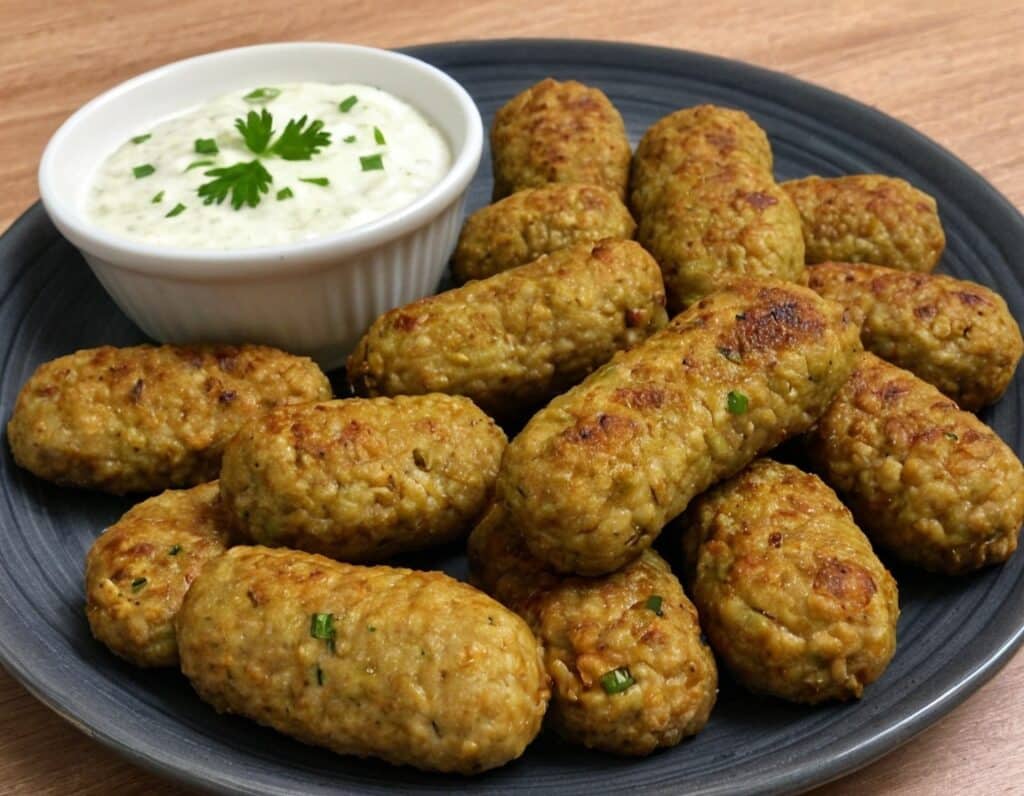
Zucchini & Oatmeal Koftas
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
These vegetarian (and with one tweak, vegan) koftas are delicious as a snack, light lunch, or side to a larger meal. Healthwise, they contain the healthiest kind of fiber, as well as omega-3 fatty acids, and beneficial herbs and spices.
You will need
- ¼ cup oatmeal
- 1 large zucchini, grated
- 1 small carrot, grated
- ¼ cup cheese (your preference; vegan is also fine)
- 2 tbsp ground flaxseed
- 2 tbsp nutritional yeast
- ¼ bulb garlic, minced
- 2 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Small handful fresh parsley, chopped
- Extra virgin olive oil, for frying
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Soak the flaxseed in 2 oz hot water for at least 5 minutes
2) Combine all of the ingredients except the olive oil (and including the water that the flax has been soaking in) in a big bowl, mixing thoroughly
3) Shape into small balls, patties, or sausage shapes, and fry until the color is golden and the structural integrity is good. If doing patties, you’ll need to gently flip them to cook both sides; otherwise, rolling them to get all sides is fine.
4) Serve! Traditional is with some kind of yogurt dip, but we’re not the boss of you, so enjoy them how you like:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- The Best Kind Of Fiber For Overall Health? ← it’s β-glucan, as found in oats
- What Omega-3 Fatty Acids Really Do For Us ← as in the flax
- The Many Health Benefits Of Garlic
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
- Monosodium Glutamate: Sinless Flavor-Enhancer Or Terrible Health Risk? ← it’s healthier than table salt
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Fast. Feast. Repeat – by Dr. Gin Stephens
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve reviewed intermittent fasting books before, so what makes this one different?
The title “Fast. Feast. Repeat.” doesn’t give much away; after all, we already know that that’s what intermittent fasting is.
After taking the reader though the basics of how intermittent fasting works and what it does for the body, much of the rest of the book is given over to improvements.
That’s what the real strength of this book is: ways to make intermittent fasting more efficient, including how to avoid plateaus. After all, sometimes it can seem like the only way to push further with intermittent fasting is to restrict the eating window further. Not so!
Instead, Dr. Stephens gives us ways to keep confusing our metabolism (in a good way) if, for example, we had a weight loss goal we haven’t met yet.
Best of all, this comes without actually having to eat less.
Bottom line: if you want to be in good physical health, and/but also believe that life is for living and you enjoy eating food, then this book can resolve that age-old dilemma!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: