An Accessible New Development Against Alzheimer’s
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dopamine vs Alzheimer’s
One of the key hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease is the formation of hardened beta-amyloid plaques around neurons. The beta-amyloid peptides themselves are supposed to be in the brain, but the hardened pieces of them that form the plaques are not.
While the full nature of the relationship between those plaques and Alzheimer’s disease is not known for sure (there are likely other factors involved, and “the amyloid hypothesis” is at this stage nominally just that, a hypothesis), one thing that has been observed is that increasing or reducing the plaques increases or reduces (respectively) Alzheimer’s symptoms such as memory loss.
Neprilysin
There is an enzyme, neprilysin, that can break down those plaques.
Neprilysin is made naturally in the brain, and/but we cannot take it as a supplement or medication, because it’s too big to pass through the blood-brain barrier.
A team of researchers led by Dr. Takaomi Saido genetically manipulated mice to produce more neprilysin, and those mice resultantly experienced fewer beta-amyloid plaques and better memory in their old age.
However wonderful for the mice (and a great proof of principle) the above approach is not useful as a treatment for humans whose genomes weren’t modified at our conception in a lab.
Since (as mentioned before) we also can’t take it as a medication/supplement, that leaves one remaining option: find a way to make our already-existing brains produce more of it.
The team’s previous research allowed them to narrow this down to “there is probably a hormone made in the hypothalamus that modulates this”, so they began experimenting with making the mice produce more hormones there.
The DREADD switch
DREADDs, or Designer Receptors Exclusively Activated by Designer Drugs, were the next tool in the toolbox. The scientists attached these designer receptors to dopamine-producing neurons in the mice, so that they could be activated by the appropriate designer drugs—basically, allowing for a “make more dopamine” button, without having to literally wire up the brains with electrodes. The “button” gets triggered instead by a chemical trigger, the designer drug. You can read more about them here:
DREADDs for Neuroscientists: A Primer
The result was positive; when the mice made more dopamine, the result was that they also made more neprilysin. So far, the hypothesis is that the presence of dopamine upregulates the production of neprilysin. In other words, the increased neprilysin levels were caused by the increased dopamine levels (the alternatives would have been: they were both caused by the same thing—in this case that’d be the DREADD activation—or the increase was caused by something else entirely that hadn’t been controlled for).
As to how the causal relationship was determined…
“But I don’t have (or want) a DREADD switch in my head”
Happily for us (and probably happily for the mice too, because dopamine causes feelings of happiness), the experiments continued.
This time, instead of using the DREADD system, they tried simply supplementing the mouse food with l-dopa, a dopamine precursor. L-dopa is often used in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease, because the molecules are small enough to pass through the blood-brain barrier, and can be converted to full dopamine inside the brain itself. So, taking l-dopa normally raises dopamine levels.
The results? The mice who were given l-dopa enjoyed:
- higher dopamine levels
- higher neprilysin levels
- lower beta-amyloid plaque levels
- better memory in tests
The next step for the researchers is to investigate how exactly dopamine regulates neprilysin in the brain, but for now, the relationship between l-dopa consumption and the reduction of Alzheimer’s symptoms seems clear.
You can read about the study here:
The dopaminergic system promotes neprilysin-mediated degradation of amyloid-β in the brain
Is there a catch?
L-dopa has common side effects that are not pleasant; the list begins with nausea and vomiting, and continues with things that one might expect from having “too much of a good thing” when it comes to dopamine, such as dyskinesia (extra movements) and hallucinations.
You can read about it more here at the Parkinson’s Foundation:
Parkinson’s Foundation | Levodopa
However! All is not lost. Rather than reaching for the heavy guns by taking l-dopa unnecessarily, there are other dopamine precursors that don’t have those side effects (and are consequently less restricted, to the point they can be purchased as supplements, or indeed, enjoyed where they occur naturally in some foods).
Top of the list of such safe* and readily-available dopamine precursors is…
N-Acetyl L-Tyrosine (NALT): The Dopamine Precursor & More
If you’d like to try that, here’s an example product on Amazon… Or you could eat fish, white beans, tofu, natto, or pumpkin seeds 😉
*Quick note on safety: “safe” is a relative term and may vary from person to person. Please speak with your own doctor to be sure, check with your pharmacist in case of any meds interactions, and be especially careful taking anything that increases dopamine levels if you have bipolar disorder or are otherwise prone to psychosis of any kind. For most people, this shouldn’t be an issue as our brains have a built-in mechanism for scrubbing excess dopamine and ensuring we don’t end up with too much, but for some people whose dopamine regulation is not so good in that regard, it can cause problems. So again, speak with your doctor to be sure, because we are not doctors, let alone your doctor.
Lastly…
If you’d like an entirely drug-free approach, that’s skipping even the “nutraceuticals”, you might enjoy:
Short On Dopamine? Science Has The Answer
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Overcome Front-Of-Hip Pain
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Alyssa Kuhn, physiotherapist, demonstrates how:
One, two, three…
One kind of pain affects a lot of related things: hip pain has an impact on everything that’s connected to the pelvis, which is basically the rest of the body, but especially the spine itself. For this reason, it’s critical to keep it in as good condition as possible.
Two primary causes of hip stiffness and pain:
- Anterior pelvic tilt due to posture, weight distribution, or pain. This tightens the front muscles and weakens the back muscles.
- Prolonged sitting, which tightens the hip muscles due to inactivity.
Three exercises are recommended by Dr. Kuhn to relieve pain and stiffness:
- Bridge exercise:
- Lie on a firm surface with your knees bent.
- Push through your feet, engage your hamstrings, and flatten your lower back.
- Hold for 3–5 seconds, relax, and repeat (10–20 reps).
- Wall exercise with arms:
- Stand with your lower back against the wall, feet a step away.
- Tilt your hips backwards, keeping your lower back in contact with the wall.
- Alternate lifting one arm at a time while maintaining back contact with the wall (10–20 reps).
- Wall exercise with legs:
- Same stance as the previous exercise but wider now.
- Lift one heel at a time while keeping your hips stable and your back against the wall.
- Practice for 30–60 seconds, maintaining good form.
As ever, consistency is key for long-term relief. Dr. Kuhn recommends doing these regularly, especially before any expected periods of prolonged sitting (e.g. at desk, or driving, etc). And of course, do try to reduce, or at least break up, those sitting marathons if you can.
For more on all of this plus visual demonstrations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Why are people on TikTok talking about going for a ‘fart walk’? A gastroenterologist weighs in
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
“Fart walks” have become a cultural phenomenon, after a woman named Mairlyn Smith posted online a now-viral video about how she and her husband go on walks about 60 minutes after dinner and release their gas.
Smith, known on TikTok as @mairlynthequeenoffibre and @mairlynsmith on Instagram, has since appeared on myriad TV and press interviews extolling the benefits of a fart walk. Countless TikTok and Instagram users and have now shared their own experiences of feeling better after taking up the #fartwalk habit.
So what’s the evidence behind the fart walk? And what’s the best way to do it?
CandyBox Images/Shutterstock Exercise can help get the gas out
We know exercise can help relieve bloating by getting gas moving and out of our bodies.
Researchers from Barcelona, Spain in 2006 asked eight patients complaining of bloating, seven of whom had irritable bowel syndrome, to avoid “gassy” foods such as beans for two days and to fast for eight hours before their study.
Each patient was asked to sit in an armchair, in order to avoid any effects of body position on the movement of gas. Gas was pumped directly into their small bowel via a thin plastic tube that went down their mouth, and the gas expelled from the body was collected into a bag via a tube placed in the rectum. This way, the researchers could determine how much gas was retained in the gut.
The patients were then asked to pedal on a modified exercise bike while remaining seated in their armchairs.
The researchers found that much less gas was retained in the patients’ gut when they exercised. They determined exercise probably helped the movement and release of intestinal gas.
Walking may have another bonus; it may trigger a nerve reflex that helps propel foods and gas contents through the gut.
Walking can also increase internal abdominal pressure as you use your abdominal muscles to stay upright and balance as you walk. This pressure on the colon helps to push intestinal gas out.
Proper fart walk technique
One study from Iran studied the effects of walking in 94 individuals with bloating.
They asked participants to carry out ten to 15 minutes of slow walking (about 1,000 steps) after eating lunch and dinner. They filled out gut symptom questionnaires before starting the program and again at the end of the four week program.
The researchers found walking after meals resulted in improvements to gut symptoms such as belching, farting, bloating and abdominal discomfort.
Now for the crucial part: in the Iranian study, there was a particular way in which participants were advised to walk. They were asked to clasp hands together behind their back and to flex their neck forward.
The clasped hands posture leads to more internal abdominal pressure and therefore more gentle squeezing out of gas from the colon. The flexed neck posture decreases the swallowing of air during walking.
This therefore is the proper fart walk technique, based on science.
Could walking with your hands behind your back yield better or more farts? candy candy/Shutterstock What about constipation?
A fart walk can help with constipation.
One study involved middle aged inactive patients with chronic constipation, who did a 12 week program of brisk walking at least 30 minutes a day – combined with 11 minutes of strength and flexibility exercises.
This program, the researchers found, improved constipation symptoms through reduced straining, less hard stools and more complete evacuation.
It also appears that the more you walk the better the benefits for gut symptoms.
In patients with irritable bowel syndrome, one study increasing the daily step count to 9,500 steps from 4,000 steps led to a 50% reduction in the severity of their symptoms.
And just 30 minutes of a fart walk has been shown to improve blood sugar levels after eating.
Walking after eating can help keep your blood sugar levels under control. IndianFaces/Shutterstock What if I can’t get outside the house?
If getting outside the house after dinner is impossible, could you try walking slowly on a treadmill or around the house for 1,000 steps?
If not, perhaps you could borrow an idea from the Barcelona research: sit back in an armchair and pedal using a modified exercise bike. Any type of exercise is better than none.
Whatever you do, don’t be a couch potato! Research has found more leisure screen time is linked to a greater risk of developing gut diseases.
We also know physical inactivity during leisure time and eating irregular meals are linked to a higher risk of abdominal pain, bloating and altered bowel motions.
Try the fart walk today
It may not be for everyone but this simple physical activity does have good evidence behind it. A fart walk can improve common symptoms such as bloating, abdominal discomfort and constipation.
It can even help lower blood sugar levels after eating.
Will you be trying a fart walk today?
Vincent Ho, Associate Professor and clinical academic gastroenterologist, Western Sydney University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Gravitas – by Caroline Goyder
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A no-nonsense guide to (more than!) public speaking that isn’t just “tell jokes in your speech and imagine the audience naked”.
Because this isn’t just about speech-writing or speech delivery, so much as giving you important life skills. The kind that weren’t taught in school, but that nevertheless make a huge impact on success… whether you’re giving a presentation or hosting a party or negotiating a deal or just attending a social event. Or making a phonecall, even.
Whereas a lot of books of this kind treat “the audience” as a nebulous and purely responsive passive crowd of extras, Goyder does better. People are individuals, even if they’re all facing the same way for a moment. She works with that! She also teaches how to deal with not just hecklers, but also simply those people who sap your confidence and find fault with you and anything you do or say.b
Bottom line is: if you for whatever reason communicate with people, and would like them to think better of you, this is the book for you.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Yes, you still need to use sunscreen, despite what you’ve heard on TikTok
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Summer is nearly here. But rather than getting out the sunscreen, some TikTokers are urging followers to chuck it out and go sunscreen-free.
They claim it’s healthier to forgo sunscreen to get the full benefits of sunshine.
Here’s the science really says.
Karolina Grabowska/Pexels How does sunscreen work?
Because of Australia’s extreme UV environment, most people with pale to olive skin or other risk factors for skin cancer need to protect themselves. Applying sunscreen is a key method of protecting areas not easily covered by clothes.
Sunscreen works by absorbing or scattering UV rays before they can enter your skin and damage DNA or supportive structures such as collagen.
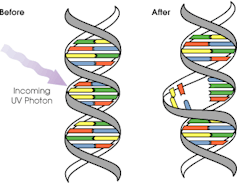
When UV particles hit DNA, the excess energy can damage our DNA. This damage can be repaired, but if the cell divides before the mistake is fixed, it causes a mutation that can lead to skin cancers.
The energy from a particle of UV (a photon) causes DNA strands to break apart and reconnect incorrectly. This causes a bump in the DNA strand that makes it difficult to copy accurately and can introduce mutations. NASA/David Herring The most common skin cancers are basal cell carcinoma (BCC) and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). Melanoma is less common, but is the most likely to spread around the body; this process is called metastasis.
Two in three Australians will have at least one skin cancer in their lifetime, and they make up 80% of all cancers in Australia.
Around 99% of skin cancers in Australia are caused by excessive exposure to UV radiation.
Excessive exposure to UV radiation also affects the appearance of your skin. UVA rays are able to penetrate deep into the skin, where they break down supportive structures such as elastin and collagen.
This causes signs of premature ageing, such as deep wrinkling, brown or white blotches, and broken capillaries.
Sunscreen can help prevent skin cancers
Used consistently, sunscreen reduces your risk of skin cancer and slows skin ageing.
In a Queensland study, participants either used sunscreen daily for almost five years, or continued their usual use.
At the end of five years, the daily-use group had reduced their risk of squamous cell carcinoma by 40% compared to the other group.
Ten years later, the daily use group had reduced their risk of invasive melanoma by 73%
Does sunscreen block the health-promoting properties of sunlight?
The answer is a bit more complicated, and involves personalised risk versus benefit trade-offs.
First, the good news: there are many health benefits of spending time in the sun that don’t rely on exposure to UV radiation and aren’t affected by sunscreen use.
Sunscreen only filters UV rays, not all light. Ron Lach/Pexels Sunscreen only filters UV rays, not visible light or infrared light (which we feel as heat). And importantly, some of the benefits of sunlight are obtained via the eyes.
Visible light improves mood and regulates circadian rhythm (which influences your sleep-wake cycle), and probably reduces myopia (short-sightedness) in children.
Infrared light is being investigated as a treatment for several skin, neurological, psychiatric and autoimmune disorders.
So what is the benefit of exposing skin to UV radiation?
Exposing the skin to the sun produces vitamin D, which is critical for healthy bones and muscles.
Vitamin D deficiency is surprisingly common among Australians, peaking in Victoria at 49% in winter and being lowest in Queensland at 6% in summer.
Luckily, people who are careful about sun protection can avoid vitamin D deficiency by taking a supplement.
Exposing the skin to UV radiation might have benefits independent of vitamin D production, but these are not proven. It might reduce the risk of autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis or cause release of a chemical that could reduce blood pressure. However, there is not enough detail about these benefits to know whether sunscreen would be a problem.
What does this mean for you?
There are some benefits of exposing the skin to UV radiation that might be blunted by sunscreen. Whether it’s worth foregoing those benefits to avoid skin cancer depends on how susceptible you are to skin cancer.
If you have pale skin or other factors that increase you risk of skin cancer, you should aim to apply sunscreen daily on all days when the UV index is forecast to reach 3.
If you have darker skin that rarely or never burns, you can go without daily sunscreen – although you will still need protection during extended times outdoors.
For now, the balance of evidence suggests it’s better for people who are susceptible to skin cancer to continue with sun protection practices, with vitamin D supplementation if needed.
Katie Lee, PhD Candidate, Dermatology Research Centre, The University of Queensland and Rachel Neale, Principal research fellow, QIMR Berghofer Medical Research Institute
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Mango vs Guava – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing mango to guava, we picked the guava.
Why?
Looking at macros first, these two fruits are about equal on carbs (nominally mango has more, but it’s by a truly tiny margin), while guava has more than 3x the protein and more than 3x the fiber. A clear win for guava.
In terms of vitamins, mango has more of vitamins A, E, and K, while guava has more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, B7, B9, and C. Another win for guava.
In the category of minerals, mango is not higher in any minerals, while guava is higher in calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc.
In short, enjoy both; both are healthy. But if you’re choosing one, there’s a clear winner here, and it’s guava.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
What’s Your Plant Diversity Score?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Could my glasses be making my eyesight worse?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
So, you got your eyesight tested and found out you need your first pair of glasses. Or you found out you need a stronger pair than the ones you have. You put them on and everything looks crystal clear. But after a few weeks things look blurrier without them than they did before your eye test. What’s going on?
Some people start to wear spectacles for the first time and perceive their vision is “bad” when they take their glasses off. They incorrectly interpret this as the glasses making their vision worse. Fear of this might make them less likely to wear their glasses.
But what they are noticing is how much better the world appears through the glasses. They become less tolerant of a blurry world when they remove them.
Here are some other things you might notice about eyesight and wearing glasses.
Lazy eyes?
Some people sense an increasing reliance on glasses and wonder if their eyes have become “lazy”.
Our eyes work in much the same way as an auto-focus camera. A flexible lens inside each eye is controlled by muscles that let us focus on objects in the distance (such as a footy scoreboard) by relaxing the muscle to flatten the lens. When the muscle contracts it makes the lens steeper and more powerful to see things that are much closer to us (such as a text message).
From the age of about 40, the lens in our eye progressively hardens and loses its ability to change shape. Gradually, we lose our capacity to focus on near objects. This is called “presbyopia” and at the moment there are no treatments for this lens hardening.
Optometrists correct this with prescription glasses that take the load of your natural lens. The lenses allow you to see those up-close images clearly by providing extra refractive power.
Once we are used to seeing clearly, our tolerance for blurry vision will be lower and we will reach for the glasses to see well again.
The wrong glasses?
Wearing old glasses, the wrong prescription (or even someone else’s glasses) won’t allow you to see as well as possible for day-to-day tasks. It could also cause eyestrain and headaches.
Incorrectly prescribed or dispensed prescription glasses can lead to vision impairment in children as their visual system is still in development.
But it is more common for kids to develop long-term vision problems as a result of not wearing glasses when they need them.
By the time children are about 10–12 years of age, wearing incorrect spectacles is less likely to cause their eyes to become lazy or damage vision in the long term, but it is likely to result in blurry or uncomfortable vision during daily wear.
Registered optometrists in Australia are trained to assess refractive error (whether the eye focuses light into the retina) as well as the different aspects of ocular function (including how the eyes work together, change focus, move around to see objects). All of these help us see clearly and comfortably.
Younger children with progressive vision impairments may need more frequent eye tests. Shutterstock What about dirty glasses?
Dirty or scratched glasses can give you the impression your vision is worse than it actually is. Just like a window, the dirtier your glasses are, the more difficult it is to see clearly through them. Cleaning glasses regularly with a microfibre lens cloth will help.
While dirty glasses are not commonly associated with eye infections, some research suggests dirty glasses can harbour bacteria with the remote but theoretical potential to cause eye infection.
To ensure best possible vision, people who wear prescription glasses every day should clean their lenses at least every morning and twice a day where required. Cleaning frames with alcohol wipes can reduce bacterial contamination by 96% – but care should be taken as alcohol can damage some frames, depending on what they are made of.
When should I get my eyes checked?
Regular eye exams, starting just before school age, are important for ocular health. Most prescriptions for corrective glasses expire within two years and contact lens prescriptions often expire after a year. So you’ll need an eye check for a new pair every year or so.
Kids with ocular conditions such as progressive myopia (short-sightedness), strabismus (poor eye alignment), or amblyopia (reduced vision in one eye) will need checks at least every year, but likely more often. Likewise, people over 65 or who have known eye conditions, such as glaucoma, will be recommended more frequent checks.
Eye checks can detect broader health issues. Shutterstock An online prescription estimator is no substitute for a full eye examination. If you have a valid prescription then you can order glasses online, but you miss out on the ability to check the fit of the frame or to have them adjusted properly. This is particularly important for multifocal lenses where even a millimetre or two of misalignment can cause uncomfortable or blurry vision.
Conditions such as diabetes or high blood pressure, can affect the eyes so regular eye checks can also help flag broader health issues. The vast majority of eye conditions can be treated if caught early, highlighting the importance of regular preventative care.
James Andrew Armitage, Professor of Optometry and Course Director, Deakin University and Nick Hockley, Lecturer in Optometric Clinical Skills, Director Deakin Collaborative Eye Care Clinic, Deakin University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: