More research shows COVID-19 vaccines are safe for young adults
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What you need to know
- Myocarditis, or inflammation of the heart muscle, is most commonly caused by a viral infection like COVID-19, not by vaccination.
- In line with previous research, a recent CDC study found no association between COVID-19 vaccination and sudden cardiac death in previously healthy young people.
- A COVID-19 infection is much more likely to cause inflammation of the heart muscle than a COVID-19 vaccine, and those cases are typically more severe.
Since the approval of the first COVID-19 vaccines, anti-vaccine advocates have raised concerns about heart muscle inflammation, also called myocarditis, after vaccination to suggest that vaccines are unsafe. They’ve also used concerns about myocarditis to spread false claims that vaccines cause sudden deaths, which is not true.
Research has consistently shown that cases of myocarditis after vaccination are extremely rare and usually mild, and a new study from the CDC found no association between sudden cardiac death and COVID-19 vaccination in young adults.
Read on to learn more about myocarditis and what the latest research says about COVID-19 vaccine safety.
What is myocarditis?
Myocarditis is inflammation of the myocardium, or the middle muscular layer of the heart wall. This inflammation weakens the heart’s ability to pump blood. Symptoms may include fatigue, shortness of breath, chest pain, rapid or irregular heartbeat, and flu-like symptoms.
Myocarditis may resolve on its own. In rare cases, it may lead to stroke, heart failure, heart attack, or death.
What causes myocarditis?
Myocarditis is typically caused by a viral infection like COVID-19. Bacteria, parasites, fungi, chemicals, and certain medications can also cause myocarditis.
In very rare cases, some people develop myocarditis after receiving a COVID-19 vaccine, but these cases are usually mild and resolve on their own. In contrast, a COVID-19 infection is much more likely to cause myocarditis, and those cases are typically more severe.
Staying up to date on vaccines reduces your risk of developing myocarditis from a COVID-19 infection.
Are COVID-19 vaccines safe for young people?
Yes. COVID-19 vaccines have been rigorously tested and monitored over the past three years and have been determined to be safe for everyone 6 months and older. A recent CDC study found no association between COVID-19 vaccination and sudden cardiac death in previously healthy young adults.
The benefits of vaccination outweigh any potential risks. Staying up to date on COVID-19 vaccines reduces your risk of severe illness, hospitalization, death, long COVID, and COVID-19-related complications, such as myocarditis.
The CDC recommends people 65 and older and immunocompromised people receive an additional dose of the updated COVID-19 vaccine this spring—if at least four months have passed since they received a COVID-19 vaccine.
For more information, talk to your health care provider.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Radical Longevity – by Dr. Ann Gittleman
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Gittleman takes a comprehensive approach, advising us about avoiding AGEs, freeing up fascia, stimulating cellular rejuvenation, the mind-gut connection, keeping the immune system healthy, and more.
The “plan” promised by the subtitle involves identifying the key factors of nutrition and lifestyle most impactful to you, and adjusting them accordingly, in a multistep, author-walks-the-reader-by-the-hand process.
There’s also, for those who prefer it, a large section (seven chapters) on a body part/system by body part/system approach, e.g. brain health, heart health, revitalizing skin, reversing hair loss, repairing bones, muscles, joints, etc.
The writing style is quite casual,butalso with a mind to education, with its call-out boxes, bullet-point summaries, and so forth. There is a “select references” section, but if one wants to find studies, it’s often necessary to go looking, as there aren’t inline citations.
Bottom line: we’d love to see better referencing, but otherwise this is a top-tier anti-aging book, and a lot more accessible than most, without skimping on depth and breadth.
Click here to check out Radical Longevity, and get rejuvenating radically!
Share This Post
-
Are plant-based burgers really bad for your heart? Here’s what’s behind the scary headlines
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’re hearing a lot about ultra-processed foods and the health effects of eating too many. And we know plant-based foods are popular for health or other reasons.
So it’s not surprising new research out this week including the health effects of ultra-processed, plant-based foods is going to attract global attention.
And the headlines can be scary if that research and the publicity surrounding it suggests eating these foods increases your risk of heart disease, stroke or dying early.
Here’s how some media outlets interpreted the research. The Daily Mail ran with:
Vegan fake meats are linked to increase in heart deaths, study suggests: Experts say plant-based diets can boost health – but NOT if they are ultra-processed
The New York Post’s headline was:
Vegan fake meats linked to heart disease, early death: study
But when we look at the study itself, it seems the media coverage has focused on a tiny aspect of the research, and is misleading.
So does eating supermarket plant-based burgers and other plant-based, ultra-processed foods really put you at greater risk of heart disease, stroke and premature death?
Here’s what prompted the research and what the study actually found.
Nina Firsova/Shutterstock Remind me, what are ultra-processed foods?
Ultra-processed foods undergo processing and reformulation with additives to enhance flavour, shelf-life and appeal. These include everything from packet macaroni cheese and pork sausages, to supermarket pastries and plant-based mince.
There is now strong and extensive evidence showing ultra-processed foods are linked with an increased risk of many physical and mental chronic health conditions.
Although researchers question which foods should be counted as ultra-processed, or if all of them are linked to poorer health, the consensus is that, generally, we should be eating less of them.
We also know plant-based diets are popular. These are linked with a reduced risk of chronic health conditions such as heart disease and stroke, cancer and diabetes. And supermarkets are stocking more plant-based, ultra-processed food options.
How about the new study?
The study looked for any health differences between eating plant-based, ultra-processed foods compared to eating non-plant based, ultra-processed foods. The researchers focused on the risk of cardiovascular disease (such as heart disease and stroke) and deaths from it.
Plant-based, ultra-processed foods in this study included mass-produced packaged bread, pastries, buns, cakes, biscuits, cereals and meat alternatives (fake meats). Ultra-processed foods that were not plant-based included milk-based drinks and desserts, sausages, nuggets and other reconstituted meat products.
The researchers used data from the UK Biobank. This is a large biomedical database that contains de-identified genetic, lifestyle (diet and exercise) and health information and biological samples from half a million UK participants. This databank allows researchers to determine links between this data and a wide range of diseases, including heart disease and stroke.
They used data from nearly 127,000 people who provided details of their diet between 2009 and 2012. The researchers linked this to their hospital records and death records. On average, the researchers followed each participant’s diet and health for nine years.
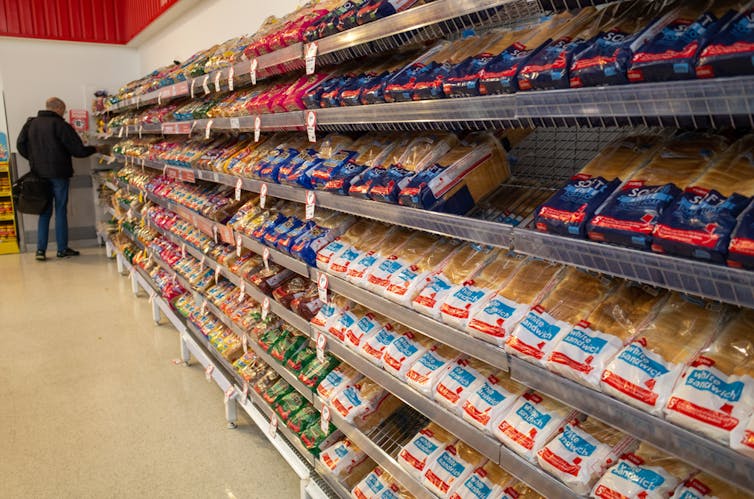
Plant-based, ultra-processed foods included in this study included packaged supermarket bread. doublelee/Shutterstock What did the study find?
With every 10% increase of total energy from plant-sourced, ultra-processed foods there was an associated 5% increased risk of cardiovascular disease (such as heart disease or stroke) and a 12% higher risk of dying from cardiovascular disease.
But for every 10% increase in plant-sourced, non-ultra-processed foods consumed there was an associated 7% lower risk of cardiovascular disease and a 13% lower risk of dying from cardiovascular disease.
The researchers found no evidence for an association between all plant-sourced foods (whether or not they were ultra-processed) and either an increased or decreased risk of cardiovascular disease or dying from it.
This was an observational study, where people recalled their diet using questionnaires. When coupled with other data, this can only tell us if someone’s diet is associated with a particular risk of a health outcome. So we cannot say that, in this case, the ultra-processed foods caused the heart disease and deaths from it.
Why has media coverage focused on fake meats?
Much of the media coverage has focused on the apparent health risks associated with eating fake meats, such as sausages, burgers, nuggets and even steaks.
These are considered ultra-processed foods. They are made by deconstructing whole plant foods such as pea, soy, wheat protein, nuts and mushrooms, and extracting the protein. They are then reformulated with additives to make the products look, taste and feel like traditional red and white meats.
However this was only one type of plant-based, ultra-processed food analysed in this study. This only accounted for an average 0.2% of the dietary energy intake of all the participants.
Compare this to bread, pastries, buns, cakes and biscuits, which are other types of plant-based, ultra-processed foods. These accounted for 20.7% of total energy intake in the study.
This image was at the top of the media release. Screenshot/Imperial It’s hard to say why the media focused on fake meat. But there is one clue in the media release issued to promote the research.
Although the media release did not mention the words “fake meat”, an image of plant-based burgers, sausages and meat balls or rissoles featured prominently.
The introduction of the study itself also mentions plant-sourced, ultra-processed foods, such as sausages, nuggets and burgers.
So it’s no wonder people can be confused.
Does this mean fake meats are fine?
Not necessarily. This study analysed the total intake of plant-based, ultra-processed foods, which included fake meats, albeit a very small proportion of people’s diets.
From this study alone we cannot tell if there would be a different outcome if someone ate large amounts of fake meats.
In fact, a recent review of fake meats found there was not enough evidence to determine their impact on health.
We also need more recent data to reflect current eating patterns of fake meats. This study used dietary data collected from 2009 to 2012, and fake meats have become more popular since.
What if I really like fake meat?
We have known for a while that ultra-processed foods can harm our health. This study tells us that regardless if an ultra-processed food is plant-based or not, it may still be harmful.
We know fake meat can contain large amounts of saturated fats (from coconut or palm oil), salt and sugar.
So like other ultra-processed foods, they should be eaten infrequently. The Australian Dietary Guidelines currently recommends people should only consume foods like this sometimes and in small amounts.
Are some fake meats healthier than others?
Check the labels and nutrition information panels. Look for those lowest in fat and salt. Burgers and sausages that are a “pressed cake” of minced ingredients such as nuts, beans and vegetables will be preferable to reformulated products that look identical to meat.
You can also eat whole plant-based protein foods such as legumes. These include beans, lentils, chickpeas and soy beans. As well as being high in protein and fibre, they also provide essential nutrients such as iron and zinc. Using spices and mushrooms alongside these in your recipes can replicate some of the umami taste associated with meat.
Evangeline Mantzioris, Program Director of Nutrition and Food Sciences, Accredited Practising Dietitian, University of South Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
The Blue Zones Kitchen – by Dan Buettner
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve previously reviewed Buettner’s other book, The Blue Zones: 9 Lessons For Living Longer From The People Who’ve Lived The Longest, and with this one, it’s now time to focus on the dietary aspect.
As the title and subtitle promises, we get 100 recipes, inspired by Blue Zone cuisines. The recipes themselves have been tweaked a little for maximum healthiness, eliminating some ingredients that do crop up in the Blue Zones but are exceptions to their higher average healthiness rather than the rule.
The recipes are arranged by geographic zone rather than by meal type, so it might take a full read-through before knowing where to find everything, but it makes it a very enjoyable “coffee-table book” to browse, as well as being practical in the kitchen. The ingredients are mostly easy to find globally, and most can be acquired at a large supermarket and/or health food store. In the case of substitutions, most are obvious, e.g. if you don’t have wild fennel where you are, use cultivated, for example.
In the category of criticism, it appears that Buettner is very unfamiliar with spices, and so has skipped them almost entirely. We at 10almonds could never skip them, and heartily recommend adding your own spices, for their health benefits and flavors. It may take a little experimentation to know what will work with what recipes, but if you’re accustomed to cooking with spices normally, it’s unlikely that you’ll err by going with your heart here.
Bottom line: we’d give this book a once-over for spice additions, but aside from that, it’s a fine book of cuisine-by-location cooking.
Click here to check out The Blue Zones Kitchen, and get cooking into your own three digits!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Here’s how to help protect your family from norovirus
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What you need to know
- Norovirus is a very contagious infection that causes vomiting and diarrhea.
- The best way to help protect against norovirus is to wash your hands often with soap and warm water, since hand sanitizer may not be effective at killing the virus.
- If someone in your household has symptoms of norovirus, isolate them away from others, watch for signs of dehydration, and take steps to help prevent it from spreading.
If you feel like everyone is sick right now, you’re not alone. Levels of respiratory illnesses like COVID-19, flu, and RSV remain remain high in many states, and the U.S. is also battling a wave of norovirus, one of several viruses that cause a very contagious infection of the stomach and intestines.
Although norovirus infections are more common during the colder months—it’s also called the “winter vomiting disease”—the virus can spread at any time. Right now, however, cases have more than doubled since last year’s peak.
Read on to learn about the symptoms of norovirus, how it spreads, and what to do if someone in your household gets sick.
What are the symptoms of norovirus?
Norovirus is a very contagious infection that causes vomiting and diarrhea, which typically begins 12 to 48 hours after exposure to the virus. Additional symptoms may include stomach pain, body aches, headaches, and a fever. Norovirus typically resolves within three days, but people who are infected may still be contagious for up to two days after symptoms resolve.
Norovirus may cause dehydration, or a dangerous loss of fluids, especially in young children and older adults. See a health care provider if you or someone in your household shows signs of dehydration, which may include decreased urination, dizziness, a dry mouth and throat, sleepiness, and crying without tears.
How can you help protect against norovirus?
You can get norovirus if you have close contact with someone who is infected, touch a contaminated surface and then touch your mouth or nose, or consume contaminated food or beverages.
The best way to help protect yourself and others against norovirus is to wash your hands often with soap and warm water, since hand sanitizer may not be effective at killing the virus. Other ways to help protect yourself may include cooking food thoroughly and washing fruits and vegetables before eating them.
You can get sick with norovirus even if you’ve had it before, since there are many different strains.
How can families help protect against the spread of norovirus at home?
If someone in your household has symptoms of norovirus, isolate them away from others and watch for signs of dehydration. If you are sick with norovirus, do not prepare food for others in your household and use a separate bathroom, if possible.
When cleaning up after someone who has norovirus, wear rubber, latex, or nitrile gloves. Then wash your hands thoroughly.
Clean surfaces using a solution containing five to 25 tablespoons of bleach (that’s 12.5 fluid ounces, or just over ¾ cup), per gallon of water. Leave the bleach-water mix on surfaces for at least five minutes before wiping it off.
For more information, talk to your health care provider.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Truth About Vaccines
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Truth About Vaccines
Yesterday we asked your views on vaccines, and we got an interesting spread of answers. Of those who responded to the poll, most were in favour of vaccines. We got quite a lot of comments this time too; we can’t feature them all, but we’ll include extracts from a few in our article today, as they raised interesting points!
Vaccines contain dangerous ingredients that will harm us more than the disease would: True or False?
False, contextually.
Many people are very understandably wary of things they know full well to be toxic, being injected into them.
One subscriber who voted for “Vaccines are poison, and/or are some manner of conspiracy ” wrote:
❝I think vaccines from 50–60 years ago are true vaccines and were safer than vaccines today. I have not had a vaccine for many, many years, and I never plan to have any kind of vaccine/shot again.❞
They didn’t say why they personally felt this way, but the notion that “things were simpler back in the day” is a common (and often correct!) observation regards health, especially when it comes to unwanted additives and ultraprocessing of food.
Things like aluminum or mercury in vaccines are much like sodium and chlorine in table salt. Sodium and chlorine are indeed both toxic to us. But in the form of sodium chloride, it’s a normal part of our diet, provided we don’t overdo it.
Additionally, the amount of unwanted metals (e.g. aluminum, mercury) in vaccines is orders of magnitude smaller than the amount in dietary sources—even if you’re a baby and your “dietary sources” are breast milk and/or formula milk.
In the case of formaldehyde (an inactivating agent), it’s also the dose that makes the poison (and the quantity in vaccines is truly miniscule).
This academic paper alone cites more sources than we could here without making today’s newsletter longer than it already is:
Vaccine Safety: Myths and Misinformation
I have a perfectly good immune system, it can handle the disease: True or False?
True! Contingently.
In fact, our immune system is so good at defending against disease, that the best thing we can do to protect ourselves is show our immune system a dead or deactivated version of a pathogen, so that when the real pathogen comes along, our immune system knows exactly what it is and what to do about it.
In other words, a vaccine.
One subscriber who voted for “Vaccines are important but in some cases the side effects can be worse ” wrote:
❝In some ways I’m vacd out. I got COVid a few months ago and had no symptoms except a cough. I have asthma and it didn’t trigger a lot of congestion. No issues. I am fully vaccinated but not sure I’ll get one in fall.❞
We’re glad this subscriber didn’t get too ill! A testimony to their robust immune system doing what it’s supposed to, after being shown a recent-ish edition of the pathogen, in deactivated form.
It’s very reasonable to start wondering: “surely I’m vaccinated enough by now”
And, hopefully, you are! But, as any given pathogen mutates over time, we eventually need to show our immune system what the new version looks like, or else it won’t recognize it.
See also: Why Experts Think You’ll Need a COVID-19 Booster Shot in the Future
So why don’t we need booster shots for everything? Often, it’s because a pathogen has stopped mutating at any meaningful rate. Polio is an example of this—no booster is needed for most people in most places.
Others, like flu, require annual boosters to keep up with the pathogens.
Herd immunity will keep us safe: True or False?
True! Ish.
But it doesn’t mean what a lot of people think it means. For example, in the UK, “herd immunity” was the strategy promoted by Prime Minister of the hour, Boris Johnson. But he misunderstood what it meant:
- What he thought it meant: everyone gets the disease, then everyone who doesn’t die is now immune
- What it actually means: if most people are immune to the disease (for example: due to having been vaccinated), it can’t easily get to the people who aren’t immune
One subscriber who voted for “Vaccines are critical for our health; vax to the max! ” wrote:
❝I had a chiropractor a few years ago, who explained to me that if the general public took vaccines, then she would not have to vaccinate her children and take a risk of having side effects❞
Obviously, we can’t speak for this subscriber’s chiropractor’s children, but this raises a good example: some people can’t safely have a given vaccine, due to underlying medical conditions—or perhaps it is not available to them, for example if they are under a certain age.
In such cases, herd immunity—other people around having been vaccinated and thus not passing on the disease—is what will keep them safe.
Here’s a useful guide from the US Dept of Health and Human Services:
How does community immunity (a.k.a. herd immunity) work?
And, for those who are more visually inclined, here’s a graphical representation of a mathematical model of how herd immunity works (you can run a simulation)!
Stay safe!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Older Americans Say They Feel Trapped in Medicare Advantage Plans
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In 2016, Richard Timmins went to a free informational seminar to learn more about Medicare coverage.
“I listened to the insurance agent and, basically, he really promoted Medicare Advantage,” Timmins said. The agent described less expensive and broader coverage offered by the plans, which are funded largely by the government but administered by private insurance companies.
For Timmins, who is now 76, it made economic sense then to sign up. And his decision was great, for a while.
Then, three years ago, he noticed a lesion on his right earlobe.
“I have a family history of melanoma. And so, I was kind of tuned in to that and thinking about that,” Timmins said of the growth, which doctors later diagnosed as malignant melanoma. “It started to grow and started to become rather painful.”
Timmins, though, discovered that his enrollment in a Premera Blue Cross Medicare Advantage plan would mean a limited network of doctors and the potential need for preapproval, or prior authorization, from the insurer before getting care. The experience, he said, made getting care more difficult, and now he wants to switch back to traditional, government-administered Medicare.
But he can’t. And he’s not alone.
“I have very little control over my actual medical care,” he said, adding that he now advises friends not to sign up for the private plans. “I think that people are not understanding what Medicare Advantage is all about.”
Enrollment in Medicare Advantage plans has grown substantially in the past few decades, enticing more than half of all eligible people, primarily those 65 or older, with low premium costs and perks like dental and vision insurance. And as the private plans’ share of the Medicare patient pie has ballooned to 30.8 million people, so too have concerns about the insurers’ aggressive sales tactics and misleading coverage claims.
Enrollees, like Timmins, who sign on when they are healthy can find themselves trapped as they grow older and sicker.
“It’s one of those things that people might like them on the front end because of their low to zero premiums and if they are getting a couple of these extra benefits — the vision, dental, that kind of thing,” said Christine Huberty, a lead benefit specialist supervising attorney for the Greater Wisconsin Agency on Aging Resources.
“But it’s when they actually need to use it for these bigger issues,” Huberty said, “that’s when people realize, ‘Oh no, this isn’t going to help me at all.’”
Medicare pays private insurers a fixed amount per Medicare Advantage enrollee and in many cases also pays out bonuses, which the insurers can use to provide supplemental benefits. Huberty said those extra benefits work as an incentive to “get people to join the plan” but that the plans then “restrict the access to so many services and coverage for the bigger stuff.”
David Meyers, assistant professor of health services, policy, and practice at the Brown University School of Public Health, analyzed a decade of Medicare Advantage enrollment and found that about 50% of beneficiaries — rural and urban — left their contract by the end of five years. Most of those enrollees switched to another Medicare Advantage plan rather than traditional Medicare.
In the study, Meyers and his co-authors muse that switching plans could be a positive sign of a free marketplace but that it could also signal “unmeasured discontent” with Medicare Advantage.
“The problem is that once you get into Medicare Advantage, if you have a couple of chronic conditions and you want to leave Medicare Advantage, even if Medicare Advantage isn’t meeting your needs, you might not have any ability to switch back to traditional Medicare,” Meyers said.
Traditional Medicare can be too expensive for beneficiaries switching back from Medicare Advantage, he said. In traditional Medicare, enrollees pay a monthly premium and, after reaching a deductible, in most cases are expected to pay 20% of the cost of each nonhospital service or item they use. And there is no limit on how much an enrollee may have to pay as part of that 20% coinsurance if they end up using a lot of care, Meyers said.
To limit what they spend out-of-pocket, traditional Medicare enrollees typically sign up for supplemental insurance, such as employer coverage or a private Medigap policy. If they are low-income, Medicaid may provide that supplemental coverage.
But, Meyers said, there’s a catch: While beneficiaries who enrolled first in traditional Medicare are guaranteed to qualify for a Medigap policy without pricing based on their medical history, Medigap insurers can deny coverage to beneficiaries transferring from Medicare Advantage plans or base their prices on medical underwriting.
Only four states — Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, and New York — prohibit insurers from denying a Medigap policy if the enrollee has preexisting conditions such as diabetes or heart disease.
Paul Ginsburg is a former commissioner on the Medicare Payment Advisory Commission, also known as MedPAC. It’s a legislative branch agency that advises Congress on the Medicare program. He said the inability of enrollees to easily switch between Medicare Advantage and traditional Medicare during open enrollment periods is “a real concern in our system; it shouldn’t be that way.”
The federal government offers specific enrollment periods every year for switching plans. During Medicare’s open enrollment period, from Oct. 15 to Dec. 7, enrollees can switch out of their private plans to traditional, government-administered Medicare.
Medicare Advantage enrollees can also switch plans or transfer to traditional Medicare during another open enrollment period, from Jan. 1 to March 31.
“There are a lot of people that say, ‘Hey, I’d love to come back, but I can’t get Medigap anymore, or I’ll have to just pay a lot more,’” said Ginsburg, who is now a professor of health policy at the University of Southern California.
Timmins is one of those people. The retired veterinarian lives in a rural community on Whidbey Island just north of Seattle. It’s a rugged, idyllic landscape and a popular place for second homes, hiking, and the arts. But it’s also a bit remote.
While it’s typically harder to find doctors in rural areas, Timmins said he believes his Premera Blue Cross plan made it more challenging to get care for a variety of reasons, including the difficulty of finding and getting in to see specialists.
Nearly half of Medicare Advantage plan directories contained inaccurate information on what providers were available, according to the most recent federal review. Beginning in 2024, new or expanding Medicare Advantage plans must demonstrate compliance with federal network expectations or their applications could be denied.
Amanda Lansford, a Premera Blue Cross spokesperson, declined to comment on Timmins’ case. She said the plan meets federal network adequacy requirements as well as travel time and distance standards “to ensure members are not experiencing undue burdens when seeking care.”
Traditional Medicare allows beneficiaries to go to nearly any doctor or hospital in the U.S., and in most cases enrollees do not need approval to get services.
Timmins, who recently finished immunotherapy, said he doesn’t think he would be approved for a Medigap policy, “because of my health issue.” And if he were to get into one, Timmins said, it would likely be too expensive.
For now, Timmins said, he is staying with his Medicare Advantage plan.
“I’m getting older. More stuff is going to happen.”
There is also a chance, Timmins said, that his cancer could resurface: “I’m very aware of my mortality.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: