Play Bold – by Magnus Penker
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This book is very different to what you might expect, from the title.
We often see: “play bold, believe in yourself, the universe rewards action” etc… Instead, this one is more: “play bold, pay attention to the data, use these metrics, learn from what these businesses did and what their results were”, etc.
We often see: “here’s an anecdote about a historical figure and/or celebrity who made a tremendous bluff and it worked out well so you should too” etc… Instead, this one is more: “see how what we think of as safety is actually anything but! And how by embracing change quickly (or ideally: proactively), we can stay ahead of disaster that may otherwise hit us”.
Penker’s background is also relevant here. He has decades of experience, having “launched 10 start-ups and acquired, turned around, and sold over 30 SMEs all over Europe”. Importantly, he’s also “still in the game”… So, unlike many authors whose last experience in the industry was in the 1970s and who wonder why people aren’t reaping the same rewards today!
Penker is the therefore opposite of many who advocate to “play bold” but simply mean “fail fast, fail often”… While quietly relying on their family’s capital and privilege to leave a trail of financial destruction behind them, and simultaneously gloating about their imagined business expertise.
In short: boldness does not equate to foolhardiness, and foolhardiness does not equate to boldness.
As for telling the difference? Well, for that we recommend reading the book—It’s a highly instructive one.
Take The First Bold Step Of Checking Out This Book On Amazon!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The DASH Diet Mediterranean Solution – by Dr. Marla Heller
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Sometimes, an author releases a series of books that could have just been one book, with various padding and rehashes. In some cases, naming no names
Dr. Mark Hyman, it means we have to carefully pick out the honestly very good and highly recommendable ones from the “you just republished for the extra income, didn’t you?” ones.In this case, today’s book is part of a series of books with very similar titles, and this one seems the most useful as a standalone book
The Mediterranean Diet is still the scientific world’s current “gold standard” in terms of most evidence-based diet for general health, and as we’ve written about, it can be tweaked to focus on being best for [your particular concern here]. In this case, it’s the DASH variant of the Mediterranean Diet, considered best for heart health specifically.
The style is repetitive, and possibly indicative of the author getting into a habit of having to pad books. Nevertheless, saying things too often is better than forgetting to say them, so hey. On which note, it is more of an educational book than a cookbook—it does have recipes, but not many.
Bottom line: if you’d like an introduction to the DASH variant of the Mediterranean Diet, this book will get you well-acquainted.
Click here to check out The DASH Diet Mediterranean Solution, and learn all about it!
Share This Post
-
You can train your nose – and 4 other surprising facts about your sense of smell
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Would you give up your sense of smell to keep your hair? What about your phone?
A 2022 US study compared smell to other senses (sight and hearing) and personally prized commodities (including money, a pet or hair) to see what people valued more.
The researchers found smell was viewed as much less important than sight and hearing, and valued less than many commodities. For example, half the women surveyed said they’d choose to keep their hair over sense of smell.
Smell often goes under the radar as one of the least valued senses. But it is one of the first sensory systems vertebrates developed and is linked to your mental health, memory and more.
Here are five fascinating facts about your olfactory system.
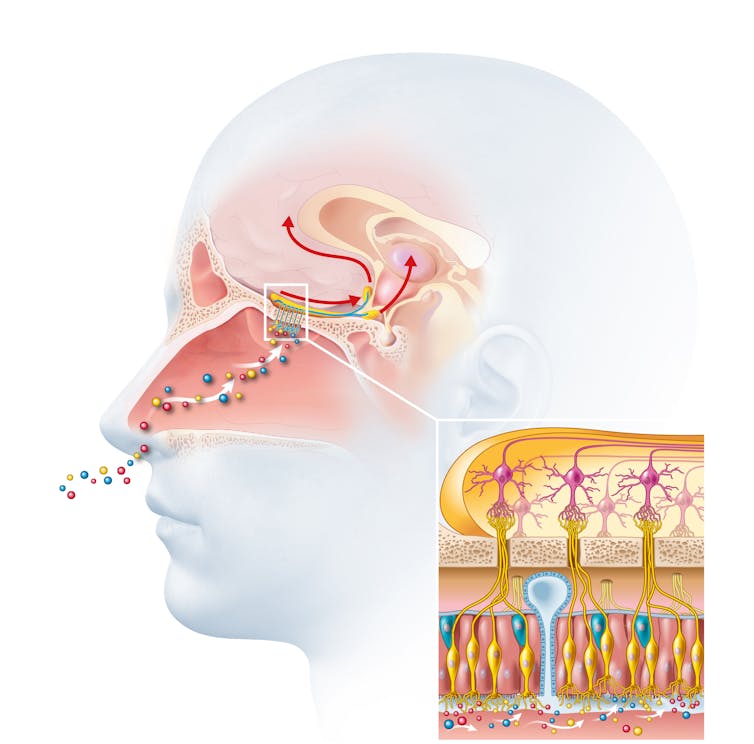
DimaBerlin/Shutterstock 1. Smell is linked to memory and emotion
Why can the waft of fresh baking trigger joyful childhood memories? And why might a certain perfume jolt you back to a painful breakup?
Smell is directly linked to both your memory and emotions. This connection was first established by American psychologist Donald Laird in 1935 (although French novelist Marcel Proust had already made it famous in his reverie about the scent of madeleines baking.)
Odours are first captured by special olfactory nerve cells inside your nose. These cells extend upwards from the roof of your nose towards the smell-processing centre of your brain, called the olfactory bulb.
Smells are first detected by nerve cells in the nose. Axel_Kock/Shutterstock From the olfactory bulb they form direct connection with the brain’s limbic system. This includes the amygdala, where emotions are generated, and the hippocampus, where memories are created.
Other senses – such as sight and hearing – aren’t directly connected to the lymbic system.
One 2004 study used functional magnetic resonance imaging to demonstrate odours trigger a much stronger emotional and memory response in the brain than a visual cue.
2. Your sense of smell constantly regenerates
You can lose your ability to smell due to injury or infection – for example during and after a COVID infection. This is known as olfactory dysfunction. In most cases it’s temporary, returning to normal within a few weeks.
This is because every few months your olfactory nerve cells die and are replaced by new cells.
We’re not entirely sure how this occurs, but it likely involves your nose’s stem cells, the olfactory bulb and other cells in the olfactory nerves.
Other areas of your nervous system – including your brain and spinal cord – cannot regenerate and repair after an injury.
Constant regeneration may be a protective mechanism, as the olfactory nerves are vulnerable to damage caused by the external environment, including toxins (such as cigarette smoke), chemicals and pathogens (such as the flu virus).
But following a COVID infection some people might continue to experience a loss of smell. Studies suggest the virus and a long-term immune response damages the cells that allow the olfactory system to regenerate.
3. Smell is linked to mental health
Around 5% of the global population suffer from anosmia – total loss of smell. An estimated 15-20% suffer partial loss, known as hyposmia.
Given smell loss is often a primary and long-term symptom of COVID, these numbers are likely to be higher since the pandemic.
Yet in Australia, the prevalence of olfactory dysfunction remains surprisingly understudied.
Losing your sense of smell is shown to impact your personal and social relationships. For example, it can mean you miss out on shared eating experiences, or cause changes in sexual desire and behaviour.
In older people, declining ability to smell is associated with a higher risk of depression and even death, although we still don’t know why.
Losing your sense of smell can have a major impact on mental health. Halfpoint/Shutterstock 4. Loss of smell can help identify neurodegenerative diseases
Partial or full loss of smell is often an early indicator for a range of neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases.
Patients frequently report losing their sense of smell years before any symptoms show in body or brain function. However many people are not aware they are losing their sense of smell.
There are ways you can determine if you have smell loss and to what extent. You may be able to visit a formal smell testing centre or do a self-test at home, which assesses your ability to identify household items like coffee, wine or soap.
5. You can train your nose back into smelling
“Smell training” is emerging as a promising experimental treatment option for olfactory dysfunction. For people experiencing smell loss after COVID, it’s been show to improve the ability to detect and differentiate odours.
Smell training (or “olfactory training”) was first tested in 2009 in a German psychology study. It involves sniffing robust odours — such as floral, citrus, aromatic or fruity scents — at least twice a day for 10—20 seconds at a time, usually over a 3—6 month period.
Participants are asked to focus on the memory of the smell while sniffing and recall information about the odour and its intensity. This is believed to help reorganise the nerve connections in the brain, although the exact mechanism behind it is unclear.
Some studies recommend using a single set of scents, while others recommend switching to a new set of odours after a certain amount of time. However both methods show significant improvement in smelling.
This training has also been shown to alleviate depressive symptoms and improve cognitive decline both in older adults and those suffering from dementia.
Just like physiotherapy after a physical injury, olfactory training is thought to act like rehabilitation for your sense of smell. It retrains the nerves in your nose and the connections it forms within the brain, allowing you to correctly detect, process and interpret odours.
Lynn Nazareth, Research Scientist in Olfactory Biology, CSIRO
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Cottage Cheese vs Ricotta – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing cottage cheese to ricotta, we picked the ricotta.
Why?
Cottage cheese is a famous health food, mostly for being a low-fat, low-carb, source of protein. And yet, ricotta beats it in most respects.
Looking at the macros first, cottage cheese has more carbs, while ricotta has more protein and fat. The fat profile is pretty much the same, and in both cases it’s two thirds saturated fat, which isn’t good in either case, but cottage cheese has less overall fat which means less saturated fat in total even if the percentage is the same. Because the difference in carbs and protein is not large, while ricotta has considerably more fat, we’ll call this category a win for cottage cheese.
In terms of vitamins, cottage cheese has more of vitamins B1, B5, and B12, while ricotta has more of vitamins A, B2, B3, B9, D, E, and K, so this one’s a win for ricotta.
In the category of minerals, cottage cheese has slightly more copper, while ricotta has much more calcium, iron, magnesium, manganese, potassium, selenium, and zinc. In particular, 2.5x more calcium, and 5x more iron! An easy and clear win for ricotta here.
Taking everything into account: yes, cottage cheese has less fat (and thus, in total, less saturated fat, although the percentage is the same), but that doesn’t make up for ricotta winning in pretty much every other respect. Still, enjoy either or both (in moderation!) if you be so inclined.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
How To Know When You’re Healing Emotionally
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The healing process can be humbling but rewarding, leading to deep fulfillment and inner peace. Discomfort in healing can be part of growth and self-integration. Because of that, progress sometimes looks and/or feels like progress… And sometimes it doesn’t. Here’s how to recognize it, though:
Small but important parts of a bigger process
Nine signs indicating you are healing:
- Allowing emotions: you acknowledge and process both negative and positive emotions instead of suppressing them.
- Improved boundaries: you improve at expressing and maintaining boundaries, overcoming fear of rejection, guilt, and shame.
- Acceptance of past: you accept difficult past experiences and their impact, reducing their hold over you.
- Less reactivity: you become less reactive and more thoughtful in responses, practicing emotional self-regulation.
- Non-linear healing: you understand that healing involves ups and downs and isn’t a straightforward journey.
- Stepping out of your comfort zone: you start taking brave steps that previously induced fear or anxiety.
- Handling disappointments: you accept setbacks and respond to them healthily, without losing motivation.
- Inner peace: you develop a sense of wholeness, and forgiveness for yourself and others, reducing self-sabotage.
- Welcoming support: you become more open to seeking and accepting help, moving beyond pride and shame.
In short: healing (especially the very first part: accepting that something needs healing) can be uncomfortable but lead to much better places in life. It’s okay if healing is slow; everyone’s journey is different, and doing your best is enough.
For more on each of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
Why You Can’t Just “Get Over” Trauma
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Exercise with Type 1 Diabetes – by Ginger Vieira
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If you or a loved one has Type 1 Diabetes, you’ll know that exercise can be especially frustrating…
- If you don’t do it, you risk weight gain and eventual insulin resistance.
- If you do it, you risk dangerous hypos, or perhaps hypers if you took off your pump or skipped a bolus.
Unfortunately, the popular medical advice is “well, just do your best”.
Ginger Vieira is Type 1 Diabetic, and writes with 20+ experience of managing her diabetes while being a keen exerciser. As T1D folks out there will also know, comorbidities are very common; in her case, fibromyalgia was the biggest additional blow to her ability to exercise, along with an underactive thyroid. So when it comes to dealing with the practical nuts and bolts of things, she (while herself observing she’s not a doctor, let alone your doctor) has a lot more practical knowledge than an endocrinologist (without diabetes) behind a desk.
Speaking of nuts and bolts, this book isn’t a pep talk.
It has a bit of that in, but most of it is really practical information, e.g: using fasted exercise (4 hours from last meal+bolus) to prevent hypos, counterintuitive as that may seem—the key is that timing a workout for when you have the least amount of fast-acting insulin in your body means your body can’t easily use your blood sugars for energy, and draws from your fat reserves instead… Win/Win!
That’s just one quick tip because this is a 1-minute review, but Vieira gives:
- whole chapters, with example datasets (real numbers)
- tech-specific advice, e.g. pump, injection, etc
- insulin-specific advice, e.g. fast vs slow, and adjustments to each in the context of exercise
- timing advice re meal/bolus/exercise for different insulins and techs
- blood-sugar management advice for different exercise types (aerobic/anaerobic, sprint/endurance, etc)
…and lots more that we don’t have room to mention here
Basically… If you or a loved one has T1D, we really recommend this book!
Order a copy of “Exercise with Type 1 Diabetes” from Amazon today!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Gut – by Dr. Giulia Enders
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
On account of being an organ (or rather, a system of organs) whose functions are almost entirely autonomic, most of us don’t think about our gut much. We usually know there’s acid in the stomach, and we usually know there are “good and bad” gut bacteria. But what of the rest of what goes on?
For anyone who has a hazy half-remembered knowledge from school, this will serve as not only a reminder, but a distinct upgrade in knowledge.
Dr. Giuliua Enders talks us through not just the processes of what goes on, but, as a medical doctor, also many instances of what can go wrong, for example:
- Why do some people’s bodies mistake nuts for a deadly threat (and consequently, accidentally elevate them to the status of actually becoming a deadly threat)?
- Why are some people lactose-intolerant, and why do food intolerances often pop up later with age?
- Why do constipation and diarrhoea happen?
- Why is it that stress can cause stomach ulcers?
The style of writing is light and easy-reading, and the illustrations are clear too. This is a very accessible book that doesn’t assume prior knowledge, and also doesn’t skimp on the scientific explanations—there’s no dumbing down here.
Bottom line: knowing what goes on in our gut as akin to knowing what goes on under the hood of a car. A lot of the time we don’t need to know, but knowing can make a big difference from time to time, and that’s when you’ll wish you’d learned!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: