No Time to Panic – by Matt Gutman
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Matt Gutman is not a doctor or a psychologist. He’s a journalist, accustomed to asking questions and then asking more probing questions, unrelenting until he gets the answers he’s looking for.
This book is the result of what happened when he needed to overcome his own anxiety and panic attacks, and went on an incisive investigative journey.
The style is as clear and accessible as you’d expect of a journalist, and presents a very human exploration, nonetheless organized in a way that will be useful to the reader.
It’s said that “experience is a great teacher, but she sends hefty bills”. In this case as in many, it’s good to learn from someone else’s experience!
By the end of the book, you’ll have a good grounding in most approaches to dealing with anxiety and panic attacks, and an idea of efficacy/applicability, and what to expect.
Bottom line: without claiming any magic bullet, this book presents six key strategies that Gutman found to work, along with his experiences of what didn’t. Valuable reading if you want to curb your own anxiety, or want to be able to help/support someone else with theirs.
Click here to check out No Time To Panic, and find the peace you deserve!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Is TikTok right? Are there health benefits to eating sea moss?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Sea moss is the latest “superfood” wellness influencers are swearing by. They claim sea moss products – usually in gel form – have multiple health benefits. These include supporting brain and immune function, or protecting against viruses and other microbes.
But do these health claims stack up? Let’s take a look.
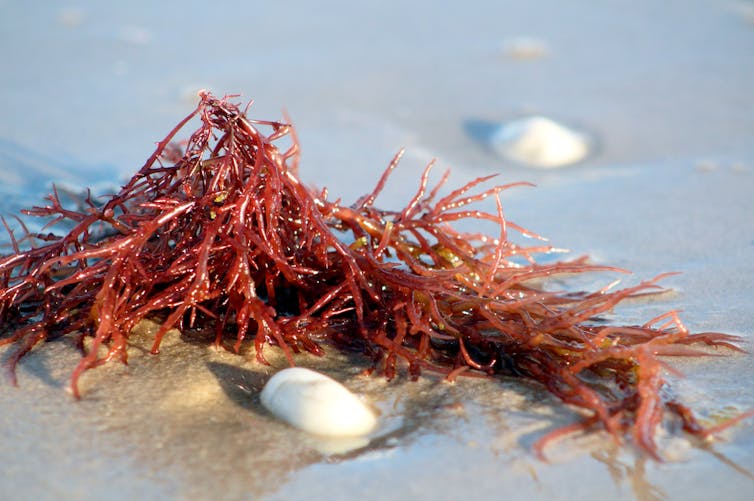
Plataresca/Shutterstock What is sea moss?
Sea moss is produced using a kind of seaweed – particularly red algae – that grow in various locations all around the world. Three main species are used in sea moss products:
- Chondrus crispus (known as Irish moss or carrageenan moss)
- Eucheuma cottonii (sea moss or seabird’s nest)
- Gracilaria (Irish moss or ogonori).
Some products also contain the brown algae Fucus vesiculosus (commonly known as bladderwrack, black tang, rockweed, sea grapes, bladder fucus, sea oak, cut weed, dyers fucus, red fucus or rock wrack).
Most sea moss products are sold as a gel that can be added to recipes, used in smoothies, frozen into ice cubes or eaten on its own. The products also come in capsule form or can be purchased “raw” and used to make your own gels at home.
Several kinds of red algae are used in commercially-available sea moss products. Nancy Ann Bowe/Shutterstock What’s the evidence?
Sea moss products claim a host of potential health benefits, from supporting immunity, to promoting skin health and enhancing mood and focus, among many others.
But is there any evidence supporting these claims?
Recent studies have reviewed the biological properties of the main sea moss species (Chondrus crispus, Eucheuma cottonii, Gracilaria and Fucus vesiculosus).
They suggest these species may have anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anticancer, antidiabetic and probiotic properties.
However, the vast majority of research relating to Chondrus crispus, Gracilaria and Fucus vesiculosus – and all of the research on Eucheuma cottonii – comes from studies done in test tubes or using cell and animal models. We should not assume the health effects seen would be the same in humans.
In cell and animal studies, researchers usually administer algae in a laboratory and use specific extracts rich in bioactive compounds rather than commercially available sea moss products.
They also use very different – often relatively larger – amounts compared to what someone would typically consume when they eat sea moss products.
This means the existing studies can’t tell us about the human body’s processes when eating and digesting sea moss.
Sea moss may have similar effects in humans. But so far there is very little evidence people who consume sea moss will experience any of the claimed health benefits.
Nutritional value
Eating sea moss does not replace the need for a balanced diet, including a variety of fruits and vegetables.
Chondrus crispus, Eucheuma cottonii and Gracilaria, like many seaweeds, are rich sources of nutrients such as fatty acids, amino acids, vitamin C and minerals. These nutrients are also likely to be present in sea moss, although some may be lost during the preparation of the product (for example, soaking may reduce vitamin C content), and those that remain could be present in relatively low quantities.
There are claims that sea moss may be harmful for people with thyroid problems. This relates to the relationship between thyroid function and iodine. The algae used to make sea moss are notable sources of iodine and excess iodine intake can contribute to thyroid problems, particularly for people with pre-existing conditions. That is why these products often carry disclaimers related to iodine sensitivity or thyroid health.
Is it worth it?
So you may be wondering if it’s worth trying sea moss. Here are a few things to consider before you decide whether to start scooping sea moss into your smoothies.
A 375mL jar costs around $A25–$30 and lasts about seven to ten days, if you follow the recommended serving suggestion of two tablespoons per day. This makes it a relatively expensive source of nutrients.
Sea moss is commonly sold as a gel that can be eaten on a kitchen bench. April Sims/Shutterstock Sea moss is often hyped for containing 92 different minerals. While there may be 92 minerals present, the amount of minerals in the algae will vary depending on growing location and conditions.
The efficiency with which minerals from algae can be absorbed and used by the body also varies for different minerals. For example, sodium is absorbed well, while only about 50% of iodine is absorbed.
But sea moss has also been shown to contain lead, mercury and other heavy metals – as well as radioactive elements (such as radon) that can be harmful to humans. Seaweeds are known for their ability to accumulate minerals from their environment, regardless of whether these are beneficial or harmful for human nutrition. Remember, more doesn’t always mean better.
What else am I eating?
While you won’t get a full nutritional breakdown on the jar, it is always wise to check what other ingredients you may be eating. Sea moss products can contain a range of other ingredients, such as lime, monk fruit powder, spirulina and ginger, among many others.
These ingredients differ between brands and products, so be aware of your needs and always check.
Despite their health claims, most sea moss products also carry disclaimers indicating that the products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease.
If you have concerns about your health, always speak to a health professional for accurate and personalised medical advice.
Margaret Murray, Senior Lecturer, Nutrition, Swinburne University of Technology
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
How much weight do you actually need to lose? It might be a lot less than you think
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If you’re one of the one in three Australians whose New Year’s resolution involved losing weight, it’s likely you’re now contemplating what weight-loss goal you should actually be working towards.
But type “setting a weight loss goal” into any online search engine and you’ll likely be left with more questions than answers.
Sure, the many weight-loss apps and calculators available will make setting this goal seem easy. They’ll typically use a body mass index (BMI) calculator to confirm a “healthy” weight and provide a goal weight based on this range.
Your screen will fill with trim-looking influencers touting diets that will help you drop ten kilos in a month, or ads for diets, pills and exercise regimens promising to help you effortlessly and rapidly lose weight.
Most sales pitches will suggest you need to lose substantial amounts of weight to be healthy – making weight loss seem an impossible task. But the research shows you don’t need to lose a lot of weight to achieve health benefits.
Using BMI to define our target weight is flawed
We’re a society fixated on numbers. So it’s no surprise we use measurements and equations to score our weight. The most popular is BMI, a measure of our body weight-to-height ratio.
BMI classifies bodies as underweight, normal (healthy) weight, overweight or obese and can be a useful tool for weight and health screening.
But it shouldn’t be used as the single measure of what it means to be a healthy weight when we set our weight-loss goals. This is because it:
- fails to consider two critical factors related to body weight and health – body fat percentage and distribution
- does not account for significant differences in body composition based on gender, ethnicity and age.
How does losing weight benefit our health?
Losing just 5–10% of our body weight – between 6 and 12kg for someone weighing 120kg – can significantly improve our health in four key ways.
1. Reducing cholesterol
Obesity increases the chances of having too much low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol – also known as bad cholesterol – because carrying excess weight changes how our bodies produce and manage lipoproteins and triglycerides, another fat molecule we use for energy.
Having too much bad cholesterol and high triglyceride levels is not good, narrowing our arteries and limiting blood flow, which increases the risk of heart disease, heart attack and stroke.
But research shows improvements in total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol and triglyceride levels are evident with just 5% weight loss.
2. Lowering blood pressure
Our blood pressure is considered high if it reads more than 140/90 on at least two occasions.
Excess weight is linked to high blood pressure in several ways, including changing how our sympathetic nervous system, blood vessels and hormones regulate our blood pressure.
Essentially, high blood pressure makes our heart and blood vessels work harder and less efficiently, damaging our arteries over time and increasing our risk of heart disease, heart attack and stroke.
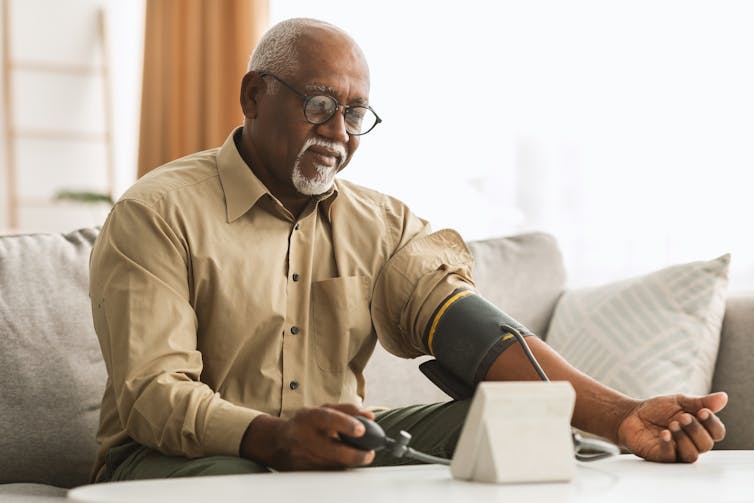
Losing weight can lower your blood pressure.
Prostock-studio/ShutterstockLike the improvements in cholesterol, a 5% weight loss improves both systolic blood pressure (the first number in the reading) and diastolic blood pressure (the second number).
A meta-analysis of 25 trials on the influence of weight reduction on blood pressure also found every kilo of weight loss improved blood pressure by one point.
3. Reducing risk for type 2 diabetes
Excess body weight is the primary manageable risk factor for type 2 diabetes, particularly for people carrying a lot of visceral fat around the abdomen (belly fat).
Carrying this excess weight can cause fat cells to release pro-inflammatory chemicals that disrupt how our bodies regulate and use the insulin produced by our pancreas, leading to high blood sugar levels.
Type 2 diabetes can lead to serious medical conditions if it’s not carefully managed, including damaging our heart, blood vessels, major organs, eyes and nervous system.
Research shows just 7% weight loss reduces risk of developing type 2 diabetes by 58%.
4. Reducing joint pain and the risk of osteoarthritis
Carrying excess weight can cause our joints to become inflamed and damaged, making us more prone to osteoarthritis.
Observational studies show being overweight doubles a person’s risk of developing osteoarthritis, while obesity increases the risk fourfold.
Small amounts of weight loss alleviate this stress on our joints. In one study each kilogram of weight loss resulted in a fourfold decrease in the load exerted on the knee in each step taken during daily activities.
Losing weight eases stress on joints.
Shutterstock/Rostislav_SedlacekFocus on long-term habits
If you’ve ever tried to lose weight but found the kilos return almost as quickly as they left, you’re not alone.
An analysis of 29 long-term weight-loss studies found participants regained more than half of the weight lost within two years. Within five years, they regained more than 80%.
When we lose weight, we take our body out of its comfort zone and trigger its survival response. It then counteracts weight loss, triggering several physiological responses to defend our body weight and “survive” starvation.
Just as the problem is evolutionary, the solution is evolutionary too. Successfully losing weight long-term comes down to:
losing weight in small manageable chunks you can sustain, specifically periods of weight loss, followed by periods of weight maintenance, and so on, until you achieve your goal weight
making gradual changes to your lifestyle to ensure you form habits that last a lifetime.
Setting a goal to reach a healthy weight can feel daunting. But it doesn’t have to be a pre-defined weight according to a “healthy” BMI range. Losing 5–10% of our body weight will result in immediate health benefits.
At the Boden Group, Charles Perkins Centre, we are studying the science of obesity and running clinical trials for weight loss. You can register here to express your interest.
Nick Fuller, Charles Perkins Centre Research Program Leader, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
How stigma perpetuates substance use
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In 2022, 54.6 million people 12 and older in the United States needed substance use disorder (SUD) treatment. Of those, only 24 percent received treatment, according to the most recent National Survey on Drug Use and Health.
SUD is a treatable, chronic medical condition that causes people to have difficulty controlling their use of legal or illegal substances, such as alcohol, tobacco, prescription opioids, heroin, methamphetamine, or cocaine. Using these substances may impact people’s health and ability to function in their daily life.
While help is available for people with SUD, the stigma they face—negative attitudes, stereotypes, and discrimination—often leads to shame, worsens their condition, and keeps them from seeking help.
Read on to find out more about how stigma perpetuates substance use.
Stigma can keep people from seeking treatment
Suzan M. Walters, assistant professor at New York University’s Grossman School of Medicine, has seen this firsthand in her research on stigma and health disparities.
She explains that people with SUD may be treated differently at a hospital or another health care setting because of their drug use, appearance (including track marks on their arms), or housing situation, which may discourage them from seeking care.
“And this is not just one case; this is a trend that I’m seeing with people who use drugs,” Walters tells PGN. “Someone said, ‘If I overdose, I’m not even going to the [emergency room] to get help because of this, because of the way I’m treated. Because I know I’m going to be treated differently.’”
People experience stigma not only because of their addiction, but also because of other aspects of their identities, Walters says, including “immigration or race and ethnicity. Hispanic folks, brown folks, Black folks [are] being treated differently and experiencing different outcomes.”
And despite the effective harm reduction tools and treatment options available for SUD, research has shown that stigma creates barriers to access.
Syringe services programs, for example, provide infectious disease testing, Narcan, and fentanyl test strips. These programs have been proven to save lives and reduce the spread of HIV and hepatitis C. SSPs don’t increase crime, but they’re often mistakenly “viewed by communities as potential settings of drug-related crime;” this myth persists despite decades of research proving that SSPs make communities safer.
To improve this bias, Walters says it’s helpful for people to take a step back and recognize how we use substances, like alcohol, in our own lives, while also humanizing those with addiction. She says, “There’s a lack of understanding that these are human beings and people … [who] are living lives, and many times very functional lives.”
Misconceptions lead to stigma
SUD results from changes in the brain that make it difficult for a person to stop using a substance. But research has shown that a big misconception that leads to stigma is that addiction is a choice and reflects a person’s willpower.
Michelle Maloney, executive clinical director of mental health and addiction recovery services for Rogers Behavioral Health, tells PGN that statements such as “you should be able to stop” can keep a patient from seeking treatment. This belief goes back to the 1980s and the War on Drugs, she adds.
“We think about public service announcements that occurred during that time: ‘Just say no to drugs,’” Maloney says. “People who have struggled, whether that be with nicotine, alcohol, or opioids, [know] it’s not as easy as just saying no.”
Stigma can worsen addiction
Stigma can also lead people with SUD to feel guilt and shame and blame themselves for their medical condition. These feelings, according to the National Institute on Drug Abuse, may “reinforce drug-seeking behavior.”
In a 2020 article, Dr. Nora D. Volkow, the director of NIDA, said that “when internalized, stigma and the painful isolation it produces encourage further drug taking, directly exacerbating the disease.”
Overall, research agrees that stigma harms people experiencing addiction and can make the condition worse. Experts also agree that debunking myths about the condition and using non-stigmatizing language (like saying someone is a person with a substance use disorder, not an addict) can go a long way toward reducing stigma.
Resources to mitigate stigma:
- CDC: Stigma Reduction
- National Harm Reduction Coalition: Respect To Connect: Undoing Stigma
- NIDA:
- Shatterproof: Addiction language guide (Disclosure: The Public Good Projects, PGN’s parent company, is a Shatterproof partner)
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Osteoporosis Breakthrough – by Dr. Doug Lucas
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
“Osteoporosis” and “break” often don’t go well together, but here they do. So, what’s the breakthrough here?
There isn’t one, honestly. But if we overlook the marketing choices and focus on the book itself, the content here is genuinely good:
The book offers a comprehensive multivector approach to combatting osteoporosis, e.g:
- Diet
- Exercise
- Other lifestyle considerations
- Supplements
- Hormones
- Drugs
The author considers drugs a good and important tool for some people with osteoporosis, but not most. The majority of people, he considers, will do better without drugs—by tackling things more holistically.
The advice here is sound and covers all reasonable angles without getting hung up on the idea of there being a single magical solution for all.
Bottom line: if you’re looking for a book that’s a one-stop-shop for strategies against osteoporosis, this is a good option.
Click here to check out The Osteoporosis Breakthrough, and keep your bones strong!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Oat Milk vs Almond Milk – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing oat milk to almond milk, we picked the almond milk.
Why?
This one’s quite straightforward, and no, it’s not just our bias for almonds
Rather, almonds contain a lot more vitamins and minerals, all of which usually make it into the milk.
Oat milk is still a fine choice though, and has a very high soluble fiber content, which is great for your heart.
Just make sure you get versions without added sugar or other unpleasantries! You can always make your own at home, too.
You can read a bit more about the pros and cons of various plant milks here:
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Age of Scientific Wellness – by Dr. Leroy Hood & Dr. Nathan Price
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We don’t usually do an author bio beyond mentioning their professional background, but in this case it’s worth mentioning that the first-listed author, Dr. Leroy Hood, is the one who invented the automated gene sequencing technology that made the Human Genome Project possible. In terms of awards, he’s won everything short of a Nobel Prize, and that’s probably less a snub and more a matter of how there isn’t a Nobel Prize for Engineering—his field is molecular biotechnology, but what he solved was an engineering problem.
In this book, the authors set out to make the case that “find it and fix it” medicine has done a respectable job of getting us where we are, but what we need now is P4 medicine:
- Predict
- Prevent
- Personalize
- Participate
The idea is that with adequate data (genomic, phenomic, and digital), we can predict the course of health sufficiently well to interrupt the process of disease at its actual (previously unseen) starting point, instead of waiting for symptoms to show up, thus preventing it proactively. The personalization is because this will not be a “one size fits all” approach, since our physiologies are different, our markers of health and disease will be somewhat too. And the participatory aspect? That’s because the only way to get enough data to do this for an entire population is with—more or less—an entire population’s involvement.
This is what happens when, for example, your fitness tracker asks if it can share anonymized health metrics for research purposes and you allow it—you are becoming part of the science (a noble and worthy act!).
You may be wondering whether this book has health advice, or is more about the big picture. And, the answer is both. It’s mostly about the big picture but it does have a lot of (data-driven!) health advice too, especially towards the end.
The style is largely narrative, talking the reader through the progresses (and setbacks) that have marked the path so far, and projecting the next part of the journey, in the hope that we can avoid being part of a generation born just too late to take advantage of this revolutionary approach to health.
Bottom line: this isn’t a very light read, but it is a worthwhile one, and it’ll surely inspire you to increase the extent to which you are proactive about your health!
Click here to check out The Age Of Scientific Wellness, and be part of it!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: