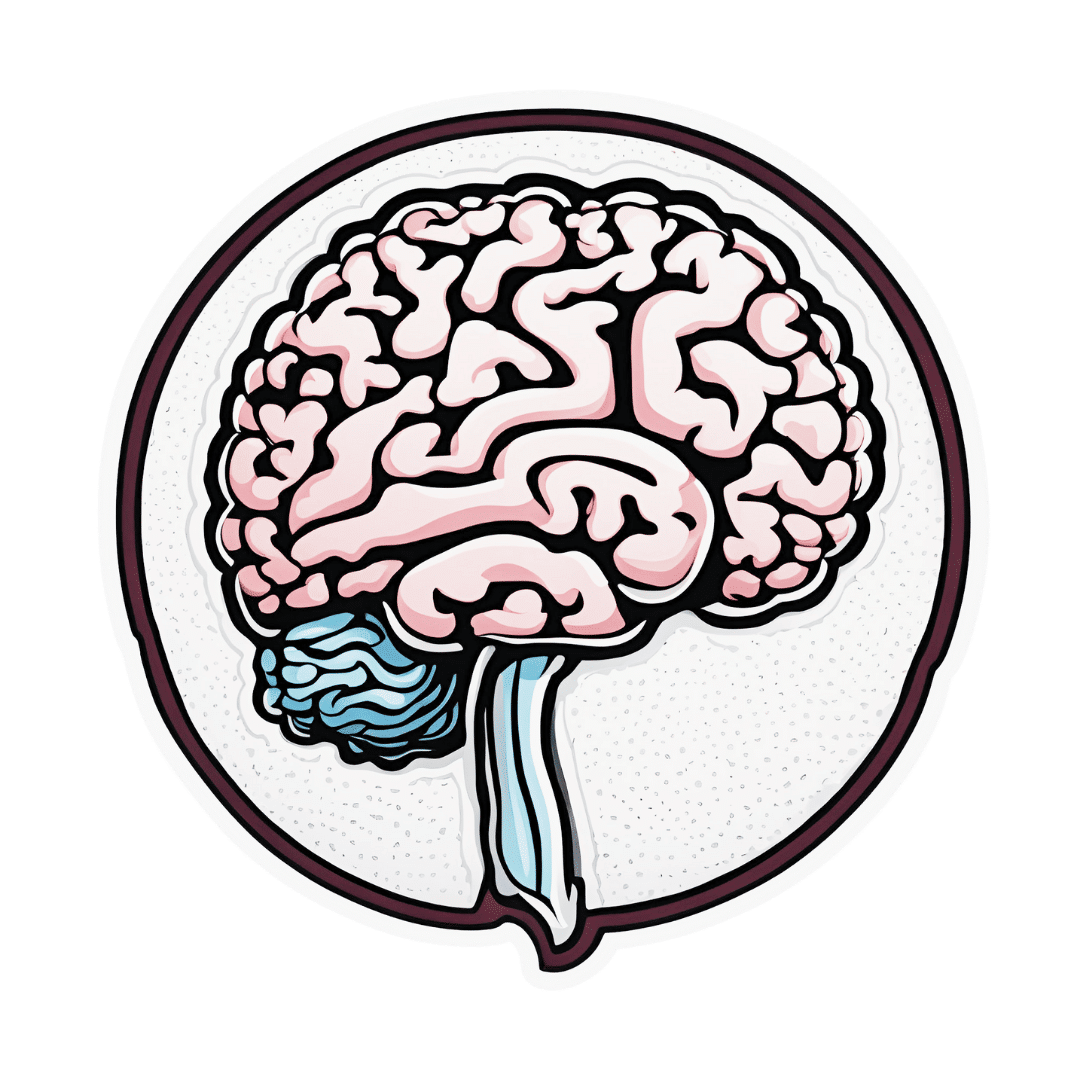
What Your Brain Is Really Doing When You’re Doing “Nothing”
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Unless we are dead, our brain is never truly inactive. And it’s not just a matter of regulating autonomic functions, either…
Default Mode Network
When the brain is at rest but not necessarily asleep, the Default Mode Network (DMN) engages. This makes up for around 20% of the brain’s overall activity, and contributes to complex cognitive processes.
What constitutes “at rest”: the DMN activates when external tasks stop and is engaged during self-reflection, mind-wandering, and relaxed memory recall (i.e. reminiscing, rather than answering questions in a difficult test, for example).
As for its neurophysiology, the DMN is connected to the hippocampus and plays a key role in episodic, prospective, and semantic memory (memories of experiences, future plans, and general knowledge), as well as being involved in self-reflection, social cognition, and understanding others’ thoughts (theory of mind). The DMN thus also helps integrate memories and thoughts to create a cohesive internal narrative and sense of self.
However, it doesn’t work alone: the DMN interacts with other networks like the salience network, which switches attention to external stimuli. Disruptions between these networks are linked to psychiatric disorders (e.g., schizophrenia, Alzheimer’s, depression), in various different ways depending on the nature of the disruption.
Sometimes, for some people in some circumstances, the option to disrupt the DMN is useful. For example, research shows that psilocybin disrupts the DMN, leading to changes in brain activity and potential therapeutic benefits for depression* and other psychiatric disorders by enhancing neuroplasticity.
*Essentially, kicking the brain out of the idling gear it got stuck in, and into action
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- The Wandering Mind – by Dr. Michael Corballis ← a book, largely about the DMN and how to use it beneficially
- Taking A Trip Through The Evidence On Psychedelics ← for a shorter read, touching on psilocybin
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The push for Medicare to cover weight-loss drugs: An explainer
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The largest U.S. insurer, Medicare, does not cover weight-loss drugs, making it tougher for older people to get access to promising new medications.
If you cover stories about drug costs in the U.S., it’s important to understand why Medicare’s Part D pharmacy program, which covers people aged 65 and older and people with certain disabilities, doesn’t cover weight-loss drugs today. It’s also important to consider what would happen if Medicare did start covering weight loss drugs. This explainer will give you a brief overview of the issues and then summarize some recent publications the benefits and costs of drugs like semaglutide and tirzepatide.
First, what are these new and newsy weight loss drugs?
Semaglutide is a medication used for both the treatment of type 2 diabetes and for long-term weight management in adults with obesity. It debuted in the United States in 2017 as an injectable diabetes drug called Ozempic, manufactured by Novo Nordisk. It’s part of a class of drugs that mimics the action of glucagon, a substance that the human body makes to aid digestion.
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) drugs like semaglutide help prompt the body to release insulin. But they also cause a minor delay in the pace of digestion, helping people feel sated after eating.
That second effect turned Ozempic into a widely used weight-loss drug, even before the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) gave its okay for this use. Doctors in the United States can prescribe medicines for uses beyond those approved by the FDA. This is known as off-label use.
In writing about her own experience in using the medicine to help her shed 40 pounds, Washington Post columnist Ruth Marcus in June noted that Novo Nordisk mentioned the potential for weight loss in its “ubiquitous cable ads (‘Oh-oh-oh, Ozempic!’)”
The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists has reported shortages of semaglutide due to demand, leaving some people with diabetes struggling to find supply of the medicine.
Novo Nordisk won Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval in 2021 to market semaglutide as an injectable weight loss drug under the name Wegovy, but with a different dosing regimen than Ozempic. Rival Eli Lilly first won FDA approval of its similar GLP-1 diabetes drug, tirzepatide, in the United States in 2022 and sells it under the brand name Mounjaro.
In November of 2023, Eli Lilly won FDA approval to sell tirzepatide as a weight-loss drug, soon-to-be marketed under the brand name Zepbound. The company said it will set a monthly list price for a month’s supply of the drug at $1,059.87, which the company described as 20% discount to the cost of rival Novo Nordisk’s Wegovy. Wegovy has a list price of $1,349.02, according to the Novo Nordisk website.
Even when their insurance plans officially cover costs for weight loss drugs, consumers may face barriers in seeking that coverage for these drugs. Commercial health plans have in place prior authorization requirements to try to limit coverage of new weight-loss shots to those who qualify for these treatments. The Wegovy shot, for example, is intended for people whose weight reaches a certain benchmark for obesity or who are overweight and have a condition related to excess weight, such as diabetes, high blood pressure or high cholesterol.
State Medicaid programs, meanwhile, have taken approaches that vary by state. For example, the most populous U.S. state, California, provides some coverage to new weight-loss injections through its Medicaid program, but many others, including Texas, the No. 2 state in terms of population, do not, according to an online tool that Novo Nordisk created to help people check on coverage.
Medicare does cover semaglutide for treatment of diabetes, and the insurer reported $3 billion in 2021 spending on the drug under Medicare Part D. Congress last year gave Medicare new tools that might help it try to lower the cost of semaglutide.
Medicare is in the midst of implementing new authority it gained through the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) of 2022 to negotiate with companies about the cost of certain medicines.
This legislation gave Medicare, for the first time, tools to directly negotiate with pharmaceutical companies on the cost of some medicines. Congress tailored this program to spare drug makers from negotiations for the first few years they put new medicines on the market, allowing them to recoup investment in these products.
Why doesn’t Medicare cover weight-loss drugs?
Congress created the Medicare Part D pharmacy program in 2003 to address a gap in coverage that had existed since the creation of Medicare in 1965. The program long covered the costs of drugs administered by doctors and those given in hospitals, but not the kinds of medicines people took on their own, like Wegovy shots.
In 2003, there seemed to be good reasons to leave weight-loss drugs out of the benefit, write Inmaculada Hernandez of the University of California, San Diego, and coauthors in their September 2023 editorial in the Journal of General Internal Medicine, “Medicare Part D Coverage of Anti-obesity Medications: a Call for Forward-Looking Policy Reform.”
When members of Congress worked on the Part D benefit, the drugs available on the market were known to have limited effectiveness and unpleasant side effects. And those members of Congress were aware of how a drug combination called fen-phen, once touted as a weight-loss miracle medicine, turned out in rare cases to cause fatal heart valve damage. In 1997, American Home Products, which later became Wyeth, took its fen-phen product off the market.
But today GLP-1 drugs like semaglutide appear to offer significant benefits, with far less risk and milder side effects, write Hernandez and coauthors.
“Other than budget impact, it is hard to find a reason to justify the historical statutory exclusion of weight loss drugs from coverage other than the stigma of the condition itself,” they write.
What’s happening today that could lead Medicare to start covering weight loss drugs?
Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly both have hired lobbyists to try to persuade lawmakers to reverse this stance, according to Senate records. Pro tip: You can use the Senate’s lobbying disclosure database to track this and other issues. Type in the name of the company of interest and then read through the forms.
Some members of Congress already have been trying for years to strike the Medicare Part D restriction on weight-loss drugs. Over the past decade, senators Tom Carper (D-DE) and Bill Cassidy, MD, (R-LA) have repeatedly introduced bills that would do that. They introduced the current version, the Treat and Reduce Obesity Act of 2023, in July. It has the support of 10 other Republican senators and seven Democratic ones, as of Dec. 19. The companion House measure has the support of 41 Democrats and 23 Republicans in that chamber, which has 435 seats.
The influential nonprofit Institute for Clinical and Economic Review conducts in-depth analyses of drugs and medical treatments in the United States. ICER last year recommended passage of a law allowing Medicare Part D to cover weight-loss medications. ICER also called for broader coverage of weight-loss medications in state Medicaid programs. Insurers, including Medicare, consider ICER’s analyses in deciding whether to cover treatments.
While offering these calls for broader coverage as part of a broad assessment of obesity management, ICER also urged companies to reduce the costs of weight-loss medicines.
Most people with obesity can’t achieve sustained weight loss through diet and exercise alone, said David Rind, ICER’s chief medical officer in an August 2022 statement. The development of newer obesity treatments represents the achievement of a long-standing goal of medical research, but prices of these new products must be reasonable to allow broad access to them, he noted.
After an extensive process of reviewing studies, engaging in public debate and processing feedback, ICER concluded that semaglutide for weight loss should have an annual cost of $7,500 to $9,800, based on its potential benefits.
What does academic research say about the benefits and the potential costs of new obesity drugs?
Here are a couple of studies to consider when covering the ongoing story of weight-loss drug costs:
Medicare Part D Coverage of Antiobesity Medications — Challenges and Uncertainty Ahead
Khrysta Baig, Stacie B. Dusetzina, David D. Kim and Ashley A. Leech. New England Journal of Medicine, March 2023In this Perspective piece, researchers at Vanderbilt University create a series of estimates about how much Medicare may have to spend annually on weight-loss drugs if the program eventually covers these drugs.
These include a high estimate — $268 billion — based on an extreme calculation, one reflecting the potential cost if virtually all people on Medicare who have obesity used semaglutide. In an announcement of the study on the Vanderbilt website, lead author Khrysta Baig described this as a “purely hypothetical scenario,” but one that “ underscores that at current prices, these medications cannot be the only way – or even the main way – we address obesity as a society.”
In a more conservative estimate, Bhaig and coauthors consider a case where only about 10% of those eligible for obesity treatment opted for semaglutide, which would result in $27 billion in new costs.
(To put these numbers in context, consider that the federal government now spends about $145 billion a year on the entire Part D program.)
It’s likely that all people enrolled in Part D would have to pay higher monthly premiums if Medicare were to cover weight-loss injections, Baig and coauthors write.
Baig and coauthors note that the recent ICER review of weight-loss drugs focused on patients younger than the Medicare population. The balance of benefits and risks associated with weight-loss drugs may be less favorable for older people than the younger ones, making it necessary to study further how these drugs work for people aged 65 and older, they write. For example, research has shown older adults with a high blood sugar level called prediabetes are less likely to develop diabetes than younger adults with this condition.
SELECTing Treatments for Cardiovascular Disease — Obesity in the Spotlight
Amit Khera and Tiffany M. Powell-Wiley. New England Journal of Medicine, Dec. 14, 2023
Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients Without Diabetes
A Michael Lincoff, et. al. New England Journal of Medicine, Dec. 14, 2023.An editorial accompanies the publication of a semaglutide study that drew a lot of coverage in the media. The Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Obesity without Diabetes (SELECT) study was a randomized controlled trial, conducted by Novo Nordisk, which looked at rates of cardiovascular events in people who already had known heart risk and were overweight, but not diabetic. Patients were randomly assigned to receive a once-weekly dose of semaglutide (Wegovy) or a placebo.
In the study, the authors report that of the 8,803 patients who took Wegovy in the trial, 569 (6.5%)
The study also reports a mean 9.4% reduction in body weight among patients taking Wegovy, while those on placebo had a mean loss of 0.88%.
The findings suggest Wegovy may be a welcome new treatment option for many people who have coronary disease and are overweight, but are not diabetic, write Khera and Powell-Wiley in their editorial.
But the duo, both of whom focus on disease prevention in their research, also call for more focus on the prevention and root causes of obesity and on the use of proven treatment approaches other than medication.
“Socioeconomic, environmental, and psychosocial factors contribute to incident obesity, and therefore equity-focused obesity prevention and treatment efforts must target multiple levels,” they write. “For instance, public policy targeting built environment features that limit healthy behaviors can be coupled with clinical care interventions that provide for social needs and access to treatments like semaglutide.”
Additional information:
The nonprofit KFF, formerly known as the Kaiser Family Foundation, has done recent reports looking at the potential for expanded coverage of semaglutide:
Medicaid Utilization and Spending on New Drugs Used for Weight Loss, Sept. 8, 2023
What Could New Anti-Obesity Drugs Mean for Medicare? May 18, 2023
And KFF held an Aug. 4 webinar, New Weight Loss Drugs Raise Issues of Coverage, Cost, Access and Equity, for which the recording is posted here.
This article first appeared on The Journalist’s Resource and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Share This Post
-
No, you don’t need the ‘Barbie drug’ to tan, whatever TikTok says. Here’s why melanotan-II is so risky
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
TikTok and Instagram influencers have been peddling the “Barbie drug” to help you tan.
But melanotan-II, as it’s called officially, is a solution that’s too good to be true. Just like tanning, this unapproved drug has a dark side.
Doctors, researchers and Australia’s drug regulator have been warning about its side effects – from nausea and vomiting to brain swelling and erection problems.
There are also safer ways of getting the tanned look, if that’s what you’re after.
AtlasStudio/Shutterstock What is melanotan-II?
No, it’s not a typo. Melanotan-II is very different from melatonin, which is a hormonal supplement used for insomnia and jet lag.
Melanotan-II is a synthetic version of the naturally ocurring hormone α-melanocyte stimulating hormone. This means the drug mimics the body’s hormone that stimulates production of the pigment melanin. This is what promotes skin darkening or tanning, even in people with little melanin.
Although the drug is promoted as a way of getting a “sunless tan”, it is usually promoted for use with UV exposure, to enhance the effect of UV and kickstart the tanning process.
Melanotan-II is related to, but different from, melanotan-I (afamelanotide), an approved drug used to treat the skin condition erythropoietic protoporphyria.
Melanotan-II is not registered for use with Australia’s Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). It is illegal to advertise it to the public or to provide it without a prescription.
However, social media has been driving unlicensed melanotan-II sales, a study published last year confirms.
There are many black market suppliers of melanotan-II injections, tablets and creams. More recently, nasal sprays have become more popular.
What are the risks?
Just like any drug, melanotan-II comes with the risk of side effects, many of which we’ve known about for more than a decade. These include changes in the size and pigmentation of moles, rapid appearance of new moles, flushing to the face, abdominal cramps, nausea, vomiting, chest pain and brain swelling.
It can also cause rhabdomyolysis, a dangerous syndrome where muscle breaks down and releases proteins into the bloodstream that damage the kidneys.
For men, the drug can cause priapism – a painful erection that does not go away and can damage the penis, requiring emergency treatment.
Its use has been linked with melanoma developing from existing moles either during or shortly after using the drug. This is thought to be due to stimulating pigment cells and causing the proliferation of abnormal cells.
Despite reports of melanoma, according to a study of social media posts the drug is often marketed as protecting against skin cancer. In fact, there’s no evidence to show it does this.
Social media posts about melanotan-II rarely mention health risks.
There are no studies on long-term safety of melanotan-II use.
Then there’s the issue of the drug not held to the high safety standards as TGA-approved products. This could result in variability in dose, undeclared ingredients and potential microbial contamination.
Thinking about melanotan-II? The drug can cause a long-lasting painful erection needing urgent medical care. Eugenio Marongiu/Shutterstock The TGA has previously warned consumers to steer clear of the drug due to its “serious side effects that can be very damaging to your health”.
According to an ABC article published earlier this week, the TGA is cracking down on the illegal promotion of the drug on various websites. However, we know banned sellers can pop back up under a different name.
TikTok has banned the hashtags #tanningnasalspray, #melanotan and #melanotan2, but these products continue to be promoted with more generic hashtags, such as #tanning.
Part of a wider trend
Australia has some of the highest rates of skin cancer in the world. The “slip, slop, slap” campaign is a public health success story, with increased awareness of sun safety, a cultural shift and a decline in melanoma in young people.
However, the image of a bronzed beach body remains a beauty standard, especially among some young people.
Disturbingly, tan lines are trending on TikTok as a sought after summer accessory and the hashtag #sunburnttanlines has millions of views. We’ve also seen a backlash against sunscreen among some young people, again promoted on TikTok.
The Cancer Council is so concerned about the trend towards normalising tanning it has launched the campaign End the Trend.
You have other options
There are options beyond spraying an illegal, unregulated product up your nose, or risking unprotected sun exposure: fake tan.
Fake tan tends to be much safer than melanotan-II and there’s more long-term safety data. It also comes with potential side effects, albeit rare ones, including breathing issues (with spray products) and skin inflammation in some people.
Better still, you can embrace your natural skin tone.
Rose Cairns, Senior Lecturer in Pharmacy, NHMRC Emerging Leadership Fellow, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
We Are Such Stuff As Fish Are Made Of
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Research Review: Collagen
For something that’s a very popular supplement, not many people understand what collagen is, where it comes from, or what it does.
In a nutshell:
Collagen is a kind of protein. Our bodies make it naturally, and we can also get more in our diet and/or take extra as a supplement.
Our bodies use collagen in connective tissue, skin, tendon, bone, and cartilage. It has many functions, but a broad description would be “holding things together”.
As we get older, our bodies produce less collagen. Signs of this include wrinkles, loss of skin hydration, and joint pain.
Quick test: pinch the skin on the middle of the back of one of your hands, and then watch what happens when you get low. How quickly and easily did your skin returns to its original shape?
If it was pretty much instantanous and flawless, congratulations, you have plenty of collagen (and also elastin). If you didn’t, you are probably low on both!
(they are quite similar proteins and are made from the same base “stuff”, so if you’re low on one, you’ll usually be low on both)
Quick note: A lot of research out there has been funded by beauty companies, so we had our work cut out for us today, and have highlighted where any research may be biased.
More than skin deep
While marketing for collagen is almost exclusively aimed at “reduce wrinkles and other signs of aging”, it does a lot more than that.
You remember we mentioned that many things from the bones outward are held together by collagen? We weren’t kidding…
Read: Osteoporosis, like skin ageing, is caused by collagen loss which is reversible
Taking extra collagen isn’t the only way
We can’t (yet!) completely halt the age-related loss of collagen, but we can slow it, with our lifestyle choices:
- Don’t smoke tobacco
- Drink only in moderation (or not at all)
- Avoid foods with added sugar, and high-processed foods in general
- Wear sunscreen when appropriate
Can I get collagen from food?
Yep! Just as collagen holds our bodies together, it holds the bodies of other animals together. And, just like collagen is found in most parts of our body but most plentifully in our skin and bones, that’s what to eat to get collagen from other animals, e.g:
- Chicken skin
- Fish skin
- Bone broth ← health benefits and recipes at this link!
What about vegans?
Yes, vegans are also held together by collagen! We do not, however, recommend eating their skin or boiling their bones into broth. Ethical considerations aside, cannibalism can give you CJD!
More seriously, if you’re vegan, you can’t get collagen from a plant-based diet, but you can get the stuff your body uses to make collagen. Basically, you want to make sure you get plenty of:
- Protein (beans, pulses, nuts, etc are all fine; it’s hard to go wrong with this)
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin D
- and Zinc
Just be sure to continue to remember to avoid highly-processed foods. So:
- Soy mince/chunks whose ingredients list reads: “soya”? Yes!
- The Incredible Burger or Linda McCartney’s Sausages? Sadly less healthy
Read: Advanced Glycation End Products in Foods and a Practical Guide to Their Reduction in the Diet
Meat-eaters might want to read that one too. By far the worst offenders for AGEs (Advanced Glycation End Products, which can not only cause collagen to stiffen, but also inactivate proteins responsible for collagen repair, along with doing much more serious damage to your body’s natural functions) include:
- Hot dogs
- Bacon
- Fried/roasted/grilled meats
Is it worth it as a supplement?
That depends on you, your age, and your lifestyle, but it’s generally considered safe*
*if you have a seafood allergy, be careful though, as many supplements are from fish or shellfish—you will need to find one that’s free from your allergen
Also, all collagen is animal-derived. So if you’re a vegan, decide for yourself whether this constitutes medicine and if so, whether that makes it ethically permissible to you.
With that out of the way:
What the science says on collagen supplementation
Collagen for skin
Read: Effects of collagen supplementation on skin aging (systematic review and meta-analysis)
The short version is that they selected 19 studies with over a thousand participants in total, and they found:
In the meta-analysis, a grouped analysis of studies showed favorable results of hydrolyzed collagen supplementation compared with placebo in terms of skin hydration, elasticity, and wrinkles.
The findings of improved hydration and elasticity were also confirmed in the subgroup meta-analysis.
Based on results, ingestion of hydrolyzed collagen for 90 days is effective in reducing skin aging, as it reduces wrinkles and improves skin elasticity and hydration.
Caveat: while that systematic review had no conflicts of interests, at least some of the 19 studies will have been funded by beauty companies. Here are two, so that you know what that looks like:
Funded by Quiris to investigate their own supplement, Elasten®:
A Collagen Supplement Improves Skin Hydration, Elasticity, Roughness, and Density
Funded by BioCell to investigate their own supplement, BioCell Collagen:
The Effects of Skin Aging Associated with the Use of BioCell Collagen
A note on funding bias: to be clear, the issue is not that the researchers might be corrupt (though that could happen).
The issue is more that sometimes companies will hire ten labs to do ten research studies… and then pull funding from ones whose results aren’t going the way they’d like.
So the “best” (for them) study is the one that gets published.
Here’s another systematic review—like the one at the top of this section—that found the same, with doses ranging from 2.5g–15g per day for 8 weeks or longer:
Read: Oral Collagen Supplementation: A Systematic Review of Dermatological Applications
Again, some of those studies will have been funded by beauty companies. The general weight of evidence does seem clear and favorable, though.
Collagen for bones
Here, we encountered a lot less in the way of potential bias, because this is simply marketed a lot less. Despite being arguably far more important!
We found a high quality multi-vector randomized controlled study with a sample size of 131 postmenopausal women. They had these women take 5g collagen supplement (or placebo), and studied the results over the course of a year.
They found:
- The intake of the supplement increased bone mineral density (BMD)
- Supplementation was also associated with a favorable shift in bone markers, indicating:
- increased bone formation
- reduced bone degradation
Read: Specific Collagen Peptides Improve Bone Mineral Density and Bone Markers in Postmenopausal Wome
A follow-up study with 31 of these women found that taking 5 grams of collagen daily for a total of 4 years was associated with a progressive increase in BMD.
You might be wondering if collagen also helps against osteoarthritis.
The answer is: yes, it does (at least, it significantly reduces the symptoms)
Read: Effect of collagen supplementation on osteoarthritis symptoms
In summary:
- You need collagen for health skin, bones, joints, and more
- Your body makes collagen from your food
- You can help it by getting plenty of protein, vitamins, and minerals
- You can also help it by not doing the usual Bad Things™ (smoking, drinking, eating processed foods, especially processed meats)
- You can also eat collagen directly in the form of other animals’ skin and bones
- You can also buy collagen supplements (but watch out for allergens)
Want to try collagen supplementation?
We don’t sell it (or anything else), but for your convenience…
Check it out: Hydrolyzed Collagen Peptides (the same as in most of the above studies), 90 days supply at 5g/day
We selected this one because it’s the same kind used in many of the studies, and it doesn’t contain any known allergens.
It’s bovine collagen, meaning it’s from cows, so it’s not vegan, and also some subscribers may want to abstain for religious reasons. We respect that, and/but make our recommendations based solely on the science of health and productivity.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
I’m Moving Forward and Facing the Uncertainty of Aging
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It takes a lot of courage to grow old.
I’ve come to appreciate this after conversations with hundreds of older adults over the past eight years for nearly 200 “Navigating Aging” columns.
Time and again, people have described what it’s like to let go of certainties they once lived with and adjust to new circumstances.
These older adults’ lives are filled with change. They don’t know what the future holds except that the end is nearer than it’s ever been.
And yet, they find ways to adapt. To move forward. To find meaning in their lives. And I find myself resolving to follow this path as I ready myself for retirement.
Patricia Estess, 85, of the Brooklyn borough of New York City spoke eloquently about the unpredictability of later life when I reached out to her as I reported a series of columns on older adults who live alone, sometimes known as “solo agers.”
Estess had taken a course on solo aging. “You realize that other people are in the same boat as you are,” she said when I asked what she had learned. “We’re all dealing with uncertainty.”
Consider the questions that older adults — whether living with others or by themselves — deal with year in and out: Will my bones break? Will my thinking skills and memory endure? Will I be able to make it up the stairs of my home, where I’m trying to age in place?
Will beloved friends and family members remain an ongoing source of support? If not, who will be around to provide help when it’s needed?
Will I have enough money to support a long and healthy life, if that’s in the cards? Will community and government resources be available, if needed?
It takes courage to face these uncertainties and advance into the unknown with a measure of equanimity.
“It’s a question of attitude,” Estess told me. “I have honed an attitude of: ‘I am getting older. Things will happen. I will do what I can to plan in advance. I will be more careful. But I will deal with things as they come up.’”
For many people, becoming old alters their sense of identity. They feel like strangers to themselves. Their bodies and minds aren’t working as they used to. They don’t feel the sense of control they once felt.
That requires a different type of courage — the courage to embrace and accept their older selves.
Marna Clarke, a photographer, spent more than a dozen years documenting her changing body and her life with her partner as they grew older. Along the way, she learned to view aging with new eyes.
“Now, I think there’s a beauty that comes out of people when they accept who they are,” she told me in 2022, when she was 70, just before her 93-year-old husband died.
Arthur Kleinman, a Harvard professor who’s now 83, gained a deeper sense of soulfulness after caring for his beloved wife, who had dementia and eventually died, leaving him grief-stricken.
“We endure, we learn how to endure, how to keep going. We’re marked, we’re injured, we’re wounded. We’re changed, in my case for the better,” he told me when I interviewed him in 2019. He was referring to a newfound sense of vulnerability and empathy he gained as a caregiver.
Herbert Brown, 68, who lives in one of Chicago’s poorest neighborhoods, was philosophical when I met him at his apartment building’s annual barbecue in June.
“I was a very wild person in my youth. I’m surprised I’ve lived this long,” he said. “I never planned on being a senior. I thought I’d die before that happened.”
Truthfully, no one is ever prepared to grow old, including me. (I’m turning 70 in February.)
Chalk it up to denial or the limits of imagination. As May Sarton, a writer who thought deeply about aging, put it so well: Old age is “a foreign country with an unknown language.” I, along with all my similarly aged friends, are surprised we’ve arrived at this destination.
For me, 2025 is a turning point. I’m retiring after four decades as a journalist. Most of that time, I’ve written about our nation’s enormously complex health care system. For the past eight years, I’ve focused on the unprecedented growth of the older population — the most significant demographic trend of our time — and its many implications.
In some ways, I’m ready for the challenges that lie ahead. In many ways, I’m not.
The biggest unknown is what will happen to my vision. I have moderate macular degeneration in both eyes. Last year, I lost central vision in my right eye. How long will my left eye pick up the slack? What will happen when that eye deteriorates?
Like many people, I’m hoping scientific advances outpace the progression of my condition. But I’m not counting on it. Realistically, I have to plan for a future in which I might become partially blind.
It’ll take courage to deal with that.
Then, there’s the matter of my four-story Denver house, where I’ve lived for 33 years. Climbing the stairs has helped keep me in shape. But that won’t be possible if my vision becomes worse.
So my husband and I are taking a leap into the unknown. We’re renovating the house, installing an elevator, and inviting our son, daughter-in-law, and grandson to move in with us. Going intergenerational. Giving up privacy. In exchange, we hope our home will be full of mutual assistance and love.
There are no guarantees this will work. But we’re giving it a shot.
Without all the conversations I’ve had over all these years, I might not have been up for it. But I’ve come to see that “no guarantees” isn’t a reason to dig in my heels and resist change.
Thank you to everyone who has taken time to share your experiences and insights about aging. Thank you for your openness, honesty, and courage. These conversations will become even more important in the years ahead, as baby boomers like me make their way through their 70s, 80s, and beyond. May the conversations continue.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
This article first appeared on KFF Health News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
I have a stuffy nose, how can I tell if it’s hay fever, COVID or something else?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
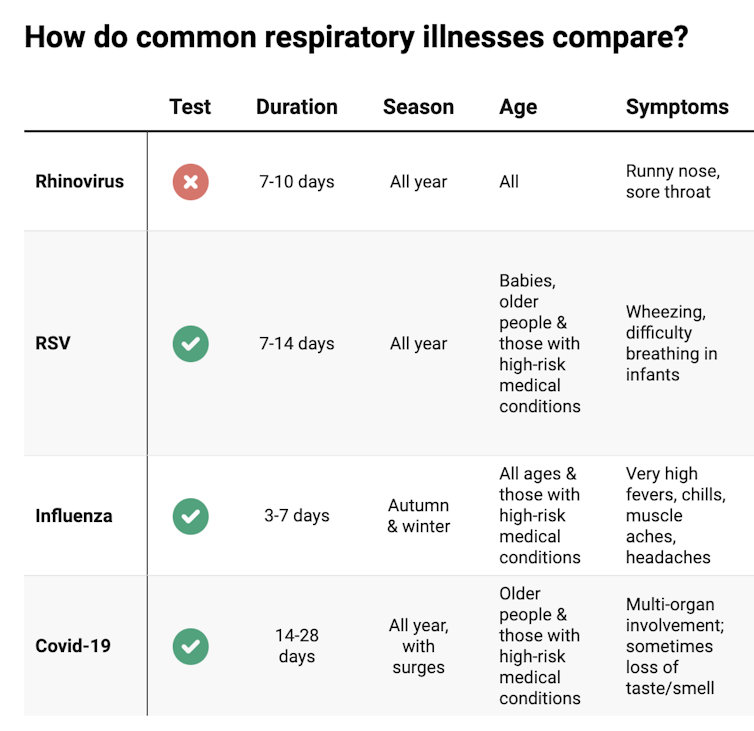
Hay fever (also called allergic rhinitis) affects 24% of Australians. Symptoms include sneezing, a runny nose (which may feel blocked or stuffy) and itchy eyes. People can also experience an itchy nose, throat or ears.
But COVID is still spreading, and other viruses can cause cold-like symptoms. So how do you know which one you’ve got?
Lysenko Andrii/Shutterstock Remind me, how does hay fever cause symptoms?
Hay fever happens when a person has become “sensitised” to an allergen trigger. This means a person’s body is always primed to react to this trigger.
Triggers can include allergens in the air (such as pollen from trees, grasses and flowers), mould spores, animals or house dust mites which mostly live in people’s mattresses and bedding, and feed on shed skin.
When the body is exposed to the trigger, it produces IgE (immunoglobulin E) antibodies. These cause the release of many of the body’s own chemicals, including histamine, which result in hay fever symptoms.
People who have asthma may find their asthma symptoms (cough, wheeze, tight chest or trouble breathing) worsen when exposed to airborne allergens. Spring and sometimes into summer can be the worst time for people with grass, tree or flower allergies.
However, animal and house dust mite symptoms usually happen year-round.
Ryegrass pollen is a common culprit. bangku ceria/Shutterstock What else might be causing my symptoms?
Hay fever does not cause a fever, sore throat, muscle aches and pains, weakness, loss of taste or smell, nor does it cause you to cough up mucus.
These symptoms are likely to be caused by a virus, such as COVID, influenza, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) or a “cold” (often caused by rhinoviruses). These conditions can occur all year round, with some overlap of symptoms:
Natasha Yates/The Conversation COVID still surrounds us. RSV and influenza rates appear higher than before the COVID pandemic, but it may be due to more testing.
So if you have a fever, sore throat, muscle aches/pains, weakness, fatigue, or are coughing up mucus, stay home and avoid mixing with others to limit transmission.
People with COVID symptoms can take a rapid antigen test (RAT), ideally when symptoms start, then isolate until symptoms disappear. One negative RAT alone can’t rule out COVID if symptoms are still present, so test again 24–48 hours after your initial test if symptoms persist.
You can now test yourself for COVID, RSV and influenza in a combined RAT. But again, a negative test doesn’t rule out the virus. If your symptoms continue, test again 24–48 hours after the previous test.
If it’s hay fever, how do I treat it?
Treatment involves blocking the body’s histamine release, by taking antihistamine medication which helps reduce the symptoms.
Doctors, nurse practitioners and pharmacists can develop a hay fever care plan. This may include using a nasal spray containing a topical corticosteroid to help reduce the swelling inside the nose, which causes stuffiness or blockage.
Nasal sprays need to delivered using correct technique and used over several weeks to work properly. Often these sprays can also help lessen the itchy eyes of hay fever.
Drying bed linen and pyjamas inside during spring can lessen symptoms, as can putting a smear of Vaseline in the nostrils when going outside. Pollen sticks to the Vaseline, and gently blowing your nose later removes it.
People with asthma should also have an asthma plan, created by their doctor or nurse practitioner, explaining how to adjust their asthma reliever and preventer medications in hay fever seasons or on allergen exposure.
People with asthma also need to be alert for thunderstorms, where pollens can burst into tinier particles, be inhaled deeper in the lungs and cause a severe asthma attack, and even death.
What if it’s COVID, RSV or the flu?
Australians aged 70 and over and others with underlying health conditions who test positive for COVID are eligible for antivirals to reduce their chance of severe illness.
Most other people with COVID, RSV and influenza will recover at home with rest, fluids and paracetamol to relieve symptoms. However some groups are at greater risk of serious illness and may require additional treatment or hospitalisation.
For RSV, this includes premature infants, babies 12 months and younger, children under two who have other medical conditions, adults over 75, people with heart and lung conditions, or health conditions that lessens the immune system response.
For influenza, people at higher risk of severe illness are pregnant women, Aboriginal people, people under five or over 65 years, or people with long-term medical conditions, such as kidney, heart, lung or liver disease, diabetes and decreased immunity.
If you’re concerned about severe symptoms of COVID, RSV or influenza, consult your doctor or call 000 in an emergency.
If your symptoms are mild but persist, and you’re not sure what’s causing them, book an appointment with your doctor or nurse practitioner. Although hay fever season is here, we need to avoid spreading other serious infectious.
For more information, you can call the healthdirect helpline on 1800 022 222 (known as NURSE-ON-CALL in Victoria); use the online Symptom Checker; or visit healthdirect.gov.au or the Australian Society of Clinical Immunology and Allergy.
Deryn Thompson, Eczema and Allergy Nurse; Lecturer, University of South Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Burden of Getting Medical Care Can Exhaust Older Patients
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Susanne Gilliam, 67, was walking down her driveway to get the mail in January when she slipped and fell on a patch of black ice.
Pain shot through her left knee and ankle. After summoning her husband on her phone, with difficulty she made it back to the house.
And then began the run-around that so many people face when they interact with America’s uncoordinated health care system.
Gilliam’s orthopedic surgeon, who managed previous difficulties with her left knee, saw her that afternoon but told her “I don’t do ankles.”
He referred her to an ankle specialist who ordered a new set of X-rays and an MRI. For convenience’s sake, Gilliam asked to get the scans at a hospital near her home in Sudbury, Massachusetts. But the hospital didn’t have the doctor’s order when she called for an appointment. It came through only after several more calls.
Coordinating the care she needs to recover, including physical therapy, became a part-time job for Gilliam. (Therapists work on only one body part per session, so she has needed separate visits for her knee and for her ankle several times a week.)
“The burden of arranging everything I need — it’s huge,” Gilliam told me. “It leaves you with such a sense of mental and physical exhaustion.”
The toll the American health care system extracts is, in some respects, the price of extraordinary progress in medicine. But it’s also evidence of the poor fit between older adults’ capacities and the health care system’s demands.
“The good news is we know so much more and can do so much more for people with various conditions,” said Thomas H. Lee, chief medical officer at Press Ganey, a consulting firm that tracks patients’ experiences with health care. “The bad news is the system has gotten overwhelmingly complex.”
That complexity is compounded by the proliferation of guidelines for separate medical conditions, financial incentives that reward more medical care, and specialization among clinicians, said Ishani Ganguli, an associate professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School.
“It’s not uncommon for older patients to have three or more heart specialists who schedule regular appointments and tests,” she said. If someone has multiple medical problems — say, heart disease, diabetes, and glaucoma — interactions with the health care system multiply.
Ganguli is the author of a new study showing that Medicare patients spend about three weeks a year having medical tests, visiting doctors, undergoing treatments or medical procedures, seeking care in emergency rooms, or spending time in the hospital or rehabilitation facilities. (The data is from 2019, before the covid pandemic disrupted care patterns. If any services were received, that counted as a day of health care contact.)
That study found that slightly more than 1 in 10 seniors, including those recovering from or managing serious illnesses, spent a much larger portion of their lives getting care — at least 50 days a year.
“Some of this may be very beneficial and valuable for people, and some of it may be less essential,” Ganguli said. “We don’t talk enough about what we’re asking older adults to do and whether that’s realistic.”
Victor Montori, a professor of medicine at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, has for many years raised an alarm about the “treatment burden” that patients experience. In addition to time spent receiving health care, this burden includes arranging appointments, finding transportation to medical visits, getting and taking medications, communicating with insurance companies, paying medical bills, monitoring health at home, and following recommendations such as dietary changes.
Four years ago — in a paper titled “Is My Patient Overwhelmed?” — Montori and several colleagues found that 40% of patients with chronic conditions such as asthma, diabetes, and neurological disorders “considered their treatment burden unsustainable.”
When this happens, people stop following medical advice and report having a poorer quality of life, the researchers found. Especially vulnerable are older adults with multiple medical conditions and low levels of education who are economically insecure and socially isolated.
Older patients’ difficulties are compounded by medical practices’ increased use of digital phone systems and electronic patient portals — both frustrating for many seniors to navigate — and the time pressures afflicting physicians. “It’s harder and harder for patients to gain access to clinicians who can problem-solve with them and answer questions,” Montori said.
Meanwhile, clinicians rarely ask patients about their capacity to perform the work they’re being asked to do. “We often have little sense of the complexity of our patients’ lives and even less insight into how the treatments we provide (to reach goal-directed guidelines) fit within the web of our patients’ daily experiences,” several physicians wrote in a 2022 paper on reducing treatment burden.
Consider what Jean Hartnett, 53, of Omaha, Nebraska, and her eight siblings went through after their 88-year-old mother had a stroke in February 2021 while shopping at Walmart.
At the time, the older woman was looking after Hartnett’s father, who had kidney disease and needed help with daily activities such as showering and going to the bathroom.
During the year after the stroke, both of Hartnett’s parents — fiercely independent farmers who lived in Hubbard, Nebraska — suffered setbacks, and medical crises became common. When a physician changed her mom’s or dad’s plan of care, new medications, supplies, and medical equipment had to be procured, and new rounds of occupational, physical, and speech therapy arranged.
Neither parent could be left alone if the other needed medical attention.
“It wasn’t unusual for me to be bringing one parent home from the hospital or doctor’s visit and passing the ambulance or a family member on the highway taking the other one in,” Hartnett explained. “An incredible amount of coordination needed to happen.”
Hartnett moved in with her parents during the last six weeks of her father’s life, after doctors decided he was too weak to undertake dialysis. He passed away in March 2022. Her mother died months later in July.
So, what can older adults and family caregivers do to ease the burdens of health care?
To start, be candid with your doctor if you think a treatment plan isn’t feasible and explain why you feel that way, said Elizabeth Rogers, an assistant professor of internal medicine at the University of Minnesota Medical School.
“Be sure to discuss your health priorities and trade-offs: what you might gain and what you might lose by forgoing certain tests or treatments,” she said. Ask which interventions are most important in terms of keeping you healthy, and which might be expendable.
Doctors can adjust your treatment plan, discontinue medications that aren’t yielding significant benefits, and arrange virtual visits if you can manage the technological requirements. (Many older adults can’t.)
Ask if a social worker or a patient navigator can help you arrange multiple appointments and tests on the same day to minimize the burden of going to and from medical centers. These professionals can also help you connect with community resources, such as transportation services, that might be of help. (Most medical centers have staff of this kind, but physician practices do not.)
If you don’t understand how to do what your doctor wants you to do, ask questions: What will this involve on my part? How much time will this take? What kind of resources will I need to do this? And ask for written materials, such as self-management plans for asthma or diabetes, that can help you understand what’s expected.
“I would ask a clinician, ‘If I chose this treatment option, what does that mean not only for my cancer or heart disease, but also for the time I’ll spend getting care?’” said Ganguli of Harvard. “If they don’t have an answer, ask if they can come up with an estimate.”
We’re eager to hear from readers about questions you’d like answered, problems you’ve been having with your care, and advice you need in dealing with the health care system. Visit http://kffhealthnews.org/columnists to submit your requests or tips.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: