What are house dust mites and how do I know if I’m allergic to them?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
People often believe they are allergic to house dust. But of the 20% of Australians suffereing with allergies, a number are are actually allergic to microscopic house dust mites.
House dust mites belong to the same family as spiders and ticks. They measure just 0.2-0.3 mm, with 50 fitting on a single pinhead. They live for 65–100 days, and females lay 60–100 eggs in their life.
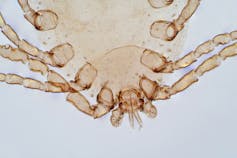
House dust mites love temperate climates and humidity. They feed off the skin cells we and animals shed, as well as mould, which they digest using special enzymes. These enzymes are excreted in their poo about 20 times a day. They also shed fragments of their exoskeletons.
All these fragments trigger allergies in people with this type of allergic rhinitis (which is also known as hay fever)

What are the symptoms?
When people with house dust mite allergy inhale the allergens, they penetrate the mucous membranes of the airways and eyes. Their body recognises the allergens as a threat, releasing chemicals including one called histamine.
This causes symptoms including a runny nose, an itchy nose, eyes and throat, sneezing, coughing and a feeling of mucus at the back of your throat (known as a post-nasal drip).
People with this type of allergy usually mouth breath, snore, rub their nose constantly (creating a nasal crease called the “dust mite salute”) and have dark shadows under their eyes.
House dust mite allergy can also cause poor sleep, constant tiredness, reduced concentration at work or school and lower quality of life.
For people with eczema, their damaged skin barrier can allow house dust mite proteins in. This prompts immune cells in the skin to release chemicals which make already flared skin become redder, sorer and itchier, especially in children.
Symptoms of house dust mite allergy occur year round, and are often worse after going to bed and when waking in the morning. But people with house dust mite allergy and pollen allergies find their year-round symptoms worsen in spring.
How is it diagnosed?
House dust mite allergy symptoms often build up over months, or even years before people seek help. But an accurate diagnosis means you can not only access the right treatment – it’s also vital for minimising exposure.

Doctor and nurse practitioners can order a blood test to check for house dust mite allergy.
Alternatively, health care providers with specialised allergy training can perform skin prick tests. This involves placing drops of the allergens on the arm, along with a positive and negative “control”. After 15 minutes, those who test positive will have developed a mosquito bite-like mark.
How is it treated?
Medication options include one or a combination of:
- daily non-sedating antihistamines
- a steroid nasal spray
- allergy eye drops.
Your health care professional will work with you to develop a rhinitis (hay fever) medical management plan to reduce your symptoms. If you’re using a nasal spray, your health provider will show you how to use it, as people often use it incorrectly.
If you also have asthma or eczema which is worsened by dust mites, your health provider will adapt your asthma action plan or eczema care plan accordingly.
If you experience severe symptoms, a longer-term option is immunotherapy. This aims to gradually turn off your immune system’s ability to recognise house dust mites as a harmful allergen.
Immunotherapy involves taking either a daily sublingual tablet, under the tongue, or a series of injections. Injections require monthly attendances over three years, after the initial weekly build-up phase.
These are effective, but are costly (as well as time-consuming). So it’s important to weigh up the potential benefits and downsides with your health-care provider.
How can you minimise house dust mites?
There are also important allergy minimisation measures you can take to reduce allergens in your home.
Each week, wash your bedding and pyjamas in hot water (over 60°C). This removes house dust mite eggs and debris.
Opt for doonas, covers or quilts that can be washed in hot water above 60°C. Alternatively, low-cost waterproof or leak proof covers can keep house dust mites out.
If you can, favour blinds and wood floors over curtains and carpet. Dust blinds and surfaces with a damp cloth each week and vacuum while wearing a mask, or have someone else do it, as house dust mites can become airborne during cleaning.
But beware of costly products with big marketing budgets and little evidence to support their use. A new mattress, for example, will always be house dust mite-free. But once slept on, the house dust mite life cycle can start.
Mattress protectors and toppers commonly claim to be “hypoallergenic”, “anti-allergy” or “allergy free”. But their pore sizes are not small enough to keep house dust mites and their poo out, or shed skin going through.
Sprays claiming to kill mites require so much spray to penetrate the product that it’s likely to become wet, may smell like the spray and, unless dried properly, may grow mould.
Finally, claims that expensive vacuum cleaners can extract all the house dust mites are unsubstantiated.
For more information, visit healthdirect.gov.au or the Australian Society of Clinical Immunology and Allergy.
Deryn Lee Thompson, Eczema and Allergy Nurse; Lecturer, University of South Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Here’s To Getting Assuredly Good Health
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
An unusual amount of excitement in the health news world this week, with health insurance in the spotlight:
Deny, Delay, Depose?
Insurance company UnitedHealthcare, which used AI with a 90% error rate to deny insurance claims (of which, disproportionately denying insurance claims of the elderly), has come under extra public scrutiny this week for its recent-years business practices:
❝Nearly 1 in 5 insured adults experienced claim denials during a 12-month period.
Those with job-based insurance or Affordable Care Act policies ran into this problem about twice as often as those covered by Medicare or Medicaid❞
…although, the company has dramatically increased its care denials for Medicare Advantage enrollees, doubling the rate of denials as it implemented its new, automated denials process.
Anesthesiologist Dr. Brain Schmutzler noted:
❝We have a bigger issue with the insurance companies in general, who, essentially, it’s their job to make money, not to actually pay for health care❞
And in those cases where healthcare is not denied, it is often dangerously delayed, as insurance companies can stall for time to decide whether they’re going to pay or not.
One useful take-away from all of this is that if your insurance claim is denied, consider fighting it, as often they can be overturned.
Specifically, it can be good to insist on knowing who (named persons) was involved in the denial process, and their qualifications. Once upon a time, this was mostly unqualified interns, which prompted insurance companies to reverse the denial rather than admit that; nowadays it’s mostly AI, which many companies can hope will shield them from culpability—either way, fighting for one’s rights can often be successful.
Read in full: Killing of UnitedHealthcare CEO prompts flurry of stories on social media over denied insurance claims
Related: With Medical Debt Burdening Millions, a Financial Regulator Steps In to Help
Rest Easy
Health insurer Elevance Health (formerly Anthem Blue Cross Blue Shield), had last month announced plans to limit its coverage for anesthesia used in operations, whereby they would pay for only a certain amount of anesthetic, and if the procedure was still ongoing when that amount had been used, then well, you were on your own.
However, on Thursday afternoon and allegedly completely coincidentally in the wake of the Wednesday assassination of the CEO who oversaw the denial of so many health insurance claims, this decision to limit paying for anesthesia was reversed, retracted, and they are now doing their best to downplay what the proposal would have meant for anesthesiologists and patients:
Read in full: Insurance company halts plan to put time limits on coverage for anesthesia during surgery
Related: The Insider’s Guide To Making Hospital As Comfortable As Possible ← an anesthesiologist’s tips
Getting a good grip of your health
What’s the best indicator of good health when it comes to age-related health issues? It’s not BMI! Could it be blood pressure? It could, but the news presently is about grip strength.
While training to have an amazing grip (and neglecting all else) will not necessarily increase your general healthspan, having a weak or strong grip is strongly associated with, respectively, having weak or strong general health in later years.
This is because unless someone has been training very unnaturally, grip strength is a good general measure of overall muscle strength, which in turn is a good indicator of metabolic health, as well as bodily robustness.
Read in full: Handgrip strength is a reliable predictor for age-related disease and disability, finds study
Related: Resistance Is Useful! (Especially As We Get Older)
Take care!
Share This Post
-
When Carbs, Proteins, & Fats Switch Metabolic Roles
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Strange Things Happening In The Islets Of Langerhans
It is generally known and widely accepted that carbs have the biggest effect on blood sugar levels (and thus insulin response), fats less so, and protein least of all.
And yet, there was a groundbreaking study published yesterday which found:
❝Glucose is the well-known driver of insulin, but we were surprised to see such high variability, with some individuals showing a strong response to proteins, and others to fats, which had never been characterized before.
Insulin plays a major role in human health, in everything from diabetes, where it is too low*, to obesity, weight gain and even some forms of cancer, where it is too high.
These findings lay the groundwork for personalized nutrition that could transform how we treat and manage a range of conditions.❞
*saying ”too low” here is potentially misleading without clarification; yes, Type 1 Diabetics will have too little [endogenous] insulin (because the pancreas is at war with itself and thus isn’t producing useful quantities of insulin, if any). Type 2, however, is more a case of acquired insulin insensitivity, because of having too much at once too often, thus the body stops listening to it, “boy who cried wolf”-style, and the pancreas also starts to get fatigued from producing so much insulin that’s often getting ignored, and does eventually produce less and less while needing more and more insulin to get the same response, so it can be legitimately said “there’s not enough”, but that’s more of a subjective outcome than an objective cause.
Back to the study itself, though…
What they found, and how they found it
Researchers took pancreatic islets from 140 heterogenous donors (varied in age and sex; ostensibly mostly non-diabetic donors, but they acknowledge type 2 diabetes could potentially have gone undiagnosed in some donors*) and tested cell cultures from each with various carbs, proteins, and fats.
They found the expected results in most of the cases, but around 9% responded more strongly to the fats than the carbs (even more strongly than to glucose specifically), and even more surprisingly 8% responded more strongly to the proteins.
*there were also some known type 2 diabetics amongst the donors; as expected, those had a poor insulin response to glucose, but their insulin response to proteins and fats were largely unaffected.
What this means
While this is, in essence, a pilot study (the researchers called for larger and more varied studies, as well as in vivo human studies), the implications so far are important:
It appears that, for a minority of people, a lot of (generally considered very good) antidiabetic advice may not be working in the way previously understood. They’re going to (for example) put fat on their carbs to reduce the blood sugar spike, which will technically still work, but the insulin response is going to be briefly spiked anyway, because of the fats, which very insulin response is what will lower the blood sugars.
In practical terms, there’s not a lot we can do about this at home just yet—even continuous glucose monitors won’t tell us precisely, because they’re monitoring glucose, not the insulin response. We could probably measure everything and do some math and work out what our insulin response has been like based on the pace of change in blood sugar levels (which won’t decrease without insulin to allow such), but even that is at best grounds for a hypothesis for now.
Hopefully, more publicly-available tests will be developed soon, enabling us all to know our “insulin response type” per the proteome predictors discovered in this study, rather than having to just blindly bet on it being “normal”.
Ironically, this very response may have hidden itself for a while—if taking fats raised insulin response without raising blood sugar levels, then if blood sugar levels are the only thing being measured, all we’ll see is “took fats at dinner; blood sugars returned to normal more quickly than when taking carbs without fats”.
You can read the study in full here:
Proteomic predictors of individualized nutrient-specific insulin secretion in health and disease
Want to know more about blood sugar management?
You might like to catch up on:
- 10 Ways To Balance Your Blood Sugars
- Track Your Blood Sugars For Better Personalized Health
- How To Turn Back The Clock On Insulin Resistance
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Why a common asthma drug will now carry extra safety warnings about depression
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Australia’s Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) recently issued a safety alert requiring extra warnings to be included with the asthma and hay fever drug montelukast.
The warnings are for users and their families to look for signs of serious behaviour and mood-related changes, such as suicidal thoughts and depression. The new warnings need to be printed at the start of information leaflets given to both patients and health-care providers (sometimes called a “boxed” warning).
So why did the TGA issue this warning? And is there cause for concern if you or a family member uses montelukast? Here’s what you need to know.
First, what is montelukast?
Montelukast is a prescription drug also known by its brand names which include Asthakast, Lukafast, Montelair and Singulair. It’s used to manage the symptoms of mild-to-moderate asthma and seasonal hay fever in children and adults.
Asthma occurs when the airways tighten and produce extra mucus, which makes it difficult to get air into the lungs. Likewise, the runny nose characteristic of hay fever occurs due to the overproduction of mucus.
Leukotrienes are an important family of chemicals found throughout the airways and involved in both mucus production and airway constriction. Montelukast is a cysteinyl leukotriene receptor antagonist, meaning it blocks the site in the airways where the leukotrienes work.
Montelukast can’t be used to treat acute asthma (an asthma attack), as it takes time for the tablet to be broken down in the stomach and for it to be absorbed into the body. Rather, it’s taken daily to help prevent asthma symptoms or seasonal hay fever.
It can be used alongside asthma puffers that contain corticosteriods and drugs like salbutamol (Ventolin) in the event of acute attacks.
What is the link to depression and suicide?
The possibility that this drug may cause behavioural changes is not new information. Manufacturers knew this as early as 2007 and issued warnings for possible side-effects including depression, suicidality and anxiousness.
The United Kingdom’s Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency has required a warning since 2008 but mandated a more detailed warning in 2019. The United States’ Food and Drug Administration has required boxed warnings for the drug since 2020.
Montelukast can help children and adults with asthma. adriaticfoto/Shutterstock Montelukast is known to potentially induce a number of behaviour and mood changes, including agitation, anxiety, depression, irritability, obsessive-compulsive symptoms, and suicidal thoughts and actions.
Initially a 2009 study that analysed data from 157 clinical trials involving more than 20,000 patients concluded there were no completed suicides due to taking the drug, and only a rare risk of suicide thoughts or attempts.
The most recent study, published in November 2024, examined data from more than 100,000 children aged 3–17 with asthma or hay fever who either took montelukast or used only inhaled corticosteroids.
It found montelukast use was associated with a 32% higher incidence of behavioural changes. The behaviour change with the strongest association was sleep disturbance, but montelukast use was also linked to increases in anxiety and mood disorders.
In the past ten years, around 200 incidences of behavioural side-effects have been reported to the TGA in connection with montelukast. This includes 57 cases of depression, 60 cases of suicidal thoughts and 17 suicide attempts or incidents of intentional self-injury. There were seven cases where patients taking the drug did complete a suicide.
This is of course tragic. But these numbers need to be seen in the context of the number of people taking the drug. Over the same time period, more than 200,000 scripts for montelukast have been filled under the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme.
Overall, we don’t know conclusively that montelukast causes depression and suicide, just that it seems to increase the risk for some people.
We’re still not sure how the drug can act on the brain to lead to behaviour changes. Elif Bayraktar/Shutterstock And if it does change behaviour, we don’t fully understand how this happens. One hypothesis is that the drug and its breakdown products (or metabolites) affect brain chemistry.
Specifically, it might interfere with how the brain detoxifies the antioxidant glutathione or alter the regulation of other brain chemicals, such as neurotransmitters.
Why is the TGA making this change now?
The new risk warning requirement comes from a meeting of the Australian Advisory Committee on Medicines where they were asked to provide advice on ways to minimise the risk for the drug given current international recommendations.
Even though the 2024 review didn’t highlight any new risks, to align with international recommendations, and help address consumer concerns, the advisory committee recommended a boxed warning be added to drug information sheets.
If you have asthma and take montelukast (or your child does), you should not just stop taking the drug, because this could put you at risk of an attack that could be life threatening. If you’re concerned, speak to your doctor who can discuss the risks and benefits of the medication for you, and, if appropriate, prescribe a different medication.
If this article has raised issues for you, or if you’re concerned about someone you know, call Lifeline on 13 11 14.
Nial Wheate, Professor of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Macquarie University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Psychoactive Drugs Are Having a Moment. The FDA Will Soon Weigh In.
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Lori Tipton is among the growing number of people who say that MDMA, also known as ecstasy, saved their lives.
Raised in New Orleans by a mother with untreated bipolar disorder who later killed herself and two others, Tipton said she endured layers of trauma that eventually forced her to seek treatment for crippling anxiety and hypervigilance. For 10 years nothing helped, and she began to wonder if she was “unfixable.”
Then she answered an ad for a clinical trial for MDMA-assisted therapy to treat post-traumatic stress disorder. Tipton said the results were immediate, and she is convinced the drug could help a lot of people. But even as regulators weigh approval of the first MDMA-based treatment, she’s worried that it won’t reach those who need it most.
“The main thing that I’m always concerned about is just accessibility,” the 43-year-old nonprofit project manager said. “I don’t want to see this become just another expensive add-on therapy for people who can afford it when people are dying every day by their own hand because of PTSD.”
MDMA is part of a new wave of psychoactive drugs that show great potential for treating conditions such as severe depression and PTSD. Investors are piling into the nascent field, and a host of medications based on MDMA, LSD, psychedelic mushrooms, ketamine, the South American plant mixture ayahuasca, and the African plant ibogaine are now under development, and in some cases vying for approval by the Food and Drug Administration.
Proponents hope the efforts could yield the first major new therapies for mental illness since the introduction of modern antidepressants in the 1980s. But not all researchers are convinced that their benefits have been validated, or properly weighed against the risks. And they can be difficult to assess using traditional clinical trials.
The first MDMA-assisted assisted therapy appeared to be on track for FDA approval this August, but a recent report from an independent review committee challenged the integrity of the trial data from the drug’s maker, Lykos Therapeutics, a startup founded by a psychedelic research and advocacy group. The FDA will convene a panel of independent investigators on June 4 to determine whether to recommend the drug’s approval.
Proponents of the new therapies also worry that the FDA will impose treatment protocols, such as requiring multiple trained clinicians to monitor a patient for extended periods, that will render them far too expensive for most people.
Tipton’s MDMA-assisted therapy included three eight-hour medication sessions overseen by two therapists, each followed by an overnight stay at the facility and an integration session the following day.
“It does seem that some of these molecules can be administered safely,” said David Olson, director of the University of California-Davis Institute for Psychedelics and Neurotherapeutics. “I think the question is can they be administered safely at the scale needed to really make major improvements in mental health care.”
Breakthrough Therapies?
Psychedelics and other psychoactive substances, among the medicines with the oldest recorded use, have long been recognized for their potential therapeutic benefits. Modern research on them started in the mid-20th century, but clinical trial results didn’t live up to the claims of advocates, and they eventually got a bad name both from their use as party drugs and from rogue CIA experiments that involved dosing unsuspecting individuals.
The 1970 Controlled Substances Act made most psychoactive drugs illegal before any treatments were brought to market, and MDMA was classified as a Schedule 1 substance in 1985, which effectively ended any research. It wasn’t until 2000 that scientists at Johns Hopkins University were granted regulatory approval to study psilocybin anew.
Ketamine was in a different category, having been approved as an anesthetic in 1970. In the early 2000s, researchers discovered its antidepressant effects, and a ketamine-based therapy, Spravato, received FDA approval in 2019. Doctors can also prescribe generic ketamine off-label, and hundreds of clinics have sprung up across the nation. A clinical trial is underway to evaluate ketamine’s effectiveness in treating suicidal depression when used with other psychiatric medications.
Ketamine’s apparent effectiveness sparked renewed interest in the therapeutic potential of other psychoactive substances.
They fall into distinct categories: MDMA is an entactogen, also known as an empathogen, which induces a sense of connectedness and emotional communion, while LSD, psylocibin, and ibogaine are psychedelics, which create altered perceptual states. Ketamine is a dissociative anesthetic, though it can produce hallucinations at the right dose.
Despite the drugs’ differences, Olson said they all create neuroplasticity and allow the brain to heal damaged neural circuits, which imaging shows can be shriveled up in patients with addiction, depression, and PTSD.
“All of these brain conditions are really disorders of neural circuits,” Olson said. “We’re basically looking for medicines that can regrow these neurons.”
Psychedelics are particularly good at doing this, he said, and hold promise for treating diseases including Alzheimer’s.
A number of psychoactive drugs have now received the FDA’s “breakthrough therapy” designation, which expedites development and review of drugs with the potential to treat serious conditions.
But standard clinical trials, in which one group of patients is given the drug and a control group is given a placebo, have proven problematic, for the simple reason that people have no trouble determining whether they’ve gotten the real thing.
The final clinical trial for Lykos’ MDMA treatment showed that 71% of participants no longer met the criteria for PTSD after 18 weeks of taking the drug versus 48% in the control group.
A March report by the Institute for Clinical and Economic Review, an independent research group, questioned the company’s clinical trial results and challenged the objectivity of MDMA advocates who participated in the study as both patients and therapists. The institute also questioned the drug’s cost-effectiveness, which insurers factor into coverage decisions.
Lykos, a public benefit company, was formed in 2014 as an offshoot of the Multidisciplinary Association for Psychedelic Studies, a nonprofit that has invested more than $150 million into psychedelic research and advocacy.
The company said its researchers developed their studies in partnership with the FDA and used independent raters to ensure the reliability and validity of the results.
“We stand behind the design and results of our clinical trials,” a Lykos spokesperson said in an email.
There are other hazards too. Psychoactive substances can put patients in vulnerable states, making them potential victims for financial exploitation or other types of abuse. In Lykos’ second clinical trial, two therapists were found to have spooned, cuddled, blindfolded, and pinned down a female patient who was in distress.
The substances can also cause shallow breathing, heart issues, and hyperthermia.
To mitigate risks, the FDA can put restrictions on how drugs are administered.
“These are incredibly potent molecules and having them available in vending machines is probably a bad idea,” said Hayim Raclaw of Negev Capital, a venture capital fund focused on psychedelic drug development.
But if the protocols are too stringent, access is likely to be limited.
Rachel del Dosso, a trauma therapist in the greater Los Angeles area who offers ketamine-assisted therapy, said she’s been following the research on drugs like MDMA and psilocybin and is excited for their therapeutic potential but has reservations about the practicalities of treatment.
“As a therapist in clinical practice, I’ve been thinking through how could I make that accessible,” she said. “Because it would cost a lot for [patients] to have me with them for the whole thing.”
Del Dosso said a group therapy model, which is sometimes used in ketamine therapy, could help scale the adoption of other psychoactive treatments, too.
Artificial Intelligence and Analogs
Researchers expect plenty of new discoveries in the field. One of the companies Negev has invested in, Mindstate Design Labs, uses artificial intelligence to analyze “trip reports,” or self-reported drug experiences, to identify potentially therapeutic molecules. Mindstate has asked the FDA to green-light a clinical trial of the first molecule identified through this method, 5-MeO-MiPT, also known as moxy.
AlphaFold, an AI program developed by Google’s DeepMind, has identified thousands of potential psychedelic molecules.
There’s also a lot of work going into so-called analog compounds, which have the therapeutic effects of hallucinogens but without the hallucinations. The maker of a psilocybin analog announced in March that the FDA had granted it breakthrough therapy status.
“If you can harness the neuroplasticity-promoting properties of LSD while also creating an antipsychotic version of it, then that can be pretty powerful,” Olson said.
This article was produced by KFF Health News, which publishes California Healthline, an editorially independent service of the California Health Care Foundation.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Resistance band Training – by James Atkinson
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
For those who’d like a full gym workout at home, without splashing out thousands on a home gym, resistance bands provide a lot of value. But how much value, really?
As James Atkinson demonstrates, there’s more exercise available than one might think.
Did you know that you can use the same band to strengthen your triceps as well as your biceps, for instance? and the same goes for your quadriceps and biceps femoris. And core strength? You bet.
The style here is not a sales pitch (though he does, at the end, offer extra resources if desired), but rather, instructional, and this book is in and of itself already a complete guide. With clear instructions and equally clear illustrations, you don’t need to spend a dime more (unless you don’t own a resistance band, in which case then yes, you will need one of those).
Bottom line: if you’d like to give your body the workout it deserves, this book is a potent resource.
Click here to check out Resistance Band Training, and get training!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Is ADHD Being Over-Diagnosed For Cash?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Is ADHD Being Systematically Overdiagnosed?
The BBC’s investigative “Panorama” program all so recently did a documentary in which one of their journalists—who does not have ADHD—went to three private clinics and got an ADHD diagnosis from each of them:
- The BBC documentary: Private ADHD Clinics Exposed (28 mins)
- Their “5 Minutes” version: ADHD Undercover: How I Was Misdiagnosed (6 mins)
So… Is it really a case of show up, pay up, and get a shiny new diagnosis?
The BBC Panorama producers cherry-picked 3 private providers, and during those clinical assessments, their journalist provided answers that would certainly lead to a diagnosis.
This was contrasted against a three-hour assessment with an NHS psychiatrist—something that rarely happens in the NHS. Which prompts the question…
How did he walk into a 3-hour psychiatrist assessment, when most people have to wait in long waiting lists for a much more cursory appointment first with assorted gatekeepers, before going on another long waiting list, for an also-much-shorter appointment with a psychiatrist?
That would be because the NHS psychiatrist was given advance notification that this was part of an investigation and would be filmed (the private clinics were not gifted the same transparency)
So, maybe just a tad unequal treatment!
In case you’re wondering, here’s what that very NHS psychiatrist had to say on the topic:
Is it really too easy to be diagnosed with ADHD?
(we’ll give you a hint—remember Betteridge’s Law!)
❝Since the documentary aired, I have heard from people concerned that GPs could now be more likely to question legitimate diagnoses.
But as an NHS psychiatrist it is clear to me that the root of this issue is not overdiagnosis.
Instead, we are facing the combined challenges of remedying decades of underdiagnosis and NHS services that were set up when there was little awareness of ADHD.❞
~ Dr. Mike Smith, Psychiatrist
The ADHD foundation, meanwhile, has issued its own response, saying:
❝We are disappointed that BBC Panorama has opted to broadcast a poorly researched, sensationalist piece of television journalism.❞
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: