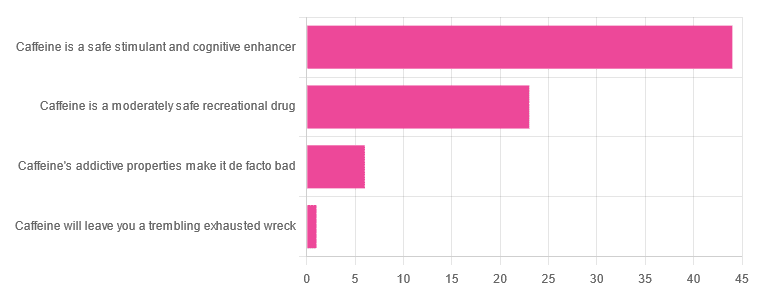
Sun-Dried Tomatoes vs Carrots – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing sun-dried tomatoes to carrots, we picked the sun-dried tomatoes.
Why?
After tomatoes lost to carrots yesterday, it turns out that sun-drying them is enough to turn the nutritional tables!
This time, it’s the sun-dried tomatoes that have more carbs and fiber, as well as the nominally lower glycemic index (although obviously, carrots are also just fine in this regard; nobody is getting metabolic disease from eating carrots). Still, by the numbers, a win for sun-dried tomatoes.
In terms of vitamins, the fact that they have less water-weight means that proportionally, gram for gram, sun-dried tomatoes have more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B9, C, E, K, and choline, while carrots still have more vitamin A. An easy win for sun-dried tomatoes on the whole, though.
When it comes to minerals, sun-dried tomatoes have more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while carrots are not higher in any mineral.
Looking at polyphenols, sun-dried tomatoes have more, including a good healthy dose of quercetin; they also have more lycopene, not technically a polyphenol by virtue of its chemical structure (it’s a carotenoid), but a powerful phytochemical nonetheless. And, the lycopene content is higher in sun-dried tomatoes (compared to raw tomatoes) not just because of the loss of water-weight making a proportional difference, but also because the process itself improves the lycopene content, much like cooking does.
All in all, a clear and overwhelming win for sun-dried tomatoes.
Just watch out, as this is about the sun-dried tomatoes themselves; if you get them packed in vegetable oil, as is common, it’ll be a very different nutritional profile!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Tomatoes vs Carrots – Which is Healthier? ← see the difference!
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Dates vs Raisins – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing dates to raisins, we picked the dates.
Why?
There are benefits for each fruit, but we say dates come out on top. See what you think:
In terms of macros, while they’re both dried fruits, dates contain more water (unless you leave them sitting open for a while), which will tend to mathematically lower the relative percentages of other components because they’re being held against water weight too. However, even though this is the case (i.e. dates are being mathematically disadvantaged), dates contain more than twice the fiber that raisins do (8g/100g compared to raisins’ 3.7g/100g).
While we’re talking macros, dates are also lower in total carbs, as well as obviously net carbs, and have a much lower glycemic index than raisins (dates have a glycemic index of 42, considered low, while raisins have a glycemic index of 64, considered medium; their respective glycemic loads are even more telling: 13 for raisins and just 2 for dates!).
About those carbs… For dates, it’s an approximately equal mix of sucrose, glucose, and fructose, while for raisins it’s 49% glucose and 49% fructose. Because sucrose is the only disaccharide here, this (as well as the fiber difference) is one of the reasons for the different glycemic indices and glycemic loads, since glucose and fructose are more quickly absorbed.
That’s more than we usually write about macros, but in this case, both fruits are ones especially often hit with the “aren’t they full of sugar though?” question, so it was important to cover the critical distinctions between the two, because they really are very different.
Summary of macros: dates win easily in every aspect we looked at
In the category of vitamins, raisins get a tally in their favor. Raisins are higher in vitamins B1, B2, C, E, K, and choline, while dates are higher in vitamins A, B3, B5, and B9, giving raisins a 6:4 lead here. In dates’ defense, the difference in vitamin K is marginal, and it’d make it a 5:4 lead if we considered that within the margin of error (because all these figures are of course based on averages), and the vitamins that dates are higher in, the margins are much wider indeed, meaning that both fruits have approximately the same overall levels of vitamins when looked at in total, but still, we’ll call this category a nominal win for raisins.
When it comes to minerals, dates have more magnesium, selenium, and zinc, while raisins have more copper, iron, phosphorus, and potassium. Nominally that’s a 4:3 lead for raisins, but if we consider that raisins also contain more sodium, it’s more like a tie here. If we have to pick one though, this is a very slight win for raisins.
Adding up the sections, we have one huge win for dates (macros) with two very marginal wins for raisins—hence, we say that dates win out.
Still, of course enjoy both; diversity is good for the health.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Chatter – by Dr. Ethan Kross
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This book is about much more than just one’s internal monologue. It does tackle that, but also the many non-verbal rabbit-holes that our brains can easily disappear into.
The author is an experimental psychologist, and brings his professional knowledge and experience to bear on this problem—citing many studies, including his own studies from his own lab, in which he undertook to answer precisely the implicit questions of “How can I…” in terms of tackling these matters, from root anxiety (for example) to end-state executive dysfunction (for example).
The writing style isn’t dense science though, and is very approachable for all.
The greatest value in this book lies in its prescriptive element, that is to say, its advice, especially in the category of evidence-based things we can do to improve matters for ourselves; beyond generic things like “mindfulness-based stress reduction” to much more specific things like “observe yourself in the 3rd person for a moment” and “take a break to imagine looking back on this later” and “interrupt yourself with a brief manual task”. With these sorts of interventions and more, we can shift the voice in our head from critic to coach.
Bottom line: if you would like your brain to let you get on with the things you actually want to do instead of constantly sidetracking you, this is the book for you.
Share This Post
-
Nori vs Wakame – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing nori to wakame, we picked the nori.
Why?
It was close, and both of these seaweed options are great!
In terms of macros, nori has more protein while wakame has more carbs; they’re about equal on fiber. While the difference in protein and carbs isn’t big, out of the two we’ll prioritize protein, and thus say nori gets a notional win here—but as it’s so close, one could just as easily call it a tie.
In the category of vitamins both are very rich in many minerals, but nori has more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B6, B12*, and C, while wakame has more of vitamins B5, B9, K, and choline. Thus, a 6:4 victory for nori.
*Yes, nori is one of those rare vegan foods that naturally contain vitamin B12; it’s because of the composition of the algae that this seaweed is made of, which includes some beneficial B12-making bacteria. Meanwhile, wakame is “just” a kelp, so it doesn’t have B12.
When it comes to minerals, nori has more potassium and zinc, while wakame has more calcium and magnesium. They’re equal on other minerals, except: it’s worth noting that wakame is moderately high in sodium, while nori has very little sodium. So, either a tie-breaking win for nori, or just a tie.
Adding up the sections gives nori the overall win; it’s only the margin of the win that’s reasonably debatable. Still, enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- A Deeper Dive Into Seaweed
- Spirulina vs Nori – Which is Healthier? ← guess which won!
- 21% Stronger Bones in a Year at 62? Yes, It’s Possible (No Calcium Supplements Needed!) ← nori and wakame both feature (very favorably) in this case study
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Head Over Hips
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve written before about managing osteoarthritis (or ideally: avoiding it, but that’s not always an option on the table, of course), so here’s a primer/refresher before we get into the meat of today’s article:
Avoiding/Managing Osteoarthritis
When the head gets in the way
Research shows that the problem with recovery in cases of osteoarthritis of the hip is in fact often not the hip itself, but rather, the head:
❝In fact, the stronger your muscles are, the more protected your joint is, and the less pain you will experience.
Our research has shown that people with hip osteoarthritis were unable to activate their muscles as efficiently, irrespective of strength.
Basically, people with hip arthritis are unable to activate their muscles properly because the brain is actively putting on the brake to stop them from using the muscle.❞
This is a case of a short-term protective response being unhelpful in the long-term. If you injure yourself, your brain will try to inhibit you from exacerbating that injury, such as by (for example) disobliging you from putting weight on an injured joint.
This is great if you merely twisted an ankle and just need to sit back and relax while your body works its healing magic, but it’s counterproductive if it’s a chronic issue like osteoarthritis. In such (i.e. chronic) cases, avoidance of use of the joint will simply cause atrophy of the surrounding muscle and other tissues, leading to more of the very wear-and-tear that led to the osteoarthritis in the first place.
So… How to deal with that?
You probably can exercise
It’s easy to get caught between the dichotomy of “exercise and inflame your joints” vs “rest and your joints seize up”, which is not pleasant.
However, the trick lies in how you exercise, per joint type:
When Bad Joints Stop You From Exercising (5 Things To Change)
…which to be clear, isn’t a case of “avoid using the joint that’s bad”, but is rather “use it in this specific way, so that it gets stronger without doing it more damage in the process”.
Which is exactly what is needed!
Further resources
For those who like learning from short videos, here’s a trio of helpers (along with our own text-based overview for each):
- The Most Underrated Hip Mobility Exercise (Not Stretching)
- Overcome Front-Of-Hip Pain
- 10 Tips To Reduce Morning Pain & Stiffness With Arthritis
And for those who prefer just reading, here’s a book we reviewed on the topic:
11 Minutes to Pain-Free Hips – by Melinda Wright
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Caffeine: Cognitive Enhancer Or Brain-Wrecker?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Two Sides Of Caffeine
We asked you for your health-related opinions on caffeine itself, not necessarily the coffee, tea, energy drinks, etc that might contain it.
We have, by the way previously written about the health effects of coffee and tea specifically:
As for our question about caffeine itself, though, we got the above-depicted, below-described, set of results:
- About 59% said “caffeine is a safe stimulant and cognitive enhancer”
- About 31% said “caffeine is a moderately safe recreational drug”
- About 8% said “caffeine’s addictive properties make it de facto bad”
- One (1) person said “caffeine will leave you a trembling exhausted wreck”
But what does the science say?
Caffeine is addictive: True or False?
True, though one will find occasional academics quibbling the definition. Most of the studies into the mechanisms of caffeine addiction have been conducted on rats, but human studies exist too and caffeine is generally considered addictive for humans, for example:
See also:
Notwithstanding its addictive status, caffeine is otherwise safe: True or False?
True-ish, for most people. Some people with heart conditions or a hypersensitivity to caffeine may find it is not safe for them at all, and for the rest of us, the dose makes the poison. For example:
❝Can too much caffeine kill you? Although quite rare, caffeine can be fatal in cases of overdose; such circumstances are generally not applicable to healthy individuals who typically consume caffeine via beverages such as tea or coffee.❞
this paper, by the way, also includes a good example of academics quibbling the definition of addiction!
Caffeine is a cognitive enhancer: True or False?
True, but only in the case of occasional use. If you are using it all the time, your physiology will normalize it and you will require caffeine in order to function at your normal level. To attain higher than that, once addicted to caffeine, would now require something else.
Read more: Caffeine: benefits and drawbacks for technical performance
Caffeine will leave you a trembling exhausted wreck: True or False?
True or False depending on usage:
- The famously moderate 3–5 cups per day will not, for most people, cause any such problems.
- Using/abusing it to make up for lost sleep (or some other source of fatigue, such as physical exhaustion from exertion), however, is much more likely to run into problems.
In the latter case, caffeine really is the “payday loan” of energy! It’ll give you an adrenal boost now (in return, you must suffer the adrenal dumping later, along with lost energy expended in the adrenaline surge), and also, the tiredness that you thought was gone, was just caffeine’s adenosine-blocking activities temporarily preventing you from being able to perceive the tiredness. So you’ll have to pay that back later, with interest, because of the extra time/exertion too.
Want to make caffeine a little more gentle on your system?
Taking l-theanine alongside caffeine can ameliorate some of caffeine’s less wonderful effects—and as a bonus, l-theanine has some nifty benefits of its own, too:
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
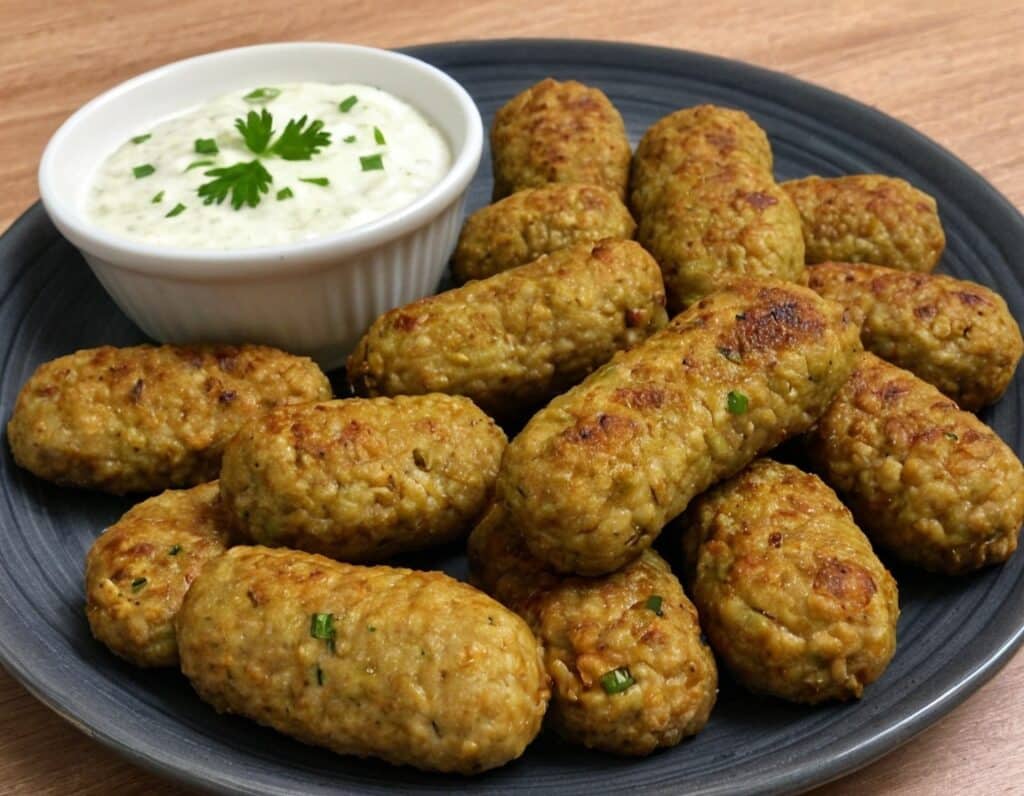
Zucchini & Oatmeal Koftas
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
These vegetarian (and with one tweak, vegan) koftas are delicious as a snack, light lunch, or side to a larger meal. Healthwise, they contain the healthiest kind of fiber, as well as omega-3 fatty acids, and beneficial herbs and spices.
You will need
- ¼ cup oatmeal
- 1 large zucchini, grated
- 1 small carrot, grated
- ¼ cup cheese (your preference; vegan is also fine)
- 2 tbsp ground flaxseed
- 2 tbsp nutritional yeast
- ¼ bulb garlic, minced
- 2 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Small handful fresh parsley, chopped
- Extra virgin olive oil, for frying
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Soak the flaxseed in 2 oz hot water for at least 5 minutes
2) Combine all of the ingredients except the olive oil (and including the water that the flax has been soaking in) in a big bowl, mixing thoroughly
3) Shape into small balls, patties, or sausage shapes, and fry until the color is golden and the structural integrity is good. If doing patties, you’ll need to gently flip them to cook both sides; otherwise, rolling them to get all sides is fine.
4) Serve! Traditional is with some kind of yogurt dip, but we’re not the boss of you, so enjoy them how you like:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- The Best Kind Of Fiber For Overall Health? ← it’s β-glucan, as found in oats
- What Omega-3 Fatty Acids Really Do For Us ← as in the flax
- The Many Health Benefits Of Garlic
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
- Monosodium Glutamate: Sinless Flavor-Enhancer Or Terrible Health Risk? ← it’s healthier than table salt
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: