A Therapeutic Journey – by Alain de Botton
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve often featured The School of Life’s videos here on 10almonds, and most of those are written by (and often voiced by) Alain de Botton.
This book lays out the case for mental health being also just health, that no person is perfectly healthy all the time, and sometimes we all need a little help. While he does suggest seeking help from reliable outside sources, he also tells a lot about how we can improve things for ourselves along the way, whether by what we can control in our environment, or just what’s between our ears.
In the category of limitations, the book is written with the assumption that you are in a position to have access to a therapist of your choice, and in a sufficiently safe and stable life situation that there is a limit to how bad things can get.
The style is… Alain de Botton’s usual style. Well-written, clear, decisive, instructive, compassionate, insightful, thought-provoking.
Bottom line: this isn’t a book for absolutely everyone, but if your problems are moderate and your resources are comfortable, then this book has a lot of insights that can make your life more easy-going and joyful, without dropping the seriousness when appropriate.
Click here to check out A Therapeutic Journey, and perhaps begin one of your own!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Comfort Book – by Matt Haig
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This book “is what it says on the tin”. Matt Haig, bestselling author of “Reasons to Stay Alive” (amongst other works) is here with “a hug in a book”.
The format of the book is an “open it at any page and you’ll find something of value” book. Its small chapters are sometimes a few pages long, but often just a page. Sometimes just a line. Always deep.
All of us, who live long enough, will ponder our mortality sometimes. The feelings we may have might vary on a range from “afraid of dying” to “despairing of living”… but Haig’s single biggest message is that life is full of wonder; each moment precious.
- That hope is an incredible (and renewable!) resource.
- That we are more than a bad week, or month, or year, or decade.
- That when things are taken from us, the things that remain have more value.
Bottom line: you might cry (this reviewer did!), but it’ll make your life the richer for it, and remind you—if ever you need it—the value of your amazing life.
Share This Post
-
Mammography AI Can Cost Patients Extra. Is It Worth It?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As I checked in at a Manhattan radiology clinic for my annual mammogram in November, the front desk staffer reviewing my paperwork asked an unexpected question: Would I like to spend $40 for an artificial intelligence analysis of my mammogram? It’s not covered by insurance, she added.
I had no idea how to evaluate that offer. Feeling upsold, I said no. But it got me thinking: Is this something I should add to my regular screening routine? Is my regular mammogram not accurate enough? If this AI analysis is so great, why doesn’t insurance cover it?
I’m not the only person posing such questions. The mother of a colleague had a similar experience when she went for a mammogram recently at a suburban Baltimore clinic. She was given a pink pamphlet that said: “You Deserve More. More Accuracy. More Confidence. More power with artificial intelligence behind your mammogram.” The price tag was the same: $40. She also declined.
In recent years, AI software that helps radiologists detect problems or diagnose cancer using mammography has been moving into clinical use. The software can store and evaluate large datasets of images and identify patterns and abnormalities that human radiologists might miss. It typically highlights potential problem areas in an image and assesses any likely malignancies. This extra review has enormous potential to improve the detection of suspicious breast masses and lead to earlier diagnoses of breast cancer.
While studies showing better detection rates are extremely encouraging, some radiologists say, more research and evaluation are needed before drawing conclusions about the value of the routine use of these tools in regular clinical practice.
“I see the promise and I hope it will help us,” said Etta Pisano, a radiologist who is chief research officer at the American College of Radiology, a professional group for radiologists. However, “it really is ambiguous at this point whether it will benefit an individual woman,” she said. “We do need more information.”
The radiology clinics that my colleague’s mother and I visited are both part of RadNet, a company with a network of more than 350 imaging centers around the country. RadNet introduced its AI product for mammography in New York and New Jersey last February and has since rolled it out in several other states, according to Gregory Sorensen, the company’s chief science officer.
Sorensen pointed to research the company conducted with 18 radiologists, some of whom were specialists in breast mammography and some of whom were generalists who spent less than 75% of their time reading mammograms. The doctors were asked to find the cancers in 240 images, with and without AI. Every doctor’s performance improved using AI, Sorensen said.
Among all radiologists, “not every doctor is equally good,” Sorensen said. With RadNet’s AI tool, “it’s as if all patients get the benefit of our very top performer.”
But is the tech analysis worth the extra cost to patients? There’s no easy answer.
“Some people are always going to be more anxious about their mammograms, and using AI may give them more reassurance,” said Laura Heacock, a breast imaging specialist at NYU Langone Health’s Perlmutter Cancer Center in New York. The health system has developed AI models and is testing the technology with mammograms but doesn’t yet offer it to patients, she said.
Still, Heacock said, women shouldn’t worry that they need to get an additional AI analysis if it’s offered.
“At the end of the day, you still have an expert breast imager interpreting your mammogram, and that is the standard of care,” she said.
About 1 in 8 women will be diagnosed with breast cancer during their lifetime, and regular screening mammograms are recommended to help identify cancerous tumors early. But mammograms are hardly foolproof: They miss about 20% of breast cancers, according to the National Cancer Institute.
The FDA has authorized roughly two dozen AI products to help detect and diagnose cancer from mammograms. However, there are currently no billing codes radiologists can use to charge health plans for the use of AI to interpret mammograms. Typically, the federal Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services would introduce new billing codes and private health plans would follow their lead for payment. But that hasn’t happened in this field yet and it’s unclear when or if it will.
CMS didn’t respond to requests for comment.
Thirty-five percent of women who visit a RadNet facility for mammograms pay for the additional AI review, Sorensen said.
Radiology practices don’t handle payment for AI mammography all in the same way.
The practices affiliated with Boston-based Massachusetts General Hospital don’t charge patients for the AI analysis, said Constance Lehman, a professor of radiology at Harvard Medical School who is co-director of the Breast Imaging Research Center at Mass General.
Asking patients to pay “isn’t a model that will support equity,” Lehman said, since only patients who can afford the extra charge will get the enhanced analysis. She said she believes many radiologists would never agree to post a sign listing a charge for AI analysis because it would be off-putting to low-income patients.
Sorensen said RadNet’s goal is to stop charging patients once health plans realize the value of the screening and start paying for it.
Some large trials are underway in the United States, though much of the published research on AI and mammography to date has been done in Europe. There, the standard practice is for two radiologists to read a mammogram, whereas in the States only one radiologist typically evaluates a screening test.
Interim results from the highly regarded MASAI randomized controlled trial of 80,000 women in Sweden found that cancer detection rates were 20% higher in women whose mammograms were read by a radiologist using AI compared with women whose mammograms were read by two radiologists without any AI intervention, which is the standard of care there.
“The MASAI trial was great, but will that generalize to the U.S.? We can’t say,” Lehman said.
In addition, there is a need for “more diverse training and testing sets for AI algorithm development and refinement” across different races and ethnicities, said Christoph Lee, director of the Northwest Screening and Cancer Outcomes Research Enterprise at the University of Washington School of Medicine.
The long shadow of an earlier and largely unsuccessful type of computer-assisted mammography hangs over the adoption of newer AI tools. In the late 1980s and early 1990s, “computer-assisted detection” software promised to improve breast cancer detection. Then the studies started coming in, and the results were often far from encouraging. Using CAD at best provided no benefit, and at worst reduced the accuracy of radiologists’ interpretations, resulting in higher rates of recalls and biopsies.
“CAD was not that sophisticated,” said Robert Smith, senior vice president of early cancer detection science at the American Cancer Society. Artificial intelligence tools today are a whole different ballgame, he said. “You can train the algorithm to pick up things, or it learns on its own.”
Smith said he found it “troubling” that radiologists would charge for the AI analysis.
“There are too many women who can’t afford any out-of-pocket cost” for a mammogram, Smith said. “If we’re not going to increase the number of radiologists we use for mammograms, then these new AI tools are going to be very useful, and I don’t think we can defend charging women extra for them.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Share This Post
-
Ricezempic: is there any evidence this TikTok trend will help you lose weight?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If you spend any time looking at diet and lifestyle content on social media, you may well have encountered a variety of weight loss “hacks”.
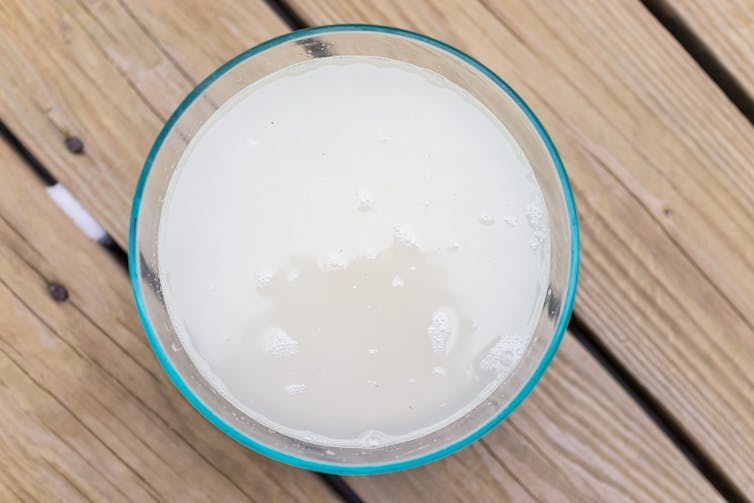
One of the more recent trends is a home-made drink called ricezempic, made by soaking uncooked rice and then straining it to drink the leftover starchy water. Sounds delicious, right?
Its proponents claim it leads to weight loss by making you feel fuller for longer and suppressing your appetite, working in a similar way to the sought-after drug Ozempic – hence the name.
So does this drink actually mimic the weight loss effects of Ozempic? Spoiler alert – probably not. But let’s look at what the evidence tells us.
New Africa/Shutterstock How do you make ricezempic?
While the recipe can vary slightly depending on who you ask, the most common steps to make ricezempic are:
- soak half a cup of white rice (unrinsed) in one cup of warm or hot water up to overnight
- drain the rice mixture into a fresh glass using a strainer
- discard the rice (but keep the starchy water)
- add the juice of half a lime or lemon to the starchy water and drink.
TikTokers advise that best results will happen if you drink this concoction once a day, first thing in the morning, before eating.
The idea is that the longer you consume ricezempic for, the more weight you’ll lose. Some claim introducing the drink into your diet can lead to a weight loss of up to 27 kilograms in two months.
Resistant starch
Those touting ricezempic argue it leads to weight loss because of the resistant starch rice contains. Resistant starch is a type of dietary fibre (also classified as a prebiotic). There’s no strong evidence it makes you feel fuller for longer, but it does have proven health benefits.
Studies have shown consuming resistant starch may help regulate blood sugar, aid weight loss and improve gut health.
Research has also shown eating resistant starch reduces the risk of obesity, diabetes, heart disease and other chronic diseases.
Ricezempic is made by soaking rice in water. Kristi Blokhin/Shutterstock Resistant starch is found in many foods. These include beans, lentils, wholegrains (oats, barley, and rice – particularly brown rice), bananas (especially when they’re under-ripe or green), potatoes, and nuts and seeds (particularly chia seeds, flaxseeds and almonds).
Half a cup of uncooked white rice (as per the ricezempic recipe) contains around 0.6 grams of resistant starch. For optimal health benefits, a daily intake of 15–20 grams of resistant starch is recommended. Although there is no concrete evidence on the amount of resistant starch that leaches from rice into water, it’s likely to be significantly less than 0.6 grams as the whole rice grain is not being consumed.
Ricezempic vs Ozempic
Ozempic was originally developed to help people with diabetes manage their blood sugar levels but is now commonly used for weight loss.
Ozempic, along with similar medications such as Wegovy and Trulicity, is a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist. These drugs mimic the GLP-1 hormone the body naturally produces. By doing so, they slow down the digestive process, which helps people feel fuller for longer, and curbs their appetite.
While the resistant starch in rice could induce some similar benefits to Ozempic (such as feeling full and therefore reducing energy intake), no scientific studies have trialled ricezempic using the recipes promoted on social media.
Ozempic has a long half-life, remaining active in the body for about seven days. In contrast, consuming one cup of rice provides a feeling of fullness for only a few hours. And simply soaking rice in water and drinking the starchy water will not provide the same level of satiety as eating the rice itself.
Other ways to get resistant starch in your diet
There are several ways to consume more resistant starch while also gaining additional nutrients and vitamins compared to what you get from ricezempic.
1. Cooked and cooled rice
Letting cooked rice cool over time increases its resistant starch content. Reheating the rice does not significantly reduce the amount of resistant starch that forms during cooling. Brown rice is preferable to white rice due to its higher fibre content and additional micronutrients such as phosphorus and magnesium.
2. More legumes
These are high in resistant starch and have been shown to promote weight management when eaten regularly. Why not try a recipe that has pinto beans, chickpeas, black beans or peas for dinner tonight?
3. Cooked and cooled potatoes
Cooking potatoes and allowing them to cool for at least a few hours increases their resistant starch content. Fully cooled potatoes are a rich source of resistant starch and also provide essential nutrients like potassium and vitamin C. Making a potato salad as a side dish is a great way to get these benefits.
In a nutshell
Although many people on social media have reported benefits, there’s no scientific evidence drinking rice water or “ricezempic” is effective for weight loss. You probably won’t see any significant changes in your weight by drinking ricezempic and making no other adjustments to your diet or lifestyle.
While the drink may provide a small amount of resistant starch residue from the rice, and some hydration from the water, consuming foods that contain resistant starch in their full form would offer significantly more nutritional benefits.
More broadly, be wary of the weight loss hacks you see on social media. Achieving lasting weight loss boils down to gradually adopting healthy eating habits and regular exercise, ensuring these changes become lifelong habits.
Emily Burch, Accredited Practising Dietitian and Lecturer, Southern Cross University and Lauren Ball, Professor of Community Health and Wellbeing, The University of Queensland
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Daily Stoic – by Ryan Holiday & Stephen Hanselman
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What’s this, a philosophy book in a health and productivity newsletter? Well, look at it this way: Aristotle basically wrote the “How To Win Friends And Influence People” of his day, and Plato before him wrote a book about management.
In this (chiefly modern!) book, we see what the later Stoic philosophers had to say about getting the most out of life—which is also what we’re about, here at 10almonds!
We tend to use the word “stoic” in modern English to refer to a person who is resolute in the face of hardship. The traditional meaning does encompass that, but also means a lot more: a whole, rounded, philosophy of life.
Philosophy in general is not an easy thing into which to “dip one’s toe”. No matter where we try to start, it seems, it turns out there were a thousand other things we needed to read first!
This book really gets around that. The format is:
- There’s a theme for each month
- Each month has one lesson per day
- Each daily lesson starts with some words from a renowned stoic philosopher, and then provides commentary on such
- The commentary provides a jumping-off point and serves as a prompt to actually, genuinely, reflect and apply the ideas.
Unlike a lot of “a year of…” day-by-day books, this is not light reading, by the way, and you are getting a weighty tome for your money.
But, the page-length daily lessons are indeed digestible—which, again, is what we like at 10almonds!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Seven-Day Sleep Prescription – by Dr. Aric Prather
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You probably already know about sleep hygiene. So, what does this book have to offer?
Dr. Aric Prather offers seven days’ worth of adjustments, practices to take up, from when you get up in the morning to when you lay your head down at night.
Some you’ll surely be familiar with, like avoiding blue light and social media at night.
Others, you might not be familiar with, like scheduling 15 minutes for worrying in the daytime. The rationale for this one is that when you find yourself inclined to worry at a time that will keep you awake, you’ll know that you can put off such thoughts to your scheduled “worrying time”. That they’ll be addressed then, and that you can thus sleep soundly meanwhile.
Where the book really comes into its own is in such things as discussing how to not just manage sleep debt, but how to actually use it in your favour.
Nor does Dr. Prather shy away from the truths of our world… That the world these days is not built for us to sleep well. That there are so many other priorities; to get our work done, to succeed and achieve, to pay bills, to support our kids and partners. That so many of these things make plenty of sense in the moment, but catch up with us eventually.
Bottom line: what this book aims to give is a genuinely sustainable approach to sleeping—controlling what we can, and working with what we can’t. If you’d like to have a better relationship with sleep, this book is an excellent choice.
Click here to check out the Seven-Day Sleep Prescription, and improve yours!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Hate Sit-Ups? Try This 10-Minute Standing Abs Routine!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Abdominal muscles are important to many people for aesthetics; they also fulfil the important role of keeping your innards in, as well as being a critical part of core stability (and you cannot have a truly healthy back without healthy abs on the other side). However, not everyone loves sit-ups and their many variations, so here’s an all-standing workout instead:
On your feet!
The exercise are as follows:
- High knees: engage core to work abs; do slow for low impact. Great for speeding up the metabolism. Jog during rest to keep moving.
- Extend & twist: raise arms high, drive them down while raising one leg into a twist. No rest, switch sides immediately.
- Extend & vertical crunch: extend leg back, drive knee forward into a crunch. Swap sides with no breaks.
- Oblique jacks: jump or slow version; targeting the obliques.
- Front toe-touch: engage core for effectiveness.
- Crossover toe-touch: no break; move into this directly from the front toe-touch.
- Wood chop: lift arms up, twist, chop down. Great for obliques. No rest between sides.
- Heisman: step side to side, bringing your other knee up towards the opposite side. Focus on core engagement rather than speed.
- Side leg raise & side bent: raise leg to side with slight bend; works obliques. No rest between sides.
That’s it!
For a visual demonstration, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Is A Visible Six-Pack Obtainable Regardless Of Genetic Predisposition?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: