The Sprout Book – by Doug Evans
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Sprouting seeds are more nutritious than most people think, and “seeds” is also a much broader category than people think. Beyond even chia and sunflower and such, this book bids us remember that onions do not just appear on supermarket shelves fully formed (to give just one example of many); most plants come from seeds and of those, most can be usefully sprouted.
The author, most well-known for his tech companies, here is selling us a very low-tech health kick with very little profit to be found except for our health. By sprouting seeds of many kinds at home, we can enjoy powerful superfoods that are not only better than, but also cheaper than, most supplements.
Nor are the benefits of sprouting things marginal; we’re not talking about a 1–10% increase in bioavailable so much as what’s often a 100–1000% increase.
After explaining the science and giving a primer on sprouting things for oneself, there is a wide selection of recipes, but the biggest benefit of the book is in just getting the reader up-and-running with at-home sprouting.
Bottom line: if you like the idea of letting food be your medicine and even like the idea of essentially growing your own food with zero gardening skills, then this is an excellent book for you.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Nobody’s Sleeping – by Dr. Bijoy John
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Firstly, let’s mention: yes, for the sake of being methodical and comprehensive this book does give the same baseline advice as every other sleep book out there. However, it gives something else, too:
It goes beyond that baseline, to a) give more personalized advice for various demographics (e.g. per age, sex, health conditions, etc) and b) give direction for further personalizing one’s own sleep improvement journey, by troubleshooting and fixing things that may pertain to you very specifically and not to most people.
This means, that if you’re doing “all the right things” but still having sleep-related problems, there is hope and there are more approaches to try.
The style in which this is delivered is very readable, which is good, because if one hasn’t been sleeping well, then chances are that an intellectual challenge would be about as welcome as a physical challenge—that is to say: not at all.
Bottom line: if sleep is not your strength and you would like it to be and all the usual things haven’t yet worked, this book may well help you to overcome the hurdles between you and a good night’s sleep each night.
Click here to check out Nobody’s Sleeping, and refute that title!
Share This Post
-
Stuck in fight-or-flight mode? 5 ways to complete the ‘stress cycle’ and avoid burnout or depression
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Can you remember a time when you felt stressed leading up to a big life event and then afterwards felt like a weight had been lifted? This process – the ramping up of the stress response and then feeling this settle back down – shows completion of the “stress cycle”.
Some stress in daily life is unavoidable. But remaining stressed is unhealthy. Chronic stress increases chronic health conditions, including heart disease and stroke and diabetes. It can also lead to burnout or depression.
Exercise, cognitive, creative, social and self-soothing activities help us process stress in healthier ways and complete the stress cycle.
What does the stress cycle look like?
Scientists and researchers refer to the “stress response”, often with a focus on the fight-or-flight reactions. The phrase the “stress cycle” has been made popular by self-help experts but it does have a scientific basis.
The stress cycle is our body’s response to a stressful event, whether real or perceived, physical or psychological. It could be being chased by a vicious dog, an upcoming exam or a difficult conversation.
The stress cycle has three stages:
- stage 1 is perceiving the threat
- stage 2 is the fight-or-flight response, driven by our stress hormones: adrenaline and cortisol
- stage 3 is relief, including physiological and psychological relief. This completes the stress cycle.
Different people will respond to stress differently based on their life experiences and genetics.
Unfortunately, many people experience multiple and ongoing stressors out of their control, including the cost-of-living crisis, extreme weather events and domestic violence.
Remaining in stage 2 (the flight-or-flight response), can lead to chronic stress. Chronic stress and high cortisol can increase inflammation, which damages our brain and other organs.
When you are stuck in chronic fight-or-flight mode, you don’t think clearly and are more easily distracted. Activities that provide temporary pleasure, such as eating junk food or drinking alcohol are unhelpful strategies that do not reduce the stress effects on our brain and body. Scrolling through social media is also not an effective way to complete the stress cycle. In fact, this is associated with an increased stress response.
Stress and the brain
In the brain, chronic high cortisol can shrink the hippocampus. This can impair a person’s memory and their capacity to think and concentrate.
Chronic high cortisol also reduces activity in the prefrontal cortex but increases activity in the amygdala.
The prefrontal cortex is responsible for higher-order control of our thoughts, behaviours and emotions, and is goal-directed and rational. The amygdala is involved in reflexive and emotional responses. Higher amygdala activity and lower prefrontal cortex activity explains why we are less rational and more emotional and reactive when we are stressed.
There are five types of activities that can help our brains complete the stress cycle. https://www.youtube.com/embed/eD1wliuHxHI?wmode=transparent&start=0 It can help to understand how the brain encounters stress.
1. Exercise – its own complete stress cycle
When we exercise we get a short-term spike in cortisol, followed by a healthy reduction in cortisol and adrenaline.
Exercise also increases endorphins and serotonin, which improve mood. Endorphins cause an elated feeling often called “runner’s high” and have anti-inflammatory effects.
When you exercise, there is more blood flow to the brain and higher activity in the prefrontal cortex. This is why you can often think more clearly after a walk or run. Exercise can be a helpful way to relieve feelings of stress.
Exercise can also increase the volume of the hippocampus. This is linked to better short-term and long-term memory processing, as well as reduced stress, depression and anxiety.
2. Cognitive activities – reduce negative thinking
Overly negative thinking can trigger or extend the stress response. In our 2019 research, we found the relationship between stress and cortisol was stronger in people with more negative thinking.
Higher amygdala activity and less rational thinking when you are stressed can lead to distorted thinking such as focusing on negatives and rigid “black-and-white” thinking.
Activities to reduce negative thinking and promote a more realistic view can reduce the stress response. In clinical settings this is usually called cognitive behaviour therapy.
At home, this could be journalling or writing down worries. This engages the logical and rational parts of our brain and helps us think more realistically. Finding evidence to challenge negative thoughts (“I’ve prepared well for the exam, so I can do my best”) can help to complete the stress cycle.
Journalling could help process stressful events and complete the stress cycle. Shutterstock/Fellers Photography 3. Getting creative – a pathway out of ‘flight or fight’
Creative activities can be art, craft, gardening, cooking or other activities such as doing a puzzle, juggling, music, theatre, dancing or simply being absorbed in enjoyable work.
Such pursuits increase prefrontal cortex activity and promote flow and focus.
Flow is a state of full engagement in an activity you enjoy. It lowers high-stress levels of noradrenaline, the brain’s adrenaline. When you are focussed like this, the brain only processes information relevant to the task and ignores non-relevant information, including stresses.
4. Getting social and releasing feel-good hormones
Talking with someone else, physical affection with a person or pet and laughing can all increase oxytocin. This is a chemical messenger in the brain that increases social bonding and makes us feel connected and safe.
Laughing is also a social activity that activates parts of the limbic system – the part of the brain involved in emotional and behavioural responses. This increases endorphins and serotonin and improves our mood.
5. Self-soothing
Breathing exercises and meditation stimulate the parasympathetic nervous system (which calms down our stress responses so we can “reset”) via the vagus nerves, and reduce cortisol.
A good cry can help too by releasing stress energy and increasing oxytocin and endorphins.
Emotional tears also remove cortisol and the hormone prolactin from the body. Our prior research showed cortisol and prolactin were associated with depression, anxiety and hostility.
Getting moving can help with stress and its effects on the brain. Shutterstock/Jaromir Chalabala Action beats distraction
Whether it’s watching a funny or sad movie, exercising, journalling, gardening or doing a puzzle, there is science behind why you should complete the stress cycle.
Doing at least one positive activity every day can also reduce our baseline stress level and is beneficial for good mental health and wellbeing.
Importantly, chronic stress and burnout can also indicate the need for change, such as in our workplaces. However, not all stressful circumstances can be easily changed. Remember help is always available.
If you have concerns about your stress or health, please talk to a doctor.
If this article has raised issues for you, or if you’re concerned about someone you know, call Lifeline on 13 11 14 or Kids Helpline on 1800 55 1800.
Theresa Larkin, Associate professor of Medical Sciences, University of Wollongong and Susan J. Thomas, Associate professor in Mental Health and Behavioural Science, University of Wollongong
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Do You Believe In Magic? – by Dr. Paul Offit
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Here at 10almonds, we like to examine and present the science wherever it leads, so this book was an interesting read.
Dr. Offit, himself a much-decorated vaccine research scientist, and longtime enemy of the anti-vax crowd, takes aim at alternative therapies in general, looking at what does work (and how), and what doesn’t (and what harm it can cause).
The style of the book is largely polemic in tone, but there’s lots of well-qualified information and stats in here too. And certainly, if there are alternative therapies you’ve left unquestioned, this book will probably prompt questions, at the very least.
And science, of course, is about asking questions, and shouldn’t be afraid of such! Open-minded skepticism is a key starting point, while being unafraid to actually reach a conclusion of “this is probably [not] so”, when and if that’s where the evidence brings us. Then, question again when and if new evidence comes along.
To that end, Dr. Offit does an enthusiastic job of looking for answers, and presenting what he finds.
If the book has downsides, they are primarily twofold:
- He is a little quick to dismiss the benefits of a good healthy diet, supplemented or otherwise.
- His keenness here seems to step from a desire to ensure people don’t skip life-saving medical treatments in the hope that their diet will cure their cancer (or liver disease, or be it what it may), but in doing so, he throws out a lot of actually good science.
- He—strangely—lumps menopausal HRT in with alternative therapies, and does the exact same kind of anti-science scaremongering that he rails against in the rest of the book.
- In his defence, this book was published ten years ago, and he may have been influenced by a stack of headlines at the time, and a popular celebrity endorsement of HRT, which likely put him off it.
Bottom line: there’s something here to annoy everyone—which makes for stimulating reading.
Click here to check out Do You Believe In Magic, and expand your knowledge!
Share This Post
- He is a little quick to dismiss the benefits of a good healthy diet, supplemented or otherwise.
Related Posts
-
Tastes from our past can spark memories, trigger pain or boost wellbeing. Here’s how to embrace food nostalgia
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Have you ever tried to bring back fond memories by eating or drinking something unique to that time and place?
It could be a Pina Colada that recalls an island holiday? Or a steaming bowl of pho just like the one you had in Vietnam? Perhaps eating a favourite dish reminds you of a lost loved one – like the sticky date pudding Nanna used to make?
If you have, you have tapped into food-evoked nostalgia.
As researchers, we are exploring how eating and drinking certain things from your past may be important for your mood and mental health.
Halfpoint/Shutterstock Bittersweet longing
First named in 1688 by Swiss medical student, Johannes Hoffer, nostalgia is that bittersweet, sentimental longing for the past. It is experienced universally across different cultures and lifespans from childhood into older age.
But nostalgia does not just involve positive or happy memories – we can also experience nostalgia for sad and unhappy moments in our lives.
In the short and long term, nostalgia can positively impact our health by improving mood and wellbeing, fostering social connection and increasing quality of life. It can also trigger feelings of loneliness or meaninglessness.
We can use nostalgia to turn around a negative mood or enhance our sense of self, meaning and positivity.
Research suggests nostalgia alters activity in the brain regions associated with reward processing – the same areas involved when we seek and receive things we like. This could explain the positive feelings it can bring.
Nostalgia can also increase feelings of loneliness and sadness, particularly if the memories highlight dissatisfaction, grieving, loss, or wistful feelings for the past. This is likely due to activation of brain areas such as the amygdala, responsible for processing emotions and the prefrontal cortex that helps us integrate feelings and memories and regulate emotion.
How to get back there
There are several ways we can trigger or tap into nostalgia.
Conversations with family and friends who have shared experiences, unique objects like photos, and smells can transport us back to old times or places. So can a favourite song or old TV show, reunions with former classmates, even social media posts and anniversaries.
What we eat and drink can trigger food-evoked nostalgia. For instance, when we think of something as “comfort food”, there are likely elements of nostalgia at play.
Foods you found comforting as a child can evoke memories of being cared for and nurtured by loved ones. The form of these foods and the stories we tell about them may have been handed down through generations.
Food-evoked nostalgia can be very powerful because it engages multiple senses: taste, smell, texture, sight and sound. The sense of smell is closely linked to the limbic system in the brain responsible for emotion and memory making food-related memories particularly vivid and emotionally charged.
But, food-evoked nostalgia can also give rise to negative memories, such as of being forced to eat a certain vegetable you disliked as a child, or a food eaten during a sad moment like a loved ones funeral. Understanding why these foods evoke negative memories could help us process and overcome some of our adult food aversions. Encountering these foods in a positive light may help us reframe the memory associated with them.
Just like mum used to make. Food might remind you of the special care you received as a child. Galina Kovalenko/Shutterstock What people told us about food and nostalgia
Recently we interviewed eight Australians and asked them about their experiences with food-evoked nostalgia and the influence on their mood. We wanted to find out whether they experienced food-evoked nostalgia and if so, what foods triggered pleasant and unpleasant memories and feelings for them.
They reported they could use foods that were linked to times in their past to manipulate and influence their mood. Common foods they described as particularly nostalgia triggering were homemade meals, foods from school camp, cultural and ethnic foods, childhood favourites, comfort foods, special treats and snacks they were allowed as children, and holiday or celebration foods. One participant commented:
I guess part of this nostalgia is maybe […] The healing qualities that food has in mental wellbeing. I think food heals for us.
Another explained
I feel really happy, and I guess fortunate to have these kinds of foods that I can turn to, and they have these memories, and I love the feeling of nostalgia and reminiscing and things that remind me of good times.
Yorkshire pudding? Don’t mind if I do. Rigsbyphoto/Shutterstock Understanding food-evoked nostalgia is valuable because it provides us with an insight into how our sensory experiences and emotions intertwine with our memories and identity. While we know a lot about how food triggers nostalgic memories, there is still much to learn about the specific brain areas involved and the differences in food-evoked nostalgia in different cultures.
In the future we may be able to use the science behind food-evoked nostalgia to help people experiencing dementia to tap into lost memories or in psychological therapy to help people reframe negative experiences.
So, if you are ever feeling a little down and want to improve your mood, consider turning to one of your favourite comfort foods that remind you of home, your loved ones or a holiday long ago. Transporting yourself back to those times could help turn things around.
Megan Lee, Senior Teaching Fellow, Psychology, Bond University; Doug Angus, Assistant Professor of Psychology, Bond University, and Kate Simpson, Sessional academic, Bond University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Tech Bliss – by Clo S., MSc.
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The popular idea of a “digital detox” is simple enough, “just unplug!”, they say.
But here in the real world, not only is that often not practical for many of us, it may not always even be entirely desirable. The Internet (and our devices with all their bells and whistles) can be a source of education, joy, and connection!
So, how to find out what’s good for us and what’s not, in our daily digital practices? Clo. S. has answers… Or rather, experiments for us to do and find out for ourselves.
These experiments range from the purely practical “try this to streamline your experience” to the more personal “how does this thing make you feel?”. A lot of the experiments will be performed via your digital devices—some, without! Others are about online interpersonal dynamics, be they one-on-one or navigating a world in which it seems everyone is out to get us, our outrage, and/or our money. Still yet others are about optimizing what you do get from the parts of your digital experience that are enriching for you.
As the title suggests, there are 30 experiments, and it’s not a stretch to do them one per day for a month. But, as the author notes, it’s by no means necessary to do them like that; it’s a workbook and reference guide, not a to-do list!
(On the topic of it being a reference guide…There’s also an extensive tools directory towards the end!)
In short: this is a great book for optimizing your online experience—whatever that might mean for you personally; you can decide for yourself along the way!
Click here to get a copy of Tech Bliss: 30 Experiments For Your Digital Wellness today!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Vaping: A Lot Of Hot Air?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Vaping: A Lot Of Hot Air?
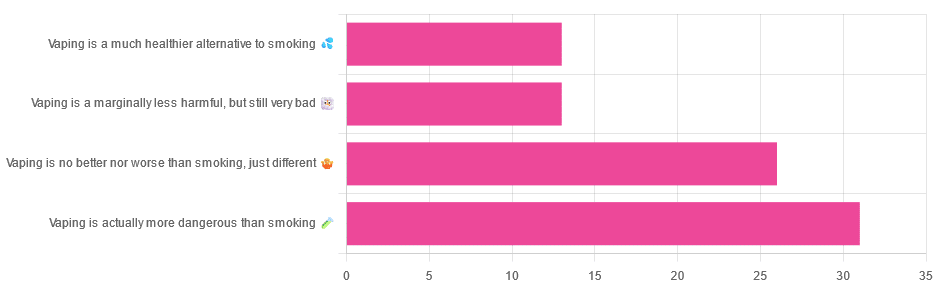
Yesterday, we asked you for your (health-related) opinions on vaping, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- A little over a third of respondents said it’s actually more dangerous than smoking
- A little under a third of respondents said it’s no better nor worse, just different
- A little over 10% of respondents said it’s marginally less harmful, but still very bad
- A little over 10% of respondents said it’s a much healthier alternative to smoking
So what does the science say?
Vaping is basically just steam inhalation, plus the active ingredient of your choice (e.g. nicotine, CBD, THC, etc): True or False?
False! There really are a lot of other chemicals in there.
And “chemicals” per se does not necessarily mean evil green glowing substances that a comicbook villain would market, but there are some unpleasantries in there too:
- Potential harmful health effects of inhaling nicotine-free shisha-pen vapor: a chemical risk assessment of the main components propylene glycol and glycerol
- Inflammatory and Oxidative Responses Induced by Exposure to Commonly Used e-Cigarette Flavoring Chemicals and Flavored e-Liquids without Nicotine
So, the substrate itself can cause irritation, and flavorings (with cinnamaldehyde, the cinnamon flavoring, being one of the worst) can really mess with our body’s inflammatory and oxidative responses.
Vaping can cause “popcorn lung”: True or False?
True and False! Popcorn lung is so-called after it came to attention when workers at a popcorn factory came down with it, due to exposure to diacetyl, a chemical used there.
That chemical was at that time also found in most vapes, but has since been banned in many places, including the US, Canada, the EU and the UK.
Vaping is just as bad as smoking: True or False?
False, per se. In fact, it’s recommended as a means of quitting smoking, by the UK’s famously thrifty NHS, that absolutely does not want people to be sick because that costs money:
Of course, the active ingredients (e.g. nicotine, in the assumed case above) will still be the same, mg for mg, as they are for smoking.
Vaping is causing a health crisis amongst “kids nowadays”: True or False?
True—it just happens to be less serious on a case-by-case basis to the risks of smoking.
However, it is worth noting that the perceived harmlessness of vapes is surely a contributing factor in their widespread use amongst young people—decades after actual smoking (thankfully) went out of fashion.
On the other hand, there’s a flipside to this:
Flavored vape restrictions lead to higher cigarette sales
So, it may indeed be the case of “the lesser of two evils”.
Want to know more?
For a more in-depth science-ful exploration than we have room for here…
BMJ | Impact of vaping on respiratory health
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: