Tasty Tabbouleh with Tahini
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Tabbouleh is a salad, but it’s not “just a salad”. It’s a special kind of salad that’s as exciting for the tastebuds as it is healthy for the body and brain. Its core ingredients have been traditional for about a dozen generations, and seasonings are always a personal matter (not to mention that Lebanese tabbouleh-makers centuries ago might not have used miso and nooch, as we will today), but the overall feel of the Gestalt of tabbouleh seasonings remains the same, and this recipe is true to that.
You will need
For the tabbouleh:
- 1 cup bulgur wheat
- 1 cup plum tomatoes, chopped
- 1 cucumber, peeled and chopped (add the peel to a jug of water and put it in the fridge; this will be refreshing cucumber water later!)
- 1 cup chickpeas, cooked without salt
- 1/2 cup parsley, chopped
- 1/2 cup mint, chopped
- 2 spring onions, finely chopped
- 2oz fresh lemon juice
- 1 tsp white miso paste
- 1 tsp garlic powder
- 1 tsp ground cumin
- 1 tsp ground celery seeds
- 1 tsp ground nigella seeds
- 1 tsp ground black pepper
- 1 tsp MSG, or 1/2 tsp low sodium salt (you can find it in supermarkets, the sodium chloride is cut with potassium chloride to make it have less sodium and more potassium)
- 1 tbsp nutritional yeast (nooch), ground (it comes in flakes; you will have to grind it in a spice grinder or with a pestle and mortar)
For the tahini sauce:
- 3 garlic cloves, crushed
- 3 tbsp tahini
- 1 tbsp fresh lemon juice
- 1 tbsp white miso paste
- 1 tsp ground cumin
To serve:
- A generous helping of leafy greens; we recommend collard greens, but whatever works for you is good; just remember that dark green is best. Consider cavolo nero, or even kale if that’s your thing, but to be honest this writer doesn’t love kale
- 1 tsp coarsely ground nigella seeds
- Balsamic vinegar, ideally aged balsamic vinegar (this is thicker and sweeter, but unlike most balsamic vinegar reductions, doesn’t have added sugar).
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Rinse the bulgur wheat and then soak it in warm water. There is no need to boil it; the warm water is enough to soften it and you don’t need to cook it (bulgur wheat has already been parboiled before it got to you).
2) While you wait, take a small bowl and mix the rest of the ingredients from the tabbouleh section (so, the lemon juice, miso paste, and all those ground spices and MSG/salt and ground nutritional yeast); you’re making a dressing out of all the ingredients here.
3) When the bulgur wheat is soft (expect it to take under 15 minutes), drain it and put it in a big bowl. Add the tomatoes, cucumber, chickpeas, parsley, mint, and spring onions. This now technically qualifies as tabbouleh already, but we’re not done.
4) Add the dressing to the tabbouleh and mix thoroughly but gently (you don’t want to squash the tomatoes, cucumber, etc). Leave it be for at least 15 minutes while the flavors blend.
5) Take the “For the tahini sauce” ingredients (all of them) and blend them with 4 oz water, until smooth. You’re going to want to drizzle this sauce, so if the consistency is too thick for drizzling, add a little more water and/or lemon juice (per your preference), 1 tbsp at a time.
6) Roughly chop the leafy greens and put them in a bowl big enough for the tabbouleh to join them there. The greens will serve as a bed for the tabbouleh itself.
7) Drizzle the tahini over the tabbouleh, and drizzle a little of the aged balsamic vinegar too.
Enjoy!

Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Vagus Nerve’s Power for Weight Loss
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Arun Dhir is a university lecturer, a gastrointestinal surgeon, an author, and a yoga and meditation instructor, and he has this to say:
Gut feelings
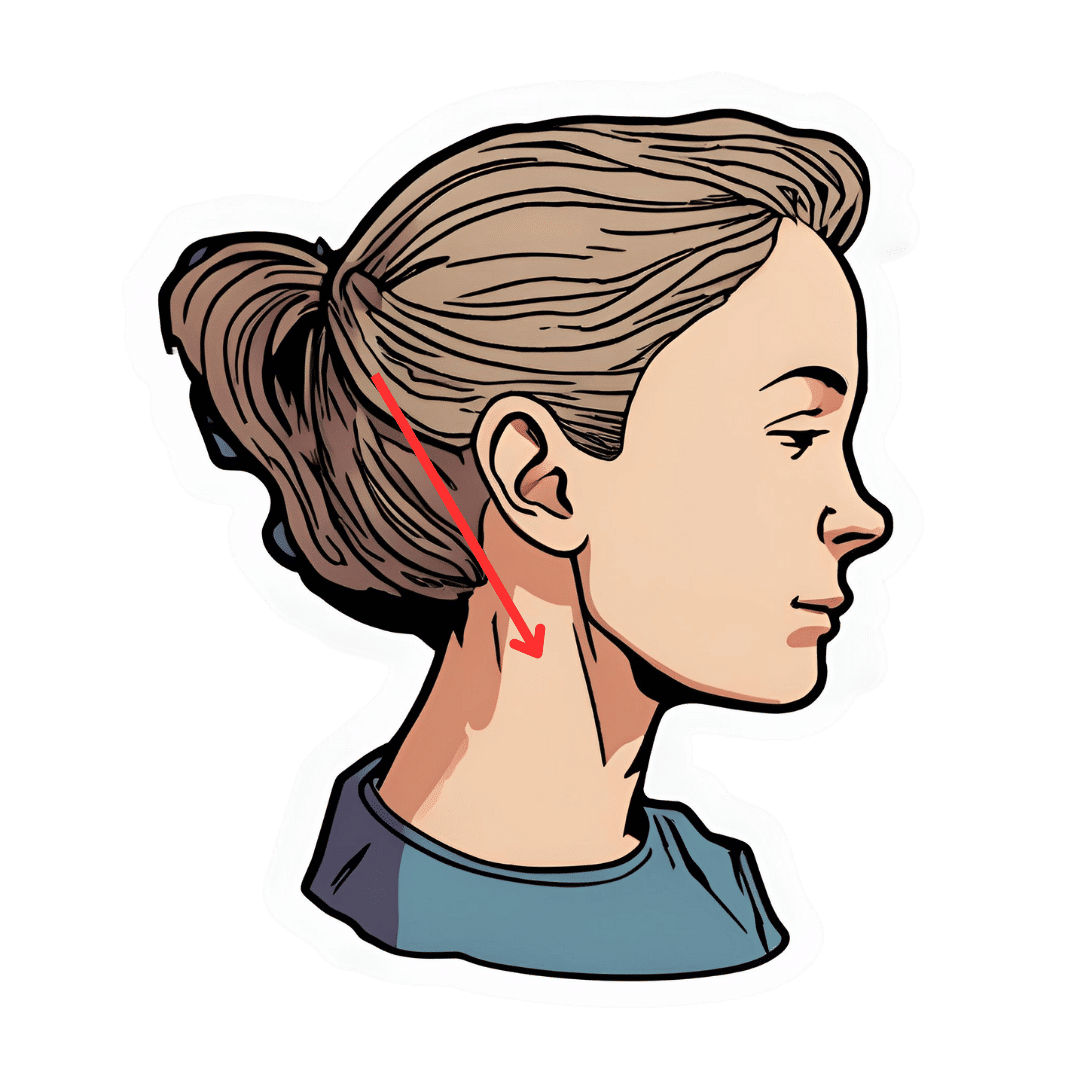
The vagus nerve is the 10th cranial nerve, also known as “vagus” (“the wanderer”), because it travels from the brain to many other body parts, including the ears, throat, heart, respiratory system, gut, pancreas, liver, and reproductive system. It’s no surprise then, that it plays a key role in brain-gut communication and metabolism regulation.
The vagus nerve is part of the parasympathetic nervous system, responsible for rest, digestion, and counteracting the stress response. Most signals through the vagus nerve travel from the gut to the brain, though there is communication in both directions.
You may be beginning to see how this works and its implications for weight management: the vagus nerve senses metabolites from the liver, pancreas, and small intestine, and regulates insulin production by stimulating beta cells in the pancreas, which is important for avoiding/managing insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome in general.
Dr. Dhir cites a study in which vagus nerve stimulation (originally used for treating epilepsy and depression) was shown to cause unintentional weight loss (6-11%) in patients, revealing a link to weight management. Of course, that is quite a specific sample, so more research is needed to say for sure, but because the principle is very sound and the mechanism of action is clear, it’s not being viewed as a controversial conclusion.
As for how get these benefits, here are seven ways:
- Cold water on the face: submerge your face in cold water in the morning while holding water in your mouth, or cover your face with a cold wet washcloth (while holding your breath please; no need to waterboard yourself!), which activates the “mammalian dive response” in which your body activates the parasympathetic nervous system in order to remain calm and thus survive for longer underwater
- Alternate hot and cold showers: switch between hot and cold water during showers for 10-second intervals; this creates eustress and activates the process of hormesis, improving your overall stress management and reducing any chronic stress response you may otherwise have going on
- Humming and gargling: the vibrations in the throat stimulate the nearby vagus nerve
- Deep breathing (pranayama): yoga breathing exercises, especially combined with somatic exercises such as the sun salutation, can stimulate the vagus nerve
- Intermittent fasting: helps recalibrate the metabolism and indirectly improves vagus nerve function
- Massage and acupressure: stimulates lymphatic channels and the vagus nerve
- Long walks in nature (“forest bathing”): helps trigger relaxation in general
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
The Vagus Nerve (And How You Can Make Use Of It)
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Top 10 Foods That Promote Lymphatic Drainage and Lymph Flow
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Melissa Gallagher, a naturopath by profession, recommends the following 10 foods that she says promote lymphatic drainage and lymph flow, as well as the below-mentioned additional properties:
Ginger
Ginger is a natural anti-inflammatory, which we wrote about here:
Ginger Does A Lot More Than You Think
Turmeric
Turmeric is another natural anti-inflammatory, which we wrote about here:
Why Curcumin (Turmeric) Is Worth Its Weight In Gold
Garlic
Garlic is—you guessed it—another natural anti-inflammatory which we wrote about here:
The Many Health Benefits Of Garlic
Pineapple
Pineapple contains a collection of enzymes collectively called bromelain—which is a unique kind of anti-inflammatory, and which we have written about here:
Bromelain vs Inflammation & Much More
Citrus
Citrus fruits like oranges, lemons, and grapefruits are rich in vitamin C, which can help support the immune system in general.
Cranberry
Cranberries contain antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds, which we wrote about here:
Health Benefits Of Cranberries (But: You’d Better Watch Out)
The video also explains how cranberry bioactives inhibit adipogenesis and reduces fat congestion in your lymphatic system.
Dandelion Tea
Dandelion is a natural diuretic and anti-inflammatory herb, which we’ve not written about yet!
Nettle Tea
Nettle is a natural diuretic and anti-inflammatory herb, which we’ve also not written about yet!
Healthy Fats
Healthy fats like avocado, nuts, and olive oil can help reduce inflammation and support the immune system.
Fermented Foods
Fermented foods, such as kimchi and sauerkraut, contain probiotics that can improve gut health, which in turn boosts the immune system. You can read all about it here:
Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
Want the full explanation? Here’s the video:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
How was the video? If you’ve discovered any great videos yourself that you’d like to share with fellow 10almonds readers, then please do email them to us!
Share This Post
-
No More Aches/Tripping When Walking: Strengthen This Oft-Neglected Muscle
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Aches and pains while walking (in the feet, shins, and/or knees), as well as fatigue, are actually mostly about the oft-neglected tibialis anterior muscle.
Fortunately, it’s quite easy to strengthen if you know how:
All about the tib
The tibialis anterior is located at the front of the shin. It lifts the toes when walking, preventing trips and stumbles. Weakness in this muscle can cause fatigue as other muscles compensate, tripping as feet catch the floor, and/or general instability while walking.
Happily, there is an easy exercise to do that gives results quite quickly:
Steps:
- Stand with back and shoulders against a wall, feet 12 inches away.
- Slightly bend knees and keep posture relaxed.
- Lift toes off the ground, hold for a few seconds, then lower.
- Repeat for 10–15 reps.
To increase difficulty:
- Step further away from the wall for more ankle movement.
- Perform a “Tib Plank” by lifting hips off the wall and keeping knees straight.
It’s recommended to do 3 sets per day, with 1-minute rests between.
For more on all of this plus visual demonstrations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
The Secret to Better Squats: Foot, Knee, & Ankle Mobility
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
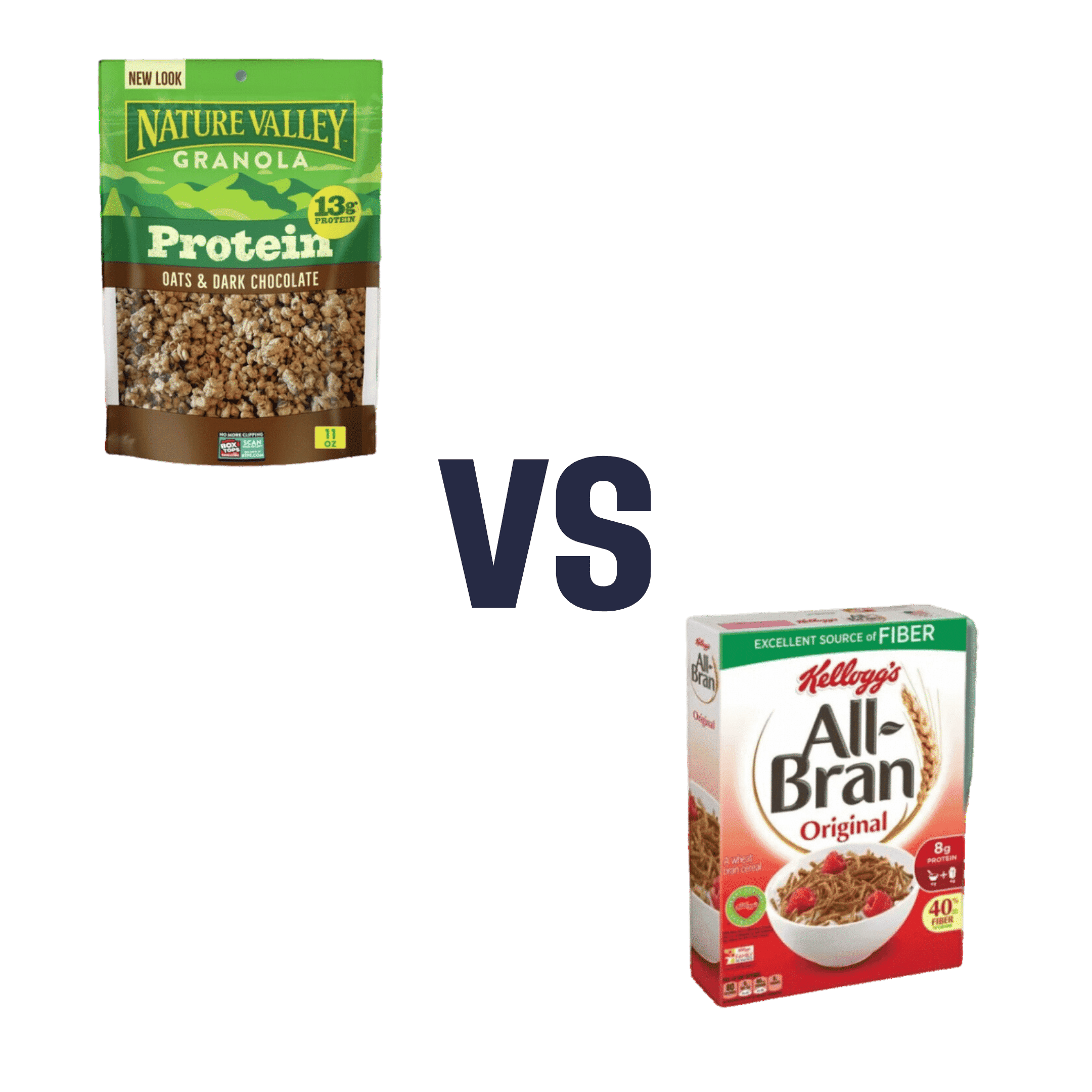
Nature Valley Protein Granola vs Kellog’s All-Bran – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing Nature Valley Protein Granola to Kellog’s All-Bran, we picked the All-Bran.
Why?
While the Protein Granola indeed contains more protein (13g/cup, compared to 5g/cup), it also contains three times as much sugar (18g/cup, compared to 9g/cup) and only ⅓ as much fiber (4g/cup, compared to 12g/cup)
Given that fiber is what helps our bodies to absorb sugar more gently (resulting in fewer spikes), this is extremely important, especially since 18g of sugar in one cup of Protein Granola is already most of the recommended daily allowance, all at once!
For reference: the AHA recommends no more than 25g added sugar for women, or 32g for men
Hence, we went for the option with 3x as much fiber and ⅓ of the sugar, the All-Bran.
For more about keeping blood sugars stable, see:
10 Ways To Balance Blood Sugars
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
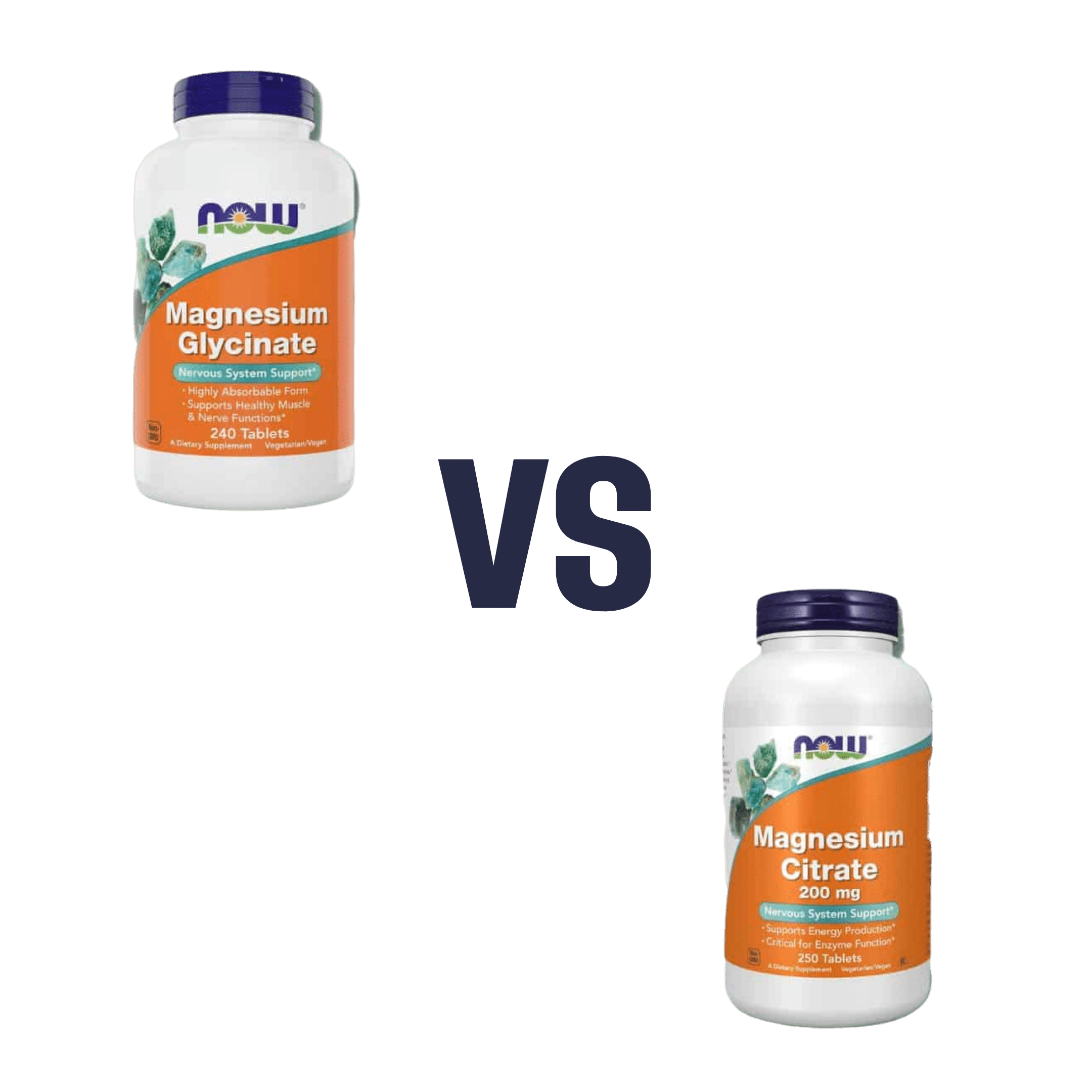
Magnesium Glycinate vs Magnesium Citrate – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing magnesium glycinate to magnesium citrate, we picked the citrate.
Why?
Both are fine sources of magnesium, a nutrient in which it’s very common to be deficient—a lot of people don’t eat many leafy greens, beans, nuts, and so forth that contain it.
A quick word on a third contender we didn’t include here: magnesium oxide is probably the most widely-sold magnesium supplement because it’s cheapest to make. It also has woeful bioavailability, to the point that there seems to be negligible benefit to taking it. So we don’t recommend that.
Magnesium glycinate and magnesium citrate are both absorbed well, but magnesium citrate is the most well-absorbed form of magnesium supplement.
In terms of the relative merits of the glycine or the citric acid (the “other part” of magnesium glycinate and magnesium citrate, respectively), both are also great nutrients, but the amount delivered with the magnesium is quite small in each case, and so there’s nothing here to swing it one way or the other.
For this reason, we went with the magnesium citrate, as the most readily bioavailable!
Want to try them out?
Here they are on Amazon:
Magnesium glycinate | Magnesium citrate
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
In Praise of Slowness – by Carl Honoré
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This isn’t just about “taking the time to smell the roses” although yes, that too. Rather, it’s mostly about looking at what drives us to speed everything up in the first place, and correcting where appropriate.
If your ancestors had time to eat fruit and lie in the sun, then why, with all of modern technology now available, are you harangued 16+ hours a day by the pressures of universally synchronized timepieces?
Honoré places a lot of the blame squarely on the industrial revolution; whereas previously our work would be limited by craftsmen who take a year to complete something, or the pace of animals in a field, now humans had to keep up with the very machines that were supposed to serve us—and it’s only got worse from there.
This book takes a tour of many areas affected by this artificial “need for speed”, and how it harms not just our work-life balance, but also our eating habits, the medical attention we get, and even our love lives.
The prescription is deceptively simple, “slow down”. But Honoré dedicates the final three chapters of the book to the “how” of this, when of course there’s a lot the outside world will not accommodate—but where we can slow down, there’s good to be gained.
Bottom line: if you’ve ever felt that you could get all of your life into order if you could just pause the outside world for a week or two, this is the book for you.
Click here to check out In Praise of Slowness, and make time for what matters most!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: