The Cold Truth About Respiratory Infections
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Pathogens That Came In From The Cold
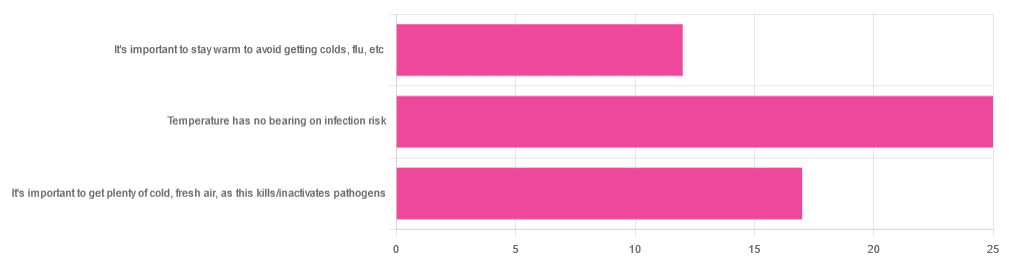
Yesterday, we asked you about your climate-themed policy for avoiding respiratory infections, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of answers:
- About 46% of respondents said “Temperature has no bearing on infection risk”
- About 31% of respondents said “It’s important to get plenty of cold, fresh air, as this kills/inactivates pathogens”
- About 22% of respondents said “It’s important to stay warm to avoid getting colds, flu, etc”
Some gave rationales, including…
For “stay warm”:
❝Childhood lessons❞
For “get cold, fresh air”:
❝I just feel that it’s healthy to get fresh air daily. Whether it kills germs, I don’t know❞
For “temperature has no bearing”:
❝If climate issue affected respiratory infections, would people in the tropics suffer more than those in colder climates? Pollutants may affect respiratory infections, but I doubt just temperature would do so.❞
So, what does the science say?
It’s important to stay warm to avoid getting colds, flu, etc: True or False?
False, simply. Cold weather does increase the infection risk, but for reasons that a hat and scarf won’t protect you from. More on this later, but for now, let’s lay to rest the idea that bodily chilling will promote infection by cold, flu, etc.
In a small-ish but statistically significant study (n=180), it was found that…
❝There was no evidence that chilling caused any acute change in symptom scores❞
Read more: Acute cooling of the feet and the onset of common cold symptoms
Note: they do mention in their conclusion that chilling the feet “causes the onset of cold symptoms in about 10% of subjects who are chilled”, but the data does not support that conclusion, and the only clear indicator is that people who are more prone to colds generally, were more prone to getting a cold after a cold water footbath.
In other words, people who were more prone to colds remained more prone to colds, just the same.
It’s important to get plenty of cold, fresh air, as this kills/inactivates pathogens: True or False?
Broadly False, though most pathogens do have an optimal operating temperature that (for obvious reasons) is around normal human body temperature.
However, given that they don’t generally have to survive outside of a host body for long to get passed on, the fact that the pathogens may be a little sluggish in the great outdoors will not change the fact that they will be delighted by the climate in your respiratory tract as soon as you get back into the warm.
With regard to the cold air not being a reliable killer/inactivator of pathogens, we call to the witness stand…
Polar Bear Dies From Bird Flu As H5N1 Spreads Across Globe
(it was found near Utqiagvik, one of the northernmost communities in Alaska)
Because pathogens like human body temperature, raising the body temperature is a way to kill/inactivate them: True or False?
True! Unfortunately, it’s also a way to kill us. Because we, too, cannot survive for long above our normal body temperature.
So, for example, bundling up warmly and cranking up the heating won’t necessarily help, because:
- if the temperature is comfortable for you, it’s comfortable for the pathogen
- if the temperature is dangerous to the pathogen, it’s dangerous to you too
This is why the fever response evolved, and/but why many people with fevers die anyway. It’s the body’s way of playing chicken with the pathogen, challenging “guess which of us can survive this for longer!”
Temperature has no bearing on infection risk: True or False?
True and/or False, circumstantially. This one’s a little complex, but let’s break it down to the essentials.
- Temperature has no direct effect, for the reasons we outlined above
- Temperature is often related to humidity, which does have an effect
- Temperature does tend to influence human behavior (more time spent in open spaces with good ventilation vs more time spent in closed quarters with poor ventilation and/or recycled air), which has an obvious effect on transmission rates
The first one we covered, and the third one is self-evident, so let’s look at the second one:
Temperature is often related to humidity, which does have an effect
When the environmental temperature is warmer, water droplets in the air will tend to be bigger, and thus drop to the ground much more quickly.
When the environmental temperature is colder, water droplets in the air will tend to be smaller, and thus stay in the air for longer (along with any pathogens those water droplets may be carrying).
Some papers on the impact of this:
- Cold temperature and low humidity are associated with increased occurrence of respiratory tract infections
- A Decrease in Temperature and Humidity Precedes Human Rhinovirus Infections in a Cold Climate
So whatever temperature you like to keep your environment, humidity is a protective factor against respiratory infections, and dry air is a risk factor.
So, for example:
- If the weather doesn’t suit having good ventilation, a humidifier is a good option
- Being in an airplane is one of the worst places to be for this, outside of a hospital
Don’t have a humidifier? Here’s an example product on Amazon, but by all means shop around.
A crock pot with hot water in and the lid off is also a very workable workaround too
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Why Has Nobody Told Me This Before? – by Dr. Julie Smith
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Superficially, this can be called a “self-help” book, but that undersells it rather. It’s a professionally-written (as in, by a professional psychologist) handbook full of resources. Its goal? Optimizing your mental health to help you stay resilient no matter what life throws your way.
While the marketing of this book is heavily centered around Dr. Smith’s Internet Celebrity™ status, a lot of her motivation for writing it seems to be precisely so that she can delve deeper into the ideas that her social media “bites” don’t allow room for.
Many authors of this genre pad their chapters with examples; there are no lengthy story-telling asides here, and her style doesn’t need them. She knows her field well, and knows well how to communicate the ideas that may benefit the reader.
The main “meat” of the book? Tips, tricks, guides, resources, systems, flowcharts, mental frameworks, and “if all else fails, do this” guidance. The style of the book is clear and simple, with very readable content that she keeps free from jargon without “dumbing down” or patronizing the reader.
All in all, a fine set of tools for anyone’s “getting through life” toolbox.
Get Your Personal Copy Of “Why Has Nobody Told Me This Before?” on Amazon Now!
Share This Post
-
I’m Moving Forward and Facing the Uncertainty of Aging
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It takes a lot of courage to grow old.
I’ve come to appreciate this after conversations with hundreds of older adults over the past eight years for nearly 200 “Navigating Aging” columns.
Time and again, people have described what it’s like to let go of certainties they once lived with and adjust to new circumstances.
These older adults’ lives are filled with change. They don’t know what the future holds except that the end is nearer than it’s ever been.
And yet, they find ways to adapt. To move forward. To find meaning in their lives. And I find myself resolving to follow this path as I ready myself for retirement.
Patricia Estess, 85, of the Brooklyn borough of New York City spoke eloquently about the unpredictability of later life when I reached out to her as I reported a series of columns on older adults who live alone, sometimes known as “solo agers.”
Estess had taken a course on solo aging. “You realize that other people are in the same boat as you are,” she said when I asked what she had learned. “We’re all dealing with uncertainty.”
Consider the questions that older adults — whether living with others or by themselves — deal with year in and out: Will my bones break? Will my thinking skills and memory endure? Will I be able to make it up the stairs of my home, where I’m trying to age in place?
Will beloved friends and family members remain an ongoing source of support? If not, who will be around to provide help when it’s needed?
Will I have enough money to support a long and healthy life, if that’s in the cards? Will community and government resources be available, if needed?
It takes courage to face these uncertainties and advance into the unknown with a measure of equanimity.
“It’s a question of attitude,” Estess told me. “I have honed an attitude of: ‘I am getting older. Things will happen. I will do what I can to plan in advance. I will be more careful. But I will deal with things as they come up.’”
For many people, becoming old alters their sense of identity. They feel like strangers to themselves. Their bodies and minds aren’t working as they used to. They don’t feel the sense of control they once felt.
That requires a different type of courage — the courage to embrace and accept their older selves.
Marna Clarke, a photographer, spent more than a dozen years documenting her changing body and her life with her partner as they grew older. Along the way, she learned to view aging with new eyes.
“Now, I think there’s a beauty that comes out of people when they accept who they are,” she told me in 2022, when she was 70, just before her 93-year-old husband died.
Arthur Kleinman, a Harvard professor who’s now 83, gained a deeper sense of soulfulness after caring for his beloved wife, who had dementia and eventually died, leaving him grief-stricken.
“We endure, we learn how to endure, how to keep going. We’re marked, we’re injured, we’re wounded. We’re changed, in my case for the better,” he told me when I interviewed him in 2019. He was referring to a newfound sense of vulnerability and empathy he gained as a caregiver.
Herbert Brown, 68, who lives in one of Chicago’s poorest neighborhoods, was philosophical when I met him at his apartment building’s annual barbecue in June.
“I was a very wild person in my youth. I’m surprised I’ve lived this long,” he said. “I never planned on being a senior. I thought I’d die before that happened.”
Truthfully, no one is ever prepared to grow old, including me. (I’m turning 70 in February.)
Chalk it up to denial or the limits of imagination. As May Sarton, a writer who thought deeply about aging, put it so well: Old age is “a foreign country with an unknown language.” I, along with all my similarly aged friends, are surprised we’ve arrived at this destination.
For me, 2025 is a turning point. I’m retiring after four decades as a journalist. Most of that time, I’ve written about our nation’s enormously complex health care system. For the past eight years, I’ve focused on the unprecedented growth of the older population — the most significant demographic trend of our time — and its many implications.
In some ways, I’m ready for the challenges that lie ahead. In many ways, I’m not.
The biggest unknown is what will happen to my vision. I have moderate macular degeneration in both eyes. Last year, I lost central vision in my right eye. How long will my left eye pick up the slack? What will happen when that eye deteriorates?
Like many people, I’m hoping scientific advances outpace the progression of my condition. But I’m not counting on it. Realistically, I have to plan for a future in which I might become partially blind.
It’ll take courage to deal with that.
Then, there’s the matter of my four-story Denver house, where I’ve lived for 33 years. Climbing the stairs has helped keep me in shape. But that won’t be possible if my vision becomes worse.
So my husband and I are taking a leap into the unknown. We’re renovating the house, installing an elevator, and inviting our son, daughter-in-law, and grandson to move in with us. Going intergenerational. Giving up privacy. In exchange, we hope our home will be full of mutual assistance and love.
There are no guarantees this will work. But we’re giving it a shot.
Without all the conversations I’ve had over all these years, I might not have been up for it. But I’ve come to see that “no guarantees” isn’t a reason to dig in my heels and resist change.
Thank you to everyone who has taken time to share your experiences and insights about aging. Thank you for your openness, honesty, and courage. These conversations will become even more important in the years ahead, as baby boomers like me make their way through their 70s, 80s, and beyond. May the conversations continue.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
This article first appeared on KFF Health News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Share This Post
-
Fluoride Toothpaste vs Non-Fluoride Toothpaste – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing fluoride toothpaste to non-fluoride toothpaste, we picked the fluoride.
Why?
Fluoride is indeed toxic; that’s why it’s in toothpaste (to kill things; namely, bacteria whose waste products would harm our teeth). However, we are much bigger than those bacteria.
Given the amount of fluoride in toothpaste (usually under 1mg per strip of toothpaste to cover a toothbrush head), the amount that people swallow unintentionally (about 1/20th of that, so about 0.1mg daily if brushing teeth twice daily), and the toxicity level of fluoride (32–64mg/kg), then even if we take the most dangerous ends of all those numbers (and an average body size), to suffer ill effects from fluoride due to brushing your teeth, would require that you brush your teeth more than 23,000 times per day.
Alternatively, if you were to ravenously eat the toothpaste instead of spitting it out, you’d only need to brush your teeth a little over 1,000 times per day.
All the same, please don’t eat toothpaste; that’s not the message here.
However! In head-to-head tests, fluoride toothpaste has almost always beaten non-fluoride toothpaste.
Almost? Yes, almost: hydroxyapatite performed equally in one study, but that’s not usually an option on as many supermarket shelves.
We found some on Amazon, though, which is the one we used for today’s head-to-head. Here it is:
However, before you rush to buy it, do be aware that the toxicity of hydroxyapatite appears to be about twice that of fluoride:
Scientific Committee on Consumer Safety Opinion On Hydroxyapatite (Nano)
…which is still very safe (you’d need to brush your teeth, and eat all the toothpaste, about 500 times per day, to get to toxic levels, if we run with the same numbers we discussed before. Again, please do not do that, though).
But, since the science so far suggests it’s about twice as toxic as fluoride, then regardless of that still being very safe, the fluoride is obviously (by the same metric) twice as safe, hence picking the fluoride.
Want more options?
Check out our previous main feature:
Less Common Oral Hygiene Options
(the above article also links back to our discussion of different toothpastes and mouthwashes, by the way)
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Science of Pilates – by Tracy Ward
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve reviewed other books in this series, “Science of Yoga” and “Science of HIIT” (they’re great too; check them out!). What does this one add to the mix?
Pilates is a top-tier “combination exercise” insofar as it checks a lot of boxes, e.g:
- Strength—especially core strength, but also limbs
- Mobility—range of motion and resultant reduction in injury risk
- Stability—impossible without the above two things, but Pilates trains this too
- Fitness—many dynamic Pilates exercises can be performed as cardio and/or HIIT.
The author, a physiotherapist, explains (as the title promises!) the science of Pilates, with:
- the beautifully clear diagrams we’ve come to expect of this series,
- equally clear explanations, with a great balance of simplicity of terms and depth where necessary, and
- plenty of citations for the claims made, linking to lots of the best up-to-date science.
Bottom line: if you are in a position to make a little time for Pilates (if you don’t already), then there is nobody who would not benefit from reading this book.
Click here to check out Science of Pilates, and keep your body well!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
It’s Not A Bloody Trend – by Kat Brown
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This one’s not a clinical book, and the author is not a clinician. However, it’s not just a personal account, either. Kat Brown is an award-winning journalist (with ADHD) and has approached this journalistically.
Not just in terms of investigative journalism, either. Rather, also with her knowledge and understanding of the industry, doing for us some meta-journalism and explaining why the press have gone for many misleading headlines.
Which in this case means for example it’s not newsworthy to say that people have gone undiagnosed and untreated for years and that many continue to go unseen; we know this also about such things as endometriosis, adenomyosis, and PCOS. But some more reactionary headlines will always get attention, e.g. “look at these malingering attention-seekers”.
She also digs into the common comorbidities of various conditions, the differences it makes to friendships, families, relationships, work, self-esteem, parenting, and more.
This isn’t a “how to” book, but there’s a lot of value here if a) you have ADHD, and/or b) you spend any amount of time with someone who does.
Bottom line: if you’d like to understand “what all the fuss is about” in one book, this is the one for ADHD.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The surprising ways ‘swimming off’ a hangover can be risky, even if alcohol has left your system
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s the morning after a big night and you’re feeling the effects of too much alcohol.
So it can be tempting to “refresh” and take the edge off a hangover with a swim at the beach, or a dip in the cool waters of your local river or pool.
But you might want to think twice.
The day after heavy drinking can affect your body, energy levels and perception of risk in many ways. This means you’re more likely to drown or make careless decisions – even without high levels of alcohol in your blood.
Wanderlust Media/Shutterstock Alcohol + water + summer = drowning
Alcohol is one of the main reasons why someone’s more likely to die due to drowning. And Australians consume a lot of it, including around the water.
The risk of drowning, and injury, including incidents involving alcohol, dramatically increases over the summer festive period – in particular on public holidays and long weekends.
Among people aged 18 and over who drowned in rivers where alcohol was involved, we found some 40% had a blood alcohol concentration of at least 0.20%. That’s four times the upper legal limit of 0.05% when driving a car on a full licence.
When we breathalysed people at four Australian rivers, we found higher levels of blood alcohol with higher temperatures, and particularly on public holidays.
At the beach, intoxication due to alcohol and/or drugs is involved in 23% of drowning deaths with an average blood alcohol concentration of 0.19%.
How about if you’re hungover?
Getting alcohol out of your body is a relatively slow process. On average, alcohol is metabolised at a rate of 0.015% per hour. So if someone stops drinking at 2am with a blood alcohol concentration of 0.20%, their alcohol levels don’t drop to zero until 4pm the next day.
Although hangovers can vary from person to person, typical symptoms include headache, muscle aches, fatigue, weakness, thirst, nausea, stomach pain, vertigo, irritability, sensitivity to light and sound, anxiety, sweating and increased blood pressure.
As well as feeling a bit dusty, the day after an evening of heavy drinking, you’re not so good at identifying risks and reacting to them.
In a pool, this might mean not noticing it’s too shallow to dive safely. In natural waterways, this might mean not noticing a strong river current or a rip current at the beach. Or someone might notice these hazards but swim or dive in anyway.
You don’t have to have alcohol in your blood to be affected. Fatigue can set in, leading you to make careless decisions. tismaja/Shutterstock In one study, we found that after a four-day Australian music festival where people drank heavily, even people who were sober (no longer had alcohol in their blood) were still affected.
Compared to baseline tests in the lab we ran three weeks before the festival, people who were sober the day after the festival had faster reaction times in a test to gauge their attention. But they made more mistakes. This suggests hangovers coupled with fatigue lead to quicker but more careless behaviour.
In and around water this could be the difference between life and death.
Positive blood alcohol readings, including of alcohol from the night before, are commonly implicated in drowning deaths as a result of risky behaviours such as jumping into the water, both at a river and along the coast. Jumping can cause physical injury or render you unconscious, leading to drowning.
Alcohol, including the day after drinking, can also make drowning more likely for a number of other reasons. It also reduces people’s coordination and reaction times.
What else is going on?
Alcohol makes the blood vessels near your skin open up (dilate). So more blood flows into them, making you feel hot. This means you may stay in colder water for longer, increasing your risk of hypothermia.
Alcohol can even make CPR (cardiopulmonary resuscitation) less effective, should you need to be resuscitated.
Normally, your body controls levels of certain minerals (or electrolytes) in the blood. But electrolyte imbalance is common after heavy drinking, including the day after. It’s the reason why hangover symptoms such as muscle pain can lead to cramps in your arms or legs. This can become dangerous when being in or on the water.
Low blood sugar levels the day after drinking is also common. This can lead to people becoming exhausted more quickly when doing physical activities, including swimming.
Other hazards include cold water, high waves and deep water, all of which your body may not be capable of dealing with if you’re feeling the effects of a big night.
What can we do about it?
Authorities regularly warn about the dangers of alcohol intoxication and being near the water. Young people and men are often targeted because these are the groups more likely to drown where alcohol is involved.
Beaches may have alcohol-free zones. Rivers rarely have the same rules, despite similar dangers. https://www.youtube.com/embed/5Salt-kkGUo?wmode=transparent&start=0 Royal Life Saving urges men to ‘make the right call’ and avoid alcohol around the water.
How to stay safe around water if you’re drinking
So take care this summer and stay out of the water if you’re not feeling your best:
- do your swimming before your drinking
- look out for your mates, especially ones who may have had a few too many or are hungover
- avoid getting back into the water after you’ve drunk alcohol or if you’re not feeling your best the next day.
Amy Peden, NHMRC Research Fellow, School of Population Health & co-founder UNSW Beach Safety Research Group, UNSW Sydney; Emmanuel Kuntsche, Director of the Centre for Alcohol Policy Research, La Trobe University, and Jasmin C. Lawes, Adjunct Senior Lecturer, UNSW Beach Safety Research Group, UNSW Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: