You can train your nose – and 4 other surprising facts about your sense of smell
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Would you give up your sense of smell to keep your hair? What about your phone?
A 2022 US study compared smell to other senses (sight and hearing) and personally prized commodities (including money, a pet or hair) to see what people valued more.
The researchers found smell was viewed as much less important than sight and hearing, and valued less than many commodities. For example, half the women surveyed said they’d choose to keep their hair over sense of smell.
Smell often goes under the radar as one of the least valued senses. But it is one of the first sensory systems vertebrates developed and is linked to your mental health, memory and more.
Here are five fascinating facts about your olfactory system.

1. Smell is linked to memory and emotion
Why can the waft of fresh baking trigger joyful childhood memories? And why might a certain perfume jolt you back to a painful breakup?
Smell is directly linked to both your memory and emotions. This connection was first established by American psychologist Donald Laird in 1935 (although French novelist Marcel Proust had already made it famous in his reverie about the scent of madeleines baking.)
Odours are first captured by special olfactory nerve cells inside your nose. These cells extend upwards from the roof of your nose towards the smell-processing centre of your brain, called the olfactory bulb.
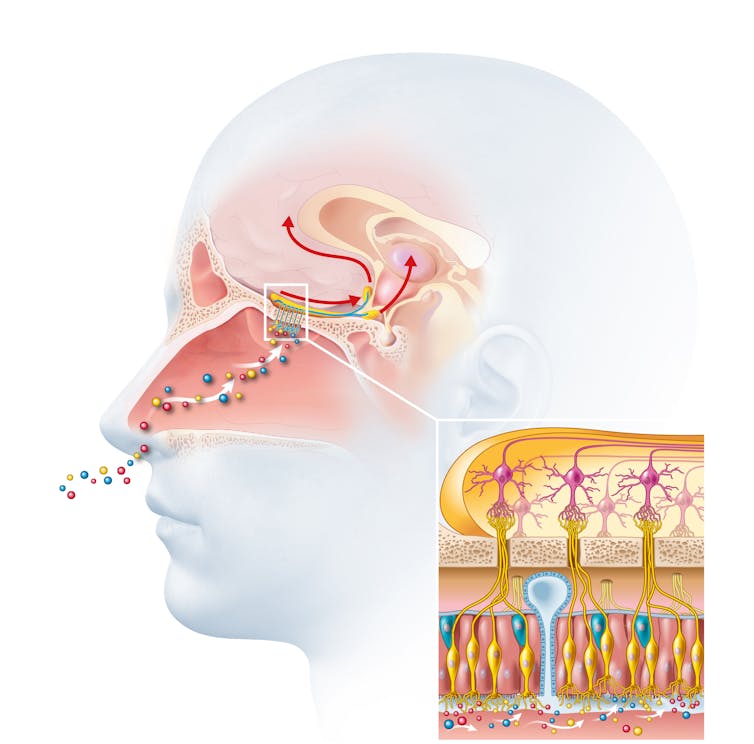
From the olfactory bulb they form direct connection with the brain’s limbic system. This includes the amygdala, where emotions are generated, and the hippocampus, where memories are created.
Other senses – such as sight and hearing – aren’t directly connected to the lymbic system.
One 2004 study used functional magnetic resonance imaging to demonstrate odours trigger a much stronger emotional and memory response in the brain than a visual cue.
2. Your sense of smell constantly regenerates
You can lose your ability to smell due to injury or infection – for example during and after a COVID infection. This is known as olfactory dysfunction. In most cases it’s temporary, returning to normal within a few weeks.
This is because every few months your olfactory nerve cells die and are replaced by new cells.
We’re not entirely sure how this occurs, but it likely involves your nose’s stem cells, the olfactory bulb and other cells in the olfactory nerves.
Other areas of your nervous system – including your brain and spinal cord – cannot regenerate and repair after an injury.
Constant regeneration may be a protective mechanism, as the olfactory nerves are vulnerable to damage caused by the external environment, including toxins (such as cigarette smoke), chemicals and pathogens (such as the flu virus).
But following a COVID infection some people might continue to experience a loss of smell. Studies suggest the virus and a long-term immune response damages the cells that allow the olfactory system to regenerate.
3. Smell is linked to mental health
Around 5% of the global population suffer from anosmia – total loss of smell. An estimated 15-20% suffer partial loss, known as hyposmia.
Given smell loss is often a primary and long-term symptom of COVID, these numbers are likely to be higher since the pandemic.
Yet in Australia, the prevalence of olfactory dysfunction remains surprisingly understudied.
Losing your sense of smell is shown to impact your personal and social relationships. For example, it can mean you miss out on shared eating experiences, or cause changes in sexual desire and behaviour.
In older people, declining ability to smell is associated with a higher risk of depression and even death, although we still don’t know why.

4. Loss of smell can help identify neurodegenerative diseases
Partial or full loss of smell is often an early indicator for a range of neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases.
Patients frequently report losing their sense of smell years before any symptoms show in body or brain function. However many people are not aware they are losing their sense of smell.
There are ways you can determine if you have smell loss and to what extent. You may be able to visit a formal smell testing centre or do a self-test at home, which assesses your ability to identify household items like coffee, wine or soap.
5. You can train your nose back into smelling
“Smell training” is emerging as a promising experimental treatment option for olfactory dysfunction. For people experiencing smell loss after COVID, it’s been show to improve the ability to detect and differentiate odours.
Smell training (or “olfactory training”) was first tested in 2009 in a German psychology study. It involves sniffing robust odours — such as floral, citrus, aromatic or fruity scents — at least twice a day for 10—20 seconds at a time, usually over a 3—6 month period.
Participants are asked to focus on the memory of the smell while sniffing and recall information about the odour and its intensity. This is believed to help reorganise the nerve connections in the brain, although the exact mechanism behind it is unclear.
Some studies recommend using a single set of scents, while others recommend switching to a new set of odours after a certain amount of time. However both methods show significant improvement in smelling.
This training has also been shown to alleviate depressive symptoms and improve cognitive decline both in older adults and those suffering from dementia.
Just like physiotherapy after a physical injury, olfactory training is thought to act like rehabilitation for your sense of smell. It retrains the nerves in your nose and the connections it forms within the brain, allowing you to correctly detect, process and interpret odours.
Lynn Nazareth, Research Scientist in Olfactory Biology, CSIRO
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Considering taking Wegovy to lose weight? Here are the risks and benefits – and how it differs from Ozempic
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The weight-loss drug Wegovy is now available in Australia.
Wegovy is administered as a once-weekly injection and is approved specifically for weight management. It’s intended to be used in combination with a reduced-energy diet and increased physical activity.
So how does Wegovy work and how much weight can you expect to lose while taking it? And what are the potential risks – and costs – for those who use it?
Let’s look at what the science says.
Halfpoint/Shutterstock What is Wegovy?
Wegovy is a brand name for the medication semaglutide. Semaglutide is a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA). This means it makes your body’s own glucagon-like peptide-1 hormone, called GLP-1 for short, work better.
Normally when you eat, the body releases the GLP-1 hormone which helps signal to your brain that you are full. Semaglutides enhance this effect, leading to a feeling of fullness, even when you haven’t eaten.
Another role of GLP-1 is to stimulate the body to produce more insulin, a hormone which helps lower the level of glucose (sugar) in the blood. That’s why semaglutides have been used for several years to treat type 2 diabetes.
Wegovy is self-injected once a week. S Becker/Shutterstock How does Wegovy differ from Ozempic?
Like Wegovy, Ozempic is a semaglutide. The way Wegovy and Ozempic work in the body are essentially the same. They’re made by the same pharmaceutical company, Novo Nordisk.
But there are two differences:
1) They are approved for two different (but related) reasons.
In Australia (and the United States), Ozempic is approved for use to improve blood glucose levels in adults with type 2 diabetes. By managing blood glucose levels effectively, the medication aims to reduce the risk of major complications, such as heart disease.
Wegovy is approved for use alongside diet and exercise for people with a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or greater, or 27 or greater but with other conditions such as high blood pressure.
Wegovy can also be used in people aged 12 years and older. Like Ozempic, Wegovy aims to reduce the risk of future health complications, including heart disease.
2) They are both injected but come in different strengths.
Ozempic is available in pre-loaded single-dose pens with varying dosages of 0.25 mg, 0.5 mg, 1 mg, or 2 mg per injection. The dose can be slowly increased, up to a maximum of 2 mg per week, if needed.
Wegovy is available in prefilled single-dose pens with doses of 0.25 mg, 0.5 mg, 1 mg, 1.7 mg, or 2.4 mg. The treatment starts with a dose of 0.25 mg once weekly for four weeks, after which the dose is gradually increased until reaching a maintenance dose of 2.4 mg weekly.
While it’s unknown what the impact of Wegovy’s introduction will be on Ozempic’s availability, Ozempic is still anticipated to be in low supply for the remainder of 2024.
Is Wegovy effective for weight loss?
Given Wegovy is a semaglutide, there is very strong evidence it can help people lose weight and maintain this weight loss.
A recent study found that over four years, participants taking Wevovy as indicated experienced an average weight loss of 10.2% body weight and a reduction in waist circumference of 7.7cm.
For those who stop taking the medication, analyses have shown that about two-thirds of weight lost is regained.
Wegovy can help people lose weight and maintain their weight loss – while they take the drug. Mladen Mitrinovic/Shutterstock What are the side effects of Wegovy?
The most common side effects are nausea and vomiting.
However, other serious side effects are also possible because of the whole-of-body impact of the medication. Thyroid tumours and cancer have been detected as a risk in animal studies, yet are rarely seen in human scientific literature.
In the four-year Wegovy trial, 16.6% of participants who received Wegovy (1,461 people) experienced an adverse event that led to them permanently discontinuing their use of the medication. This was higher than the 8.2% of participants (718 people) who received the placebo (with no active ingredient).
Side effects included gastrointestinal disorders (including nausea and vomiting), which affected 10% of people who used Wegovy compared to 2% of people who used the placebo.
Gallbladder-related disorders occurred in 2.8% of people who used Wegovy, and 2.3% of people who received the placebo.
Recently, concerns about suicidal thoughts and behaviours have been raised, after a global analysis reviewed more than 36 million reports of adverse events from semaglutide (Ozempic or Wegovy) since 2000.
There were 107 reports of suicidal thoughts and self-harm among people taking semaglutide, sadly including six actual deaths. When people stopped the medication, 62.5% found the thoughts went away. What we don’t know is whether dose, weight loss, or previous mental health status or use of antidepressants had a role to play.
Finally, concerns are growing about the negative effect of semaglutides on our social and emotional connection with food. Anecdotal and scientific evidence suggests people who use semaglutides significantly reduce their daily dietary intake (as anticipated) by skipping meals and avoiding social occasions – not very enjoyable for people and their loved ones.
How can people access Wegovy?
Wegovy is available for purchase at pharmacists with a prescription from a doctor.
But there is a hefty price tag. Wegovy is not currently subsidised through the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme, leaving patients to cover the cost. The current cost is estimated at around A$460 per month dose.
If you’re considering Wegovy, make an appointment with your doctor for individual advice.
Lauren Ball, Professor of Community Health and Wellbeing, The University of Queensland and Emily Burch, Accredited Practising Dietitian and Lecturer, Southern Cross University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
The High-Protein, High-Fiber Superfood Salad You’ll Want To Enjoy Daily
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This salad from Nisha Vora at Rainbow Plant Life has 30g protein and takes minutes to prepare, while being tasty enough to look forward to eating each day:
Easy preparation
Prepare the toppings first; you can do a week’s in advance at once:
- Roasted chickpeas:
- Drain, rinse, and dry two cans of chickpeas.
- Toss with olive oil, salt, and pepper.
- Roast at 425°F for 30–35 minutes.
- Roasted walnuts:
- Chop and toss with olive oil, salt, and pepper.
- Roast at 350°F for 12 minutes after chickpeas finish.
As for the salad base:
- Kale:
- Remove tough stems, slice thinly.
- Wash and massage with lemon juice and salt to soften.
- Cabbage:
- Slice thinly with a knife or mandolin.
- Store in a sealed bag in the fridge for up to a week.
Red wine vinaigrette dressing:
- Key ingredients: red wine vinegar, lemon juice, red pepper flakes, garlic, olive oil.
- Can be stored in the fridge for up to 10 days.
Putting it all together:
- Toss kale and cabbage with vinaigrette by hand.
- Add roasted chickpeas and walnuts for crunch.
- Include a protein source like tofu (store-bought curry tofu recommended).
- Mix in fresh vegetables like grated carrots, sliced bell peppers, or beets.
- Add extras like sauerkraut, avocado, pickled onions, and such.
- Top with fresh herbs (she recommends parsley, basil, or dill).
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
21 Most Beneficial Polyphenols & What Foods Have Them
Take care!
Share This Post
- Roasted chickpeas:
-
Pneumonia: Prevention Is Better Than Cure
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Pneumonia: What We Can & Can’t Do About It
Pneumonia is a significant killer of persons over the age of 65, with the risk increasing with age after that, rising very sharply around the age of 85:
While pneumonia is treatable, especially in young healthy adults, the risks get more severe in the older age brackets, and it’s often the case that someone goes into hospital with one thing, then develops pneumonia, which the person was already not in good physical shape to fight, because of whatever hospitalized them in the first place:
American Lung Association | Pneumonia Treatment and Recovery
Other risk factors besides age
There are a lot of things that can increase our risk factor for pneumonia; they mainly fall into the following categories:
- Autoimmune diseases
- Other diseases of the immune system (e.g. HIV)
- Medication-mediated immunosuppression (e.g. after an organ transplant)
- Chronic lung diseases (e.g. asthma, COPD, Long Covid, emphysema, etc)
- Other serious health conditions ← we know this one’s broad, but it encompasses such things as diabetes, heart disease, and cancer
See also:
Why Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Is More Likely Than You Think
Things we can do about it
When it comes to risks, we can’t do much about our age and some of the other above factors, but there are other things we can do to reduce our risk, including:
- Get vaccinated against pneumonia if you are over 65 and/or have one of the aforementioned risk factors. This is not perfect (it only reduces the risk for certain kinds of infection) and may not be advisable for everyone (like most vaccines, it can put the body through its paces a bit after taking it), so speak with your own doctor about this, of course.
- See also: Vaccine Mythbusting
- Avoid contagion. While pneumonia itself is not spread person-to-person, it is caused by bacteria or viruses (there are numerous kinds) that are opportunistic and often become a secondary infection when the immune system is already busy with the first one. So, if possible avoid being in confined spaces with many people, and do wash your hands regularly (as a lot of germs are transferred that way and can get into the respiratory tract because you touched your face or such).
- See also: The Truth About Handwashing
- If you have a cold, or flu, or other respiratory infection, take it seriously, rest well, drink fluids, get good immune-boosting nutrients. There’s no such thing as “just a cold”; not anymore.
- Look after your general health too—health doesn’t exist in a vacuum, and nor does disease. Every part of us affects every other part of us, so anything that can be in good order, you want to be in good order.
This last one, by the way? It’s an important reminder that while some diseases (such as some of the respiratory infections that can precede pneumonia) are seasonal, good health isn’t.
We need to take care of our health as best we can every day along the way, because we never know when something could change.
Want to do more?
Check out: Seven Things To Do For Good Lung Health!
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Want to sleep longer? Adding mini-bursts of exercise to your evening routine can help – new study
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Exercising before bed has long been discouraged as the body doesn’t have time to wind down before the lights go out.
But new research has found breaking up a quiet, sedentary evening of watching television with short bursts of resistance exercise can lead to longer periods of sleep.
Adults spend almost one third of the 24-hour day sleeping. But the quality and length of sleep can affect long-term health. Sleeping too little or waking often in the night is associated with an increased risk of heart disease and diabetes.
Physical activity during the day can help improve sleep. However, current recommendations discourage intense exercise before going to bed as it can increase a person’s heart rate and core temperature, which can ultimately disrupt sleep.
Nighttime habits
For many, the longest period of uninterrupted sitting happens at home in the evening. People also usually consume their largest meal during this time (or snack throughout the evening).
Insulin (the hormone that helps to remove sugar from the blood stream) tends to be at a lower level in the evening than in the morning.
Together these factors promote elevated blood sugar levels, which over the long term can be bad for a person’s health.
Our previous research found interrupting evening sitting every 30 minutes with three minutes of resistance exercise reduces the amount of sugar in the bloodstream after eating a meal.
But because sleep guidelines currently discourage exercising in the hours before going to sleep, we wanted to know if frequently performing these short bursts of light activity in the evening would affect sleep.
Activity breaks for better sleep
In our latest research, we asked 30 adults to complete two sessions based in a laboratory.
During one session the adults sat continuously for a four-hour period while watching streaming services. During the other session, they interrupted sitting by performing three minutes of body-weight resistance exercises (squats, calf raises and hip extensions) every 30 minutes.
After these sessions, participants went home to their normal life routines. Their sleep that evening was measured using a wrist monitor.
Our research found the quality of sleep (measured by how many times they woke in the night and the length of these awakenings) was the same after the two sessions. But the night after the participants did the exercise “activity breaks” they slept for almost 30 minutes longer.
Identifying the biological reasons for the extended sleep in our study requires further research.
But regardless of the reason, if activity breaks can extend sleep duration, then getting up and moving at regular intervals in the evening is likely to have clear health benefits.
Time to revisit guidelines
These results add to earlier work suggesting current sleep guidelines, which discourage evening exercise before bed, may need to be reviewed.
As the activity breaks were performed in a highly controlled laboratory environment, future research should explore how activity breaks performed in real life affect peoples sleep.
We selected simple, body-weight exercises to use in this study as they don’t require people to interrupt the show they may be watching, and don’t require a large space or equipment.
If people wanted to incorporate activity breaks in their own evening routines, they could probably get the same benefit from other types of exercise. For example, marching on the spot, walking up and down stairs, or even dancing in the living room.
The key is to frequently interrupt evening sitting time, with a little bit of whole-body movement at regular intervals.
In the long run, performing activity breaks may improve health by improving sleep and post-meal blood sugar levels. The most important thing is to get up frequently and move the body, in a way the works best for a person’s individual household.
Jennifer Gale, PhD candidate, Department of Human Nutrition, University of Otago and Meredith Peddie, Senior Lecturer, Department of Human Nutrition, University of Otago
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Buckwheat vs Oats – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing buckwheat to oats, we picked the oats.
Why?
First of all, for any thinking about the health concerns sometimes associated with wheat: buckwheat is not a kind of wheat, nor is it even in the same family; it’s not a grain, but a flowering plant. Buckwheat is to wheat as a lionfish is to lions.
That said, while these are both excellent foods, one of them is so good it makes the other one look bad in comparison:
In terms of macros, oats have more carbs, but also more protein and more fiber.
When it comes to vitamins, a clear winner emerges: oats have more of vitamins B1, B2, B5, B6, and B9, while buckwheat is higher in vitamin K and choline.
In the category of minerals, things are even more pronounced: oats are higher in calcium, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc. On the other hand, buckwheat is higher in selenium.
All in all: as ever, enjoy both, but if you’re picking one, oats cannot be beaten.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
The Best Kind Of Fiber For Overall Health?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Growing Inequality in Life Expectancy Among Americans
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The life expectancy among Native Americans in the western United States has dropped below 64 years, close to life expectancies in the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Haiti. For many Asian Americans, it’s around 84 — on par with life expectancies in Japan and Switzerland.
Americans’ health has long been unequal, but a new study shows that the disparity between the life expectancies of different populations has nearly doubled since 2000. “This is like comparing very different countries,” said Tom Bollyky, director of the global health program at the Council on Foreign Relations and an author of the study.
Called “Ten Americas,” the analysis published late last year in The Lancet found that “one’s life expectancy varies dramatically depending on where one lives, the economic conditions in that location, and one’s racial and ethnic identity.” The worsening health of specific populations is a key reason the country’s overall life expectancy — at 75 years for men and 80 for women — is the shortest among wealthy nations.
To deliver on pledges from the new Trump administration to make America healthy again, policymakers will need to fix problems undermining life expectancy across all populations.
“As long as we have these really severe disparities, we’re going to have this very low life expectancy,” said Kathleen Harris, a sociologist at the University of North Carolina. “It should not be that way for a country as rich as the U.S.”
Since 2000, the average life expectancy of many American Indians and Alaska Natives has been steadily shrinking. The same has been true since 2014 for Black people in low-income counties in the southeastern U.S.
“Some groups in the United States are facing a health crisis,” Bollyky said, “and we need to respond to that because it’s worsening.”
Heart disease, car fatalities, diabetes, covid-19, and other common causes of death are directly to blame. But research shows that the conditions of people’s lives, their behaviors, and their environments heavily influence why some populations are at higher risk than others.
Native Americans in the West — defined in the “Ten Americas” study as more than a dozen states excluding California, Washington, and Oregon — were among the poorest in the analysis, living in counties where a person’s annual income averages below about $20,000. Economists have shown that people with low incomes generally live shorter lives.
Studies have also linked the stress of poverty, trauma, and discrimination to detrimental coping behaviors like smoking and substance use disorders. And reservations often lack grocery stores and clean, piped water, which makes it hard to buy and cook healthy food.
About 1 in 5 Native Americans in the Southwest don’t have health insurance, according to a KFF report. Although the Indian Health Service provides coverage, the report says the program is weak due to chronic underfunding. This means people may delay or skip treatments for chronic illnesses. Postponed medical care contributed to the outsize toll of covid among Native Americans: About 1 of every 188 Navajo people died of the disease at the peak of the pandemic.
“The combination of limited access to health care and higher health risks has been devastating,” Bollyky said.
At the other end of the spectrum, the study’s category of Asian Americans maintained the longest life expectancies since 2000. As of 2021, it was 84 years.
Education may partly underlie the reasons certain groups live longer. “People with more education are more likely to seek out and adhere to health advice,” said Ali Mokdad, an epidemiologist at the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation at the University of Washington, and an author of the paper. Education also offers more opportunities for full-time jobs with health benefits. “Money allows you to take steps to take care of yourself,” Mokdad said.
The group with the highest incomes in most years of the analysis was predominantly composed of white people, followed by the mainly Asian group. The latter, however, maintained the highest rates of college graduation, by far. About half finished college, compared with fewer than a third of other populations.
The study suggests that education partly accounts for differences among white people living in low-income counties, where the individual income averaged less than $32,363. Since 2000, white people in low-income counties in southeastern states — defined as those in Appalachia and the Lower Mississippi Valley — had far lower life expectancies than those in upper midwestern states including Montana, Nebraska, and Iowa. (The authors provide details on how the groups were defined and delineated in their report.)
Opioid use and HIV rates didn’t account for the disparity between these white, low-income groups, Bollyky said. But since 2010, more than 90% of white people in the northern group were high school graduates, compared with around 80% in the southeastern U.S.
The education effect didn’t hold true for Latino groups compared with others. Latinos saw lower rates of high school graduation than white people but lived longer on average. This long-standing trend recently changed among Latinos in the Southwest because of covid. Hispanic or Latino and Black people were nearly twice as likely to die from the disease.
On average, Black people in the U.S. have long experienced worse health than other races and ethnicities in the United States, except for Native Americans. But this analysis reveals a steady improvement in Black people’s life expectancy from 2000 to about 2012. During this period, the gap between Black and white life expectancies shrank.
This is true for all three groups of Black people in the analysis: Those in low-income counties in southeastern states like Mississippi, Louisiana, and Alabama; those in highly segregated and metropolitan counties, such as Queens, New York, and Wayne, Michigan, where many neighborhoods are almost entirely Black or entirely white; and Black people everywhere else.
Better drugs to treat high blood pressure and HIV help account for the improvements for many Americans between 2000 to 2010. And Black people, in particular, saw steep rises in high school graduation and gains in college education in that period.
However, progress stagnated for Black populations by 2016. Disparities in wealth grew. By 2021, Asian and many white Americans had the highest incomes in the study, living in counties with per capita incomes around $50,000. All three groups of Black people in the analysis remained below $30,000.
A wealth gap between Black and white people has historical roots, stretching back to the days of slavery, Jim Crow laws, and policies that prevented Black people from owning property in neighborhoods that are better served by public schools and other services. For Native Americans, a historical wealth gap can be traced to a near annihilation of the population and mass displacement in the 19th and 20th centuries.
Inequality has continued to rise for several reasons, such as a widening pay gap between predominantly white corporate leaders and low-wage workers, who are disproportionately people of color. And reporting from KFF Health News shows that decisions not to expand Medicaid have jeopardized the health of hundreds of thousands of people living in poverty.
Researchers have studied the potential health benefits of reparation payments to address historical injustices that led to racial wealth gaps. One new study estimates that such payments could reduce premature death among Black Americans by 29%.
Less controversial are interventions tailored to communities. Obesity often begins in childhood, for example, so policymakers could invest in after-school programs that give children a place to socialize, be active, and eat healthy food, Harris said. Such programs would need to be free for children whose parents can’t afford them and provide transportation.
But without policy changes that boost low wages, decrease medical costs, put safe housing and strong public education within reach, and ensure access to reproductive health care including abortion, Harris said, the country’s overall life expectancy may grow worse.
“If the federal government is really interested in America’s health,” she said, “they could grade states on their health metrics and give them incentives to improve.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
This article first appeared on KFF Health News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: